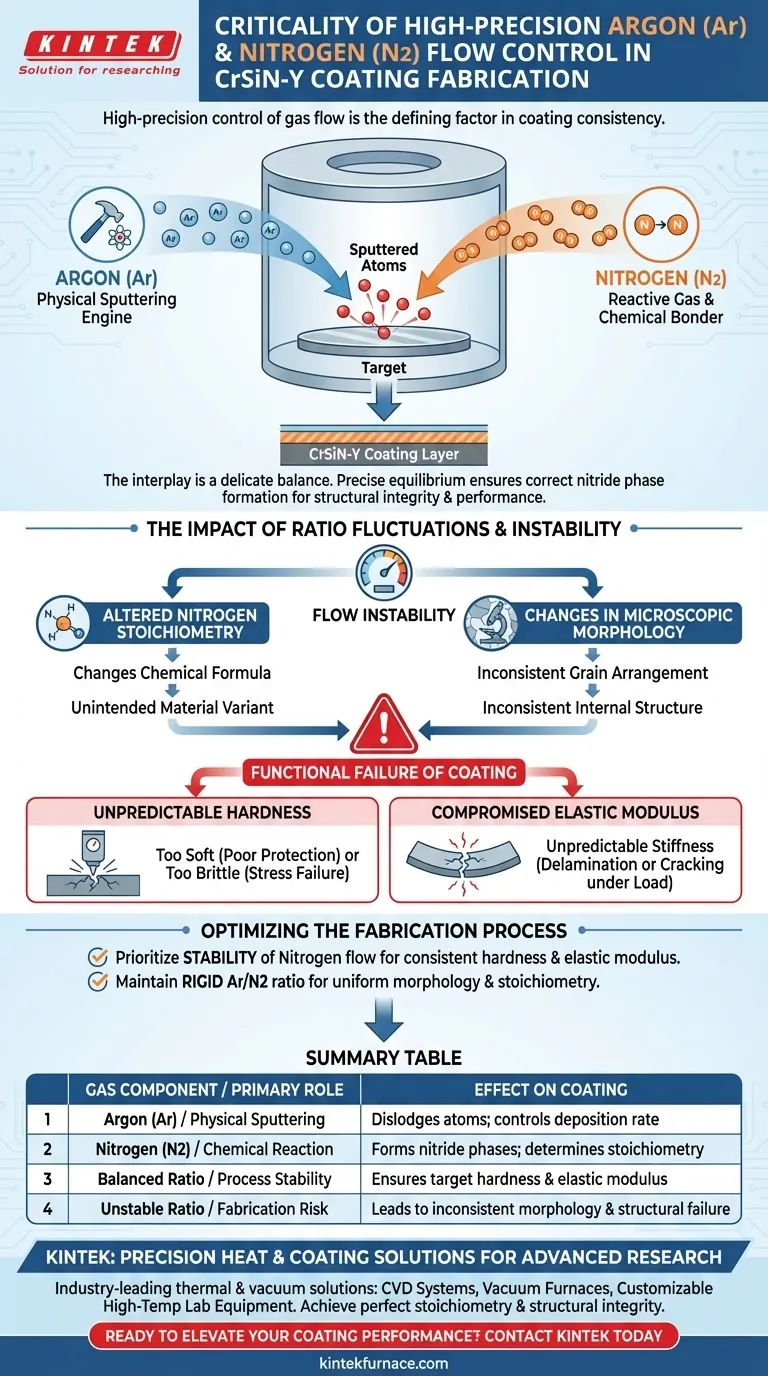
High-precision control of gas flow is the defining factor in coating consistency. In the CrSiN-Y fabrication process, the specific ratio of argon to nitrogen directly dictates the chemical composition (stoichiometry) of the final layer. Even minor fluctuations in this balance alter the coating's physical structure, fundamentally compromising its mechanical properties such as hardness and elasticity.
The interplay between argon and nitrogen is a delicate balance between physical force and chemical reaction. Maintaining a precise equilibrium ensures the correct formation of nitride phases, which are essential for the coating's structural integrity and performance.
The Distinct Roles of Working Gases
To understand why precision is non-negotiable, you must first understand the conflicting yet complementary roles these two gases play inside the vacuum chamber.
Argon Drives Physical Sputtering
Argon serves as the mechanical engine of the process. It is used exclusively for the physical sputtering of target atoms.
