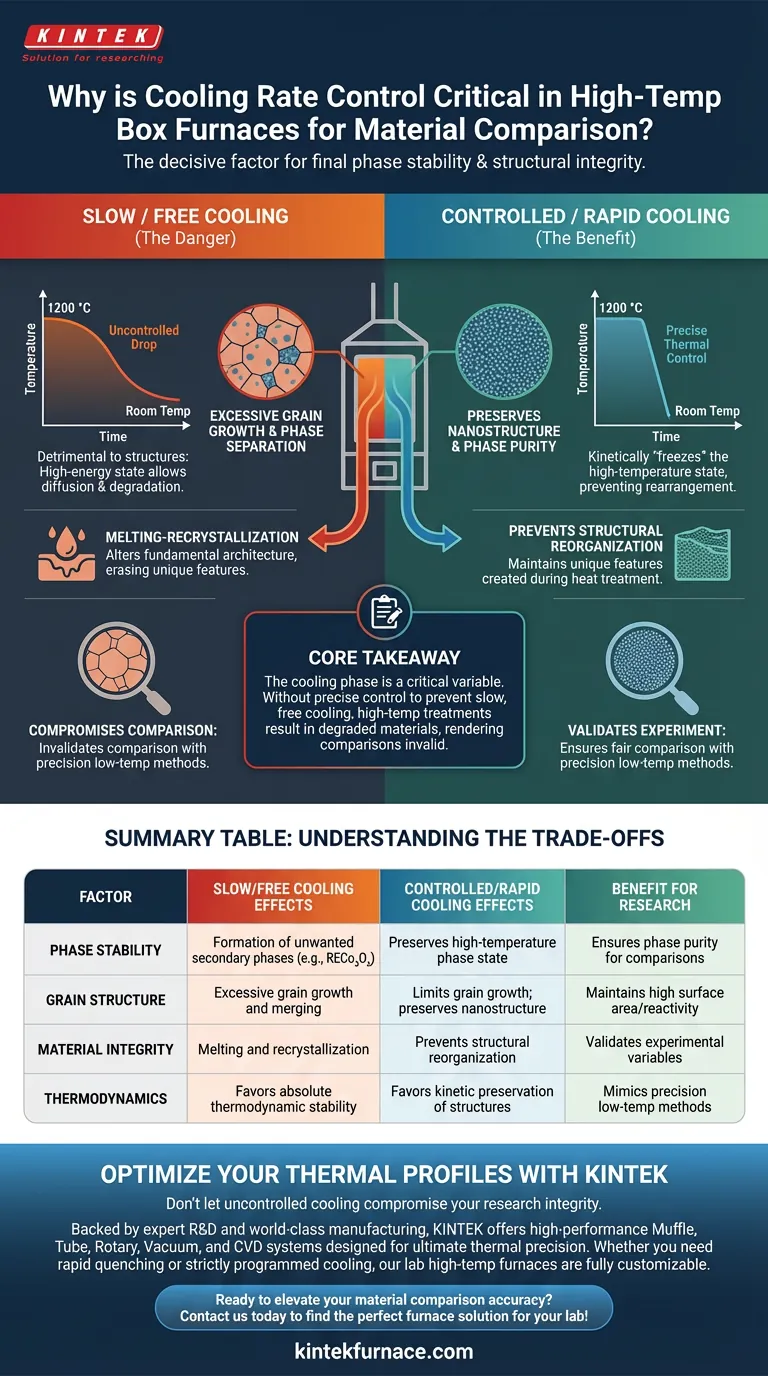
Controlling the cooling rate in a high-temperature box furnace is the decisive factor in determining the final phase stability and structural integrity of your material. When transitioning from extreme temperatures like 1200 °C, the speed at which the sample returns to room temperature dictates whether it retains desirable characteristics or degrades into unwanted secondary phases.
Core Takeaway The cooling phase is not merely the end of a process; it is a critical variable that defines the material's final state. Without precise thermal control to prevent slow, free cooling, high-temperature treatments will inevitably result in grain growth and phase separation, rendering comparisons with precision low-temperature methods invalid.

The Thermodynamics of Transition
The Danger of "Free Cooling"
In many standard furnace operations, the unit is simply turned off after the dwell time, allowing the sample to cool naturally.
At high temperatures (1200 °C), this slow, free cooling is detrimental to maintaining specific material structures. It keeps the material in a high-energy state for too long, allowing diffusion processes to continue well past the intended treatment time.
Impact on Phase Stability
The transition from 1200 °C to room temperature is where phase stability is often lost.
