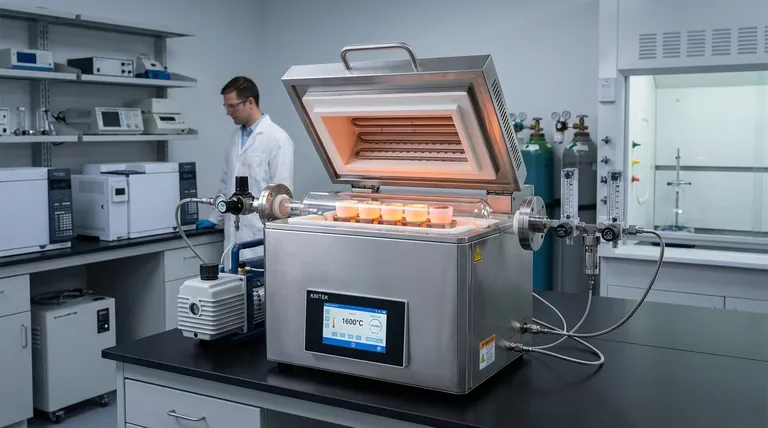
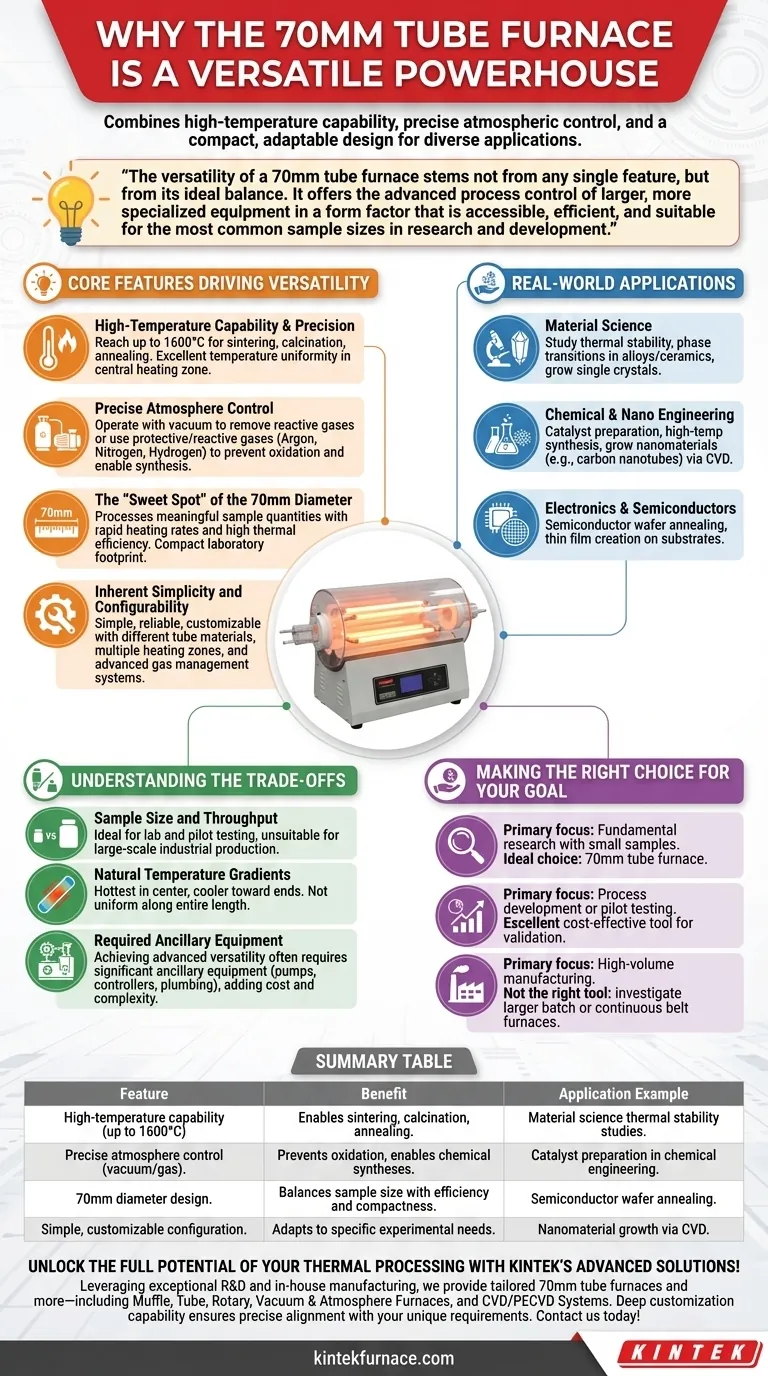
At its core, the 70mm tube furnace is considered highly versatile because it combines high-temperature capability and precise atmospheric control within a compact and adaptable design. This unique blend of features makes it a standard tool for a vast range of thermal processing applications across multiple scientific and industrial fields.
