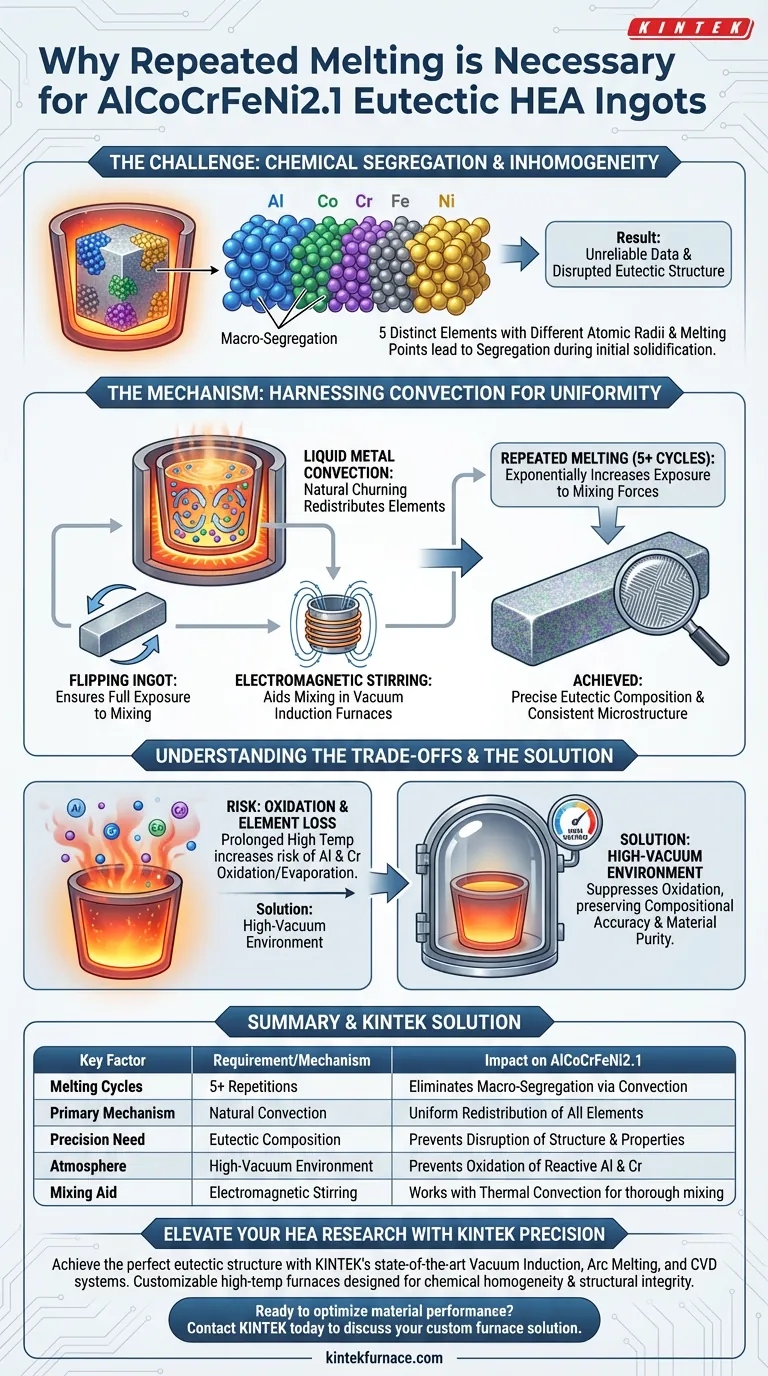
Repeated melting is strictly necessary to eliminate chemical segregation. For AlCoCrFeNi2.1 eutectic high-entropy alloys, performing this process five or more times utilizes the natural convection effect within the liquid metal. This ensures the precise chemical uniformity required for consistent microstructure and reproducible material performance.
The complex nature of multi-principal element alloys means they are prone to inhomogeneity during the initial melt. Repeated melting drives homogenization through convection, ensuring the final ingot represents a true eutectic composition rather than a mixture of segregated elements.

The Challenge of Homogeneity
The Problem of Chemical Segregation
High-entropy alloys (HEAs) are composed of multiple principal elements rather than a single solvent base. In the case of AlCoCrFeNi2.1, you are combining five distinct metals.
These elements possess significantly different atomic radii and melting points. Without intervention, they tend to separate or "segregate" during solidification.
This leads to macro-segregation, where the chemical composition varies across the ingot. An ingot with segregation yields unreliable data, as the microstructure will differ from one sample to the next.
The Sensitivity of Eutectic Compositions
AlCoCrFeNi2.1 is a eutectic alloy, meaning it has a specific composition that melts at a single, lowest possible temperature.