If the temperature drops too slowly, the material seeks its most thermodynamically stable state. While stability sounds positive, in this context, it often means the formation of unwanted secondary phases, such as RECo₃Oₐ, rather than the specific phase you intended to isolate.
Structural Consequences of Uncontrolled Cooling
Melting and Recrystallization
Slow cooling rates frequently lead to melting-recrystallization.
This phenomenon alters the fundamental architecture of the material. Instead of preserving the unique features created during the heat treatment, the material reorganizes itself, often erasing the properties you were trying to study.
Excessive Grain Growth
Control over cooling is essential to limit grain growth.
Extended exposure to high heat during a slow cool allows grains to merge and enlarge. This destroys fine nanostructures, significantly altering the material's surface area and reactivity.
The Context of Comparison
High-Temp vs. Low-Temp Methods
To scientifically compare high-temperature furnace treatments with low-temperature methods (such as glycothermal processes), you must isolate the variables.
Glycothermal methods are renowned for maintaining high phase purity and preserving delicate nanostructures.
Validating the Experiment
If your high-temperature sample suffers from uncontrolled cooling, you are no longer comparing two synthesis methods.
You are comparing a precision low-temperature method against a high-temperature sample that has been degraded by a secondary thermal history (the cooling phase). Precise thermal control is the only way to demonstrate the true differences between these processing techniques.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Thermodynamic Stability vs. Kinetic Preservation
There is an inherent trade-off between reaching the most stable state and preserving a specific structure.
Slow cooling favors thermodynamics. It allows the atoms to settle into the absolute lowest energy configuration, which often results in large grains and secondary phases like RECo₃Oₐ.
Controlled (rapid) cooling favors kinetics. It "freezes" the high-temperature state, preventing the atoms from rearranging into those secondary phases. You must decide which outcome aligns with your research goals.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When designing your thermal profile, consider the specific comparative data you need to generate.
- If your primary focus is preserving nanostructures: You must avoid free cooling to prevent grain growth and maintain parity with precision low-temperature methods.
- If your primary focus is thermodynamic equilibrium: You should allow for slow cooling, accepting that this will likely result in the formation of secondary phases like RECo₃Oₐ and significant recrystallization.
Precision in the cooling phase is the difference between a ruined sample and a scientifically valid comparison.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Slow/Free Cooling Effects | Controlled/Rapid Cooling Effects | Benefit for Research |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phase Stability | Formation of unwanted secondary phases (e.g., RECo₃Oₐ) | Preserves high-temperature phase state | Ensures phase purity for comparisons |
| Grain Structure | Excessive grain growth and merging | Limits grain growth; preserves nanostructure | Maintains high surface area/reactivity |
| Material Integrity | Melting and recrystallization | Prevents structural reorganization | Validates experimental variables |
| Thermodynamics | Favors absolute thermodynamic stability | Favors kinetic preservation of structures | Mimics precision low-temp methods |
Optimize Your Thermal Profiles with KINTEK
Don't let uncontrolled cooling compromise your research integrity. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed for ultimate thermal precision. Whether you need rapid quenching or strictly programmed cooling, our lab high-temp furnaces are fully customizable to meet your unique material synthesis needs.
Ready to elevate your material comparison accuracy? Contact us today to find the perfect furnace solution for your lab!
Visual Guide
References
- Paweł A. Krawczyk, Władysław W. Kubiak. Synthesis and Catalytic Performance of High-Entropy Rare-Earth Perovskite Nanofibers: (Y0.2La0.2Nd0.2Gd0.2Sm0.2)CoO3 in Low-Temperature Carbon Monoxide Oxidation. DOI: 10.3390/ma17081883
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- How does airflow differ between muffle furnaces and drying ovens during operation? Discover the Key Design Differences
- What temperature range can an electric muffle furnace typically reach? Explore Key Ranges and Uses
- What is the significance of using a box-type furnace for molybdenum aluminide coating oxidation? Master Thermal Testing
- How does a muffle furnace system integrated with a nitrogen gas supply facilitate the preparation of biochar?
- What safety precautions should be followed when using a muffle furnace? Essential Steps for Safe and Efficient Operation
- What is the significance of using a high-temperature muffle furnace for Co3O4 nanotube stabilization? Ensure Robustness & Chemical Resilience.
- How should alkaline substances be handled in a muffle furnace? Protect Your Equipment from Corrosion
- What are some technical specifications of advanced muffle furnaces? Unlock Precision and Efficiency in Your Lab



