The versatility of a 70mm tube furnace stems not from any single feature, but from its ideal balance. It offers the advanced process control of larger, more specialized equipment in a form factor that is accessible, efficient, and suitable for the most common sample sizes in research and development.

The Core Features Driving Versatility
A tube furnace's utility is defined by its ability to create a highly controlled thermal environment. The 70mm model excels by integrating several key features that make this environment easily configurable for different tasks.
High-Temperature Capability & Precision
A key enabler is the ability to reach very high temperatures, often up to 1600°C.
This high-temperature range allows for processes like sintering, calcination, and annealing of a wide variety of materials. Crucially, modern controllers provide excellent temperature uniformity within the central heating zone, ensuring consistent and repeatable results.
Precise Atmosphere Control
Versatility is dramatically expanded by the ability to control the gaseous environment inside the tube.
Furnaces can be operated with a vacuum to remove reactive gases like oxygen, or they can be flooded with specific protective or reactive gases like argon, nitrogen, or hydrogen. This control is essential for preventing oxidation and enabling specific chemical syntheses.
The "Sweet Spot" of the 70mm Diameter
The 70mm internal diameter is a significant factor in the furnace's adaptability.
This size is large enough to process meaningful sample quantities for research and pilot studies but small enough to ensure rapid heating rates and high thermal efficiency. Its compact physical footprint also makes it easy to integrate into a crowded laboratory.
Inherent Simplicity and Configurability
Tube furnace technology is mature, resulting in a design that is simple, reliable, and relatively inexpensive.
This foundational simplicity allows for extensive customization. Users can select different furnace tube materials (e.g., quartz, alumina), add multiple heating zones, or integrate advanced gas management systems to tailor the furnace to a specific experimental need.
A Look at Real-World Applications
The combination of these features translates into a broad application base, making the 70mm tube furnace a common sight in diverse technical fields.
In Material Science
Researchers use it to study the thermal stability of new compounds, observe phase transitions in alloys and ceramics, and grow single crystals.
In Chemical & Nano Engineering
It is a workhorse for catalyst preparation and testing, performing high-temperature chemical synthesis, and growing nanomaterials like carbon nanotubes or nanowires through chemical vapor deposition (CVD).
In Electronics & Semiconductors
The furnace is critical for processes like semiconductor wafer annealing to repair crystal lattice damage and for creating thin films on substrates for electronic components.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While versatile, the 70mm tube furnace is not without its limitations. Objectively understanding these trade-offs is key to using it effectively.
Sample Size and Throughput
The most obvious limitation is sample size. The 70mm diameter is ideal for labs and pilot testing but is unsuitable for large-scale industrial production or processing bulk materials.
Natural Temperature Gradients
By design, a tube furnace is hottest in its center and cooler toward the ends. While this provides a highly uniform zone in the middle, it means that the entire length of the tube is not at a uniform temperature. This can be a drawback if a very long, uniform hot zone is required.
Required Ancillary Equipment
A base model tube furnace is a simple heater. Achieving true versatility for advanced applications often requires significant ancillary equipment, such as vacuum pumps, mass flow controllers, and gas plumbing, which adds to the overall cost and complexity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To leverage its versatility, you must align the furnace's capabilities with your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is fundamental research with small samples: The precision, atmospheric control, and compact size of a 70mm tube furnace make it an ideal choice.
- If your primary focus is process development or pilot testing: This furnace serves as an excellent, cost-effective tool for validating a thermal process before scaling up.
- If your primary focus is high-volume manufacturing: The 70mm tube furnace is not the right tool; you should investigate larger batch furnaces or continuous belt furnaces instead.
Understanding the principles of its design and its inherent limitations is the first step toward successful thermal processing.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit | Application Example |
|---|---|---|
| High-temperature capability (up to 1600°C) | Enables sintering, calcination, and annealing | Material science thermal stability studies |
| Precise atmosphere control (vacuum/gas) | Prevents oxidation, enables chemical syntheses | Catalyst preparation in chemical engineering |
| 70mm diameter design | Balances sample size with efficiency and compactness | Semiconductor wafer annealing |
| Simple, customizable configuration | Adapts to specific experimental needs | Nanomaterial growth via CVD |
Unlock the full potential of your thermal processing with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored 70mm tube furnaces and more—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental requirements, boosting efficiency and reliability. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your lab's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability



