Achieving this specific eutectic structure requires extreme compositional precision. Even slight local variations caused by segregation can disrupt the lamellar structure and alter mechanical properties.
The Mechanism of Homogeneity
Harnessing Liquid Metal Convection
The primary mechanism for fixing segregation is the convection effect of the liquid metal.
When the alloy is melted, temperature gradients create fluid motion (convection) within the melt pool. This natural churning acts as a mixer, redistributing the elements.
However, a single melt is rarely sufficient to move all heavier and lighter elements into a uniform solution.
The Role of Repetition
By repeating the melting process five or more times, you exponentially increase the exposure of the alloy to these convective forces.
Supplementary techniques, such as flipping the ingot between melts, further assist this process. This ensures that areas previously at the bottom of the melt pool are exposed to the full intensity of the mixing action.
Electromagnetic Stirring
In vacuum induction furnaces, the process is aided by induction stirring.
The electromagnetic field generates forces within the conductive liquid metal, physically stirring the mixture. This works in tandem with thermal convection to break down segregations and ensure the five elements are thoroughly mixed in the liquid phase.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Balancing Homogeneity with Oxidation
While repeated melting improves mixing, it prolongs the time the material spends at high temperatures.
This increases the risk of oxidizing reactive elements, specifically Aluminum (Al) and Chromium (Cr). If these elements oxidize and evaporate, the actual composition of the alloy will drift away from the target formula.
The Necessity of Vacuum Environments
To mitigate the loss of active elements, this process must occur in a high-vacuum environment (such as a vacuum induction or arc melting furnace).
The vacuum suppresses oxidation, allowing for the necessary multiple melting cycles without degrading the material's purity or altering its stoichiometry.
Ensuring Research Integrity
When preparing AlCoCrFeNi2.1 ingots, the melting protocol determines the validity of your subsequent data.
- If your primary focus is Structural Consistency: Ensure you perform at least five melting cycles. This is the threshold identified to sufficiently utilize convection for eliminating segregation in this specific alloy system.
- If your primary focus is Compositional Accuracy: Monitor the vacuum level strictly. A compromised vacuum during repeated melting will lead to the loss of Aluminum and Chromium, shifting the alloy away from the eutectic point.
Ultimately, repeated melting is not a redundancy; it is the fundamental step that transforms a mix of raw metals into a scientifically usable high-entropy alloy.
Summary Table:
| Key Factor | Requirement/Mechanism | Impact on AlCoCrFeNi2.1 |
|---|---|---|
| Melting Cycles | 5 or more repetitions | Utilizes liquid metal convection to eliminate macro-segregation. |
| Primary Mechanism | Natural Convection | Ensures uniform redistribution of elements with different atomic radii. |
| Precision Need | Eutectic Composition | Prevents disruption of the lamellar structure and mechanical properties. |
| Atmosphere | High-Vacuum Environment | Prevents oxidation and evaporation of reactive elements like Al and Cr. |
| Mixing Aid | Electromagnetic Stirring | Works with thermal convection to thoroughly mix the five principal elements. |
Elevate Your HEA Research with KINTEK Precision
Achieving the perfect eutectic structure in AlCoCrFeNi2.1 requires more than just raw materials; it demands the right thermal processing environment. KINTEK provides state-of-the-art Vacuum Induction, Arc Melting, and CVD systems designed specifically for the rigorous requirements of high-entropy alloy synthesis.
Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, our lab high-temp furnaces are fully customizable to meet your unique compositional needs, ensuring your research is built on a foundation of chemical homogeneity and structural integrity.
Ready to optimize your material performance? Contact KINTEK today to discuss your custom furnace solution.
Visual Guide
References
- Effect of Heat Treatment on Corrosion of an AlCoCrFeNi2.1 Eutectic High-Entropy Alloy in 3.5 wt% NaCl Solution. DOI: 10.3390/met15060681
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace Molybdenum Wire Vacuum Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the core functions of the High Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace? Optimize DD5 Superalloy Purification
- What role does the vacuum chamber play in the melting process? Enhance Metal Purity and Efficiency
- What are the benefits of the compact and lightweight design of induction furnaces? Maximize Efficiency in Limited Space
- What are the advantages of induction melting furnaces in metal processing? Boost Efficiency, Quality, and Safety
- What industries commonly use melt furnaces? Key Applications in Metal, Aerospace, and More
- Why is a vacuum environment important in a VIM furnace? Unlock Purity and Performance in Metal Melting
- What types of materials can channel induction furnaces melt? The Ideal High-Volume Metal Melting Solution
- How does induction heating contribute to a cleaner work environment? Boost Quality & Sustainability



















