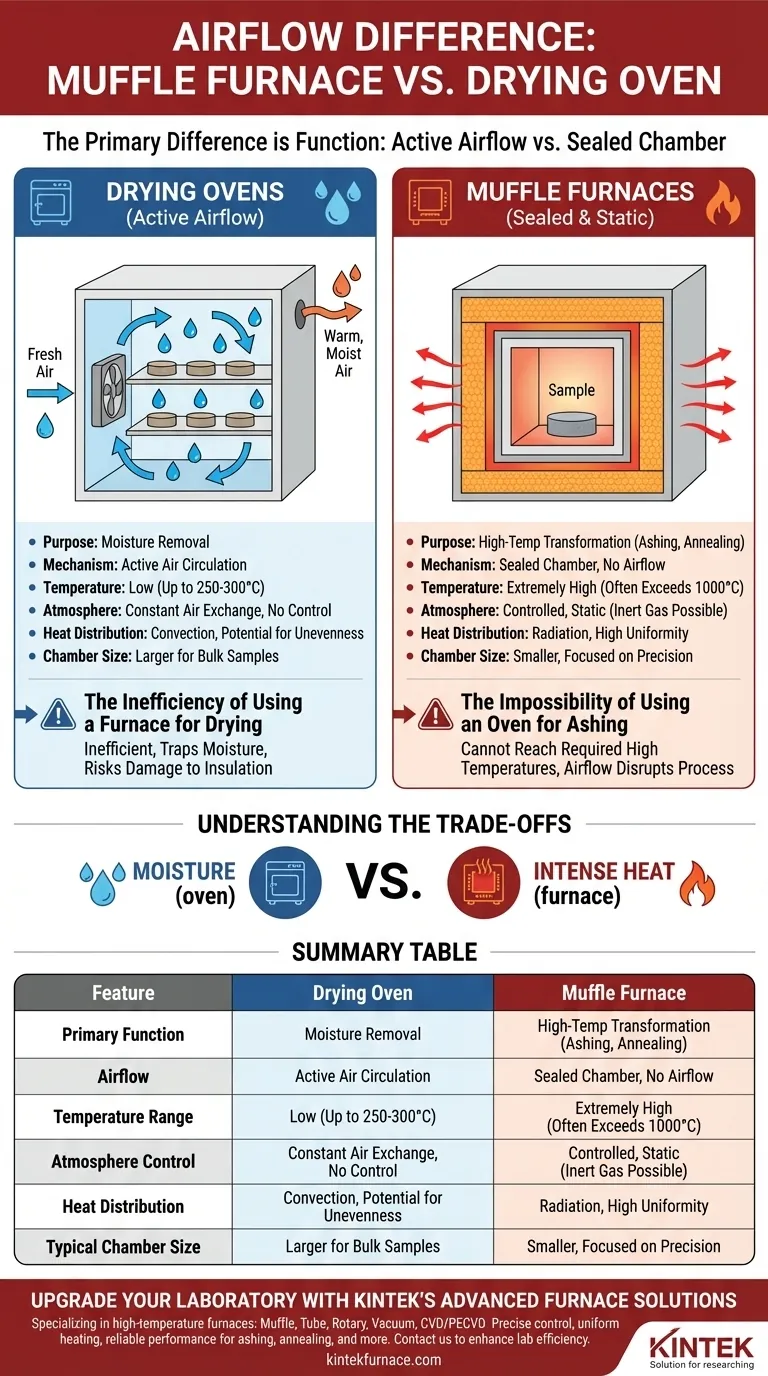
In short, the primary difference is function. A drying oven uses active airflow to remove moisture, while a muffle furnace uses a sealed chamber with no airflow to achieve very high temperatures and maintain a controlled atmosphere. This fundamental distinction in purpose dictates every aspect of their design and operation.
The choice between a muffle furnace and a drying oven is not about which is "better," but about which is built for your specific task. Ovens are designed for low-temperature moisture removal via air circulation, whereas furnaces are designed for high-temperature material transformation in a sealed, static environment.
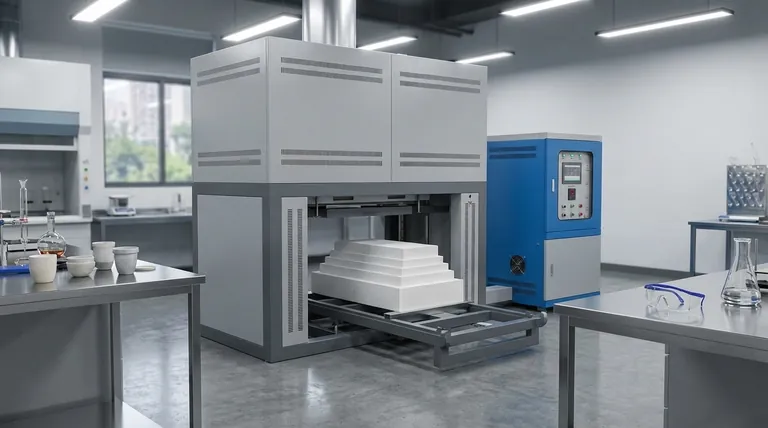

The Fundamental Difference: Purpose-Driven Design
The presence or absence of airflow is not an arbitrary feature; it is a direct consequence of what each machine is engineered to accomplish.