By bombarding the target material, argon dislodges atoms into the vacuum environment. Without stable argon flow, the rate at which source material is released becomes unpredictable.
Nitrogen Drives Chemical Reaction
Nitrogen acts as the reactive gas. Its purpose is to bond chemically with the sputtered atoms to create the necessary nitride phases.
The availability of nitrogen determines how effectively the CrSiN-Y compound forms. It transforms the raw sputtered material into a functional ceramic coating.
The Impact of Ratio Fluctuations
The critical challenge in this process is that the gases must be balanced against each other in real-time. High-precision mass flow controllers are required to maintain the necessary partial pressure balance.
Altering Nitrogen Stoichiometry
The primary risk of flow instability is a change in nitrogen stoichiometry.
If the ratio drifts, the chemical formula of the coating changes on the fly. You are no longer producing the intended material, but rather a variant with different chemical bonding ratios.
Changes in Microscopic Morphology
These chemical shifts manifest physically in the coating's microstructure.
The microscopic morphology—the actual arrangement of grains and structures within the coating—is dependent on the gas ratio. An inconsistent flow results in an inconsistent internal structure.
The Risks of Flow Instability
When the gas ratio fluctuates, the consequences are not just cosmetic; they result in a functional failure of the coating's design specifications.
Unpredictable Hardness
The hardness of the CrSiN-Y coating is directly linked to the formation of specific nitride phases.
If the nitrogen flow drops or spikes relative to the argon, the resulting stoichiometry will fail to achieve the target hardness. The coating may become too soft to protect the substrate or too brittle to endure stress.
Compromised Elastic Modulus
The elastic modulus, or the coating's stiffness, is equally sensitive to the gas ratio.
Variations in the gas mixture lead to unpredictable elasticity. This can cause the coating to delaminate or crack under loads it was designed to withstand.
Optimizing the Fabrication Process
Achieving a high-performance CrSiN-Y coating requires prioritizing the stability of your mass flow control system above all other variables.
- If your primary focus is mechanical durability: Prioritize the stability of the nitrogen flow to ensure consistent nitride phase formation, which governs hardness and the elastic modulus.
- If your primary focus is structural uniformity: Maintain a rigid argon-to-nitrogen ratio to prevent variations in microscopic morphology and stoichiometry.
Precision in gas regulation is the only way to transform raw sputtered atoms into a reliable, high-performance surface.
Summary Table:
| Gas Component | Primary Role | Effect on Coating |
|---|---|---|
| Argon (Ar) | Physical Sputtering | Dislodges target atoms; controls deposition rate |
| Nitrogen (N2) | Chemical Reaction | Forms nitride phases; determines stoichiometry |
| Balanced Ratio | Process Stability | Ensures target hardness and elastic modulus |
| Unstable Ratio | Fabrication Risk | Leads to inconsistent morphology and structural failure |
Precision Heat and Coating Solutions for Advanced Research
Consistency in coating fabrication depends on the precision of your equipment. KINTEK provides industry-leading thermal and vacuum solutions, including CVD systems, Vacuum Furnaces, and customizable high-temperature lab equipment designed to meet the rigorous demands of material science.
Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, we help you achieve perfect stoichiometry and structural integrity for your unique material needs.
Ready to elevate your coating performance?
Contact KINTEK today for a customized solution
Visual Guide
References
- Lishan Dong, Zhifeng Wang. Porous High-Entropy Oxide Anode Materials for Li-Ion Batteries: Preparation, Characterization, and Applications. DOI: 10.3390/ma17071542
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD)? Master Thin Film Coating for Enhanced Materials
- Why is a rapid water quenching system necessary for 7075 aluminum? Unlock Peak Alloy Strength & Hardness
- How are laboratory ovens and analytical balances used for banana powder moisture content? Precision Testing Guide
- What is the primary purpose of operating a laboratory oven at 383 K for 24 hours? Precision Drying for Carbon Prep
- What is the primary function of a high-precision drop furnace? Master Flash Smelting Simulation Kinetics
- What is the benefit of accessing furnace technical guides? Optimize Your Research with Precise Equipment Data
- How does the secondary calcination process improve Na2WO4-loaded catalysts? Optimize Surface Performance Today
- What is the function of the annealing furnace? Strategically Control Material Properties for Reliability



