Drying Ovens: Engineered for Moisture Removal
A drying oven's main goal is to remove moisture from a sample at relatively low temperatures.
To do this, it actively circulates air. A fan pulls fresh air into the chamber, heats it using heating elements, and passes it over the samples. This warm, moving air absorbs moisture before being vented out.
This constant air exchange is critical for efficient drying but limits the maximum achievable temperature and prevents any control over the chamber's atmosphere.
Muffle Furnaces: Engineered for High-Temperature Transformation
A muffle furnace is designed for processes like ashing, annealing, or heat-treating materials, which require extremely high temperatures (often exceeding 1000°C).
To achieve and maintain these temperatures efficiently, the chamber must be perfectly sealed and heavily insulated. Airflow would introduce cool air and disrupt the process, making it impossible to reach the target temperature or control the atmosphere.
The term "muffle" refers to the sealed inner chamber that separates the sample from the heating elements, ensuring uniform heat without direct exposure or circulation.
Key Distinctions in Operation and Construction
The core purposes of drying and high-temperature heating lead to several key differences in how these machines are built and operated.
Air Circulation vs. Sealed Atmosphere
This is the most direct answer to the initial question. Drying ovens rely on forced convection, constantly moving air to carry away moisture. Muffle furnaces operate with a completely static, sealed atmosphere to maintain temperature and, if needed, allow for the introduction of inert gases like argon or nitrogen.
Temperature Range and Insulation
Drying ovens typically operate at lower temperatures, usually up to 250-300°C. As a result, they have minimal insulation.
Muffle furnaces are built with thick, heavy-duty refractory insulation to contain extreme heat. This robust construction is necessary to operate safely and efficiently at temperatures of 1100°C or higher.
Heat Distribution and Uniformity
Because a muffle furnace's chamber is sealed and insulated, heat is distributed very evenly through radiation, leading to high temperature uniformity.
In contrast, the convection heating in a drying oven can sometimes create uneven heating, with potential hot and cold spots depending on the airflow pattern and sample placement.
Chamber Size and Capacity
Drying ovens are often larger, designed to accommodate bulky materials or a high volume of samples for simple drying.
Muffle furnaces typically have smaller, more precisely constructed chambers. The focus is on the quality and control of the heating environment, not bulk capacity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Using the wrong instrument for your process is not just inefficient—it can lead to failed experiments and damaged equipment.
The Inefficiency of Using a Furnace for Drying
While a muffle furnace can certainly remove moisture, it is highly inefficient for this task. Its sealed design traps moisture, which must be carefully vented to avoid damaging the insulation and interior. It is an overpowered and ill-suited tool for simple drying.
The Impossibility of Using an Oven for Ashing
A drying oven cannot be used for high-temperature applications like ashing or melting metals. It lacks the necessary insulation to reach the required temperatures, and its constant airflow is counterproductive to the controlled heating process required.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Select your equipment based on the thermal process you need to perform.
- If your primary focus is removing moisture at low temperatures: You need a drying oven for its efficient air circulation.
- If your primary focus is ashing, calcination, or annealing: You need a muffle furnace for its high-temperature capabilities and sealed chamber.
- If your primary focus is heat-treating in a specific atmosphere (e.g., inert gas): You must use a muffle furnace that allows for atmosphere control.
- If your primary focus is simply heating samples in air below 300°C: A drying or convection oven is the correct and more energy-efficient choice.
Ultimately, understanding that airflow is a tool for drying and its absence is a requirement for high-temperature heating will ensure you always select the right instrument for your work.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Drying Oven | Muffle Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Moisture removal at low temperatures | High-temperature material transformation (e.g., ashing, annealing) |
| Airflow | Active circulation with fan for efficient drying | Sealed chamber with no airflow; static atmosphere |
| Temperature Range | Up to 250-300°C | Often exceeds 1000°C |
| Atmosphere Control | No control; constant air exchange | Controlled atmosphere possible (e.g., inert gases) |
| Heat Distribution | Convection heating, potential for unevenness | Radiation heating, high uniformity |
| Typical Chamber Size | Larger for bulk samples | Smaller, focused on precision and control |
Upgrade Your Laboratory with KINTEK's Advanced Furnace Solutions
Struggling to choose the right equipment for your thermal processes? KINTEK specializes in high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your unique needs. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer a comprehensive product line—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—all backed by strong deep customization capabilities. Whether you're in research, materials science, or industrial applications, our furnaces ensure precise temperature control, uniform heating, and reliable performance for processes like ashing, annealing, and more. Don't let equipment limitations hold back your experiments—contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your lab's efficiency and achieve your specific experimental goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control



















