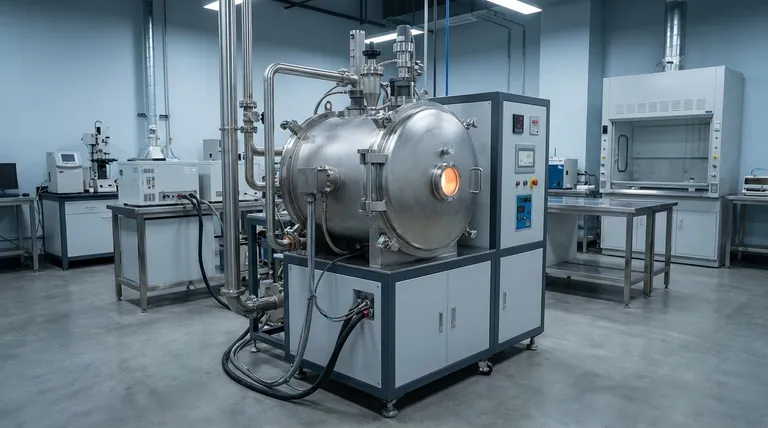
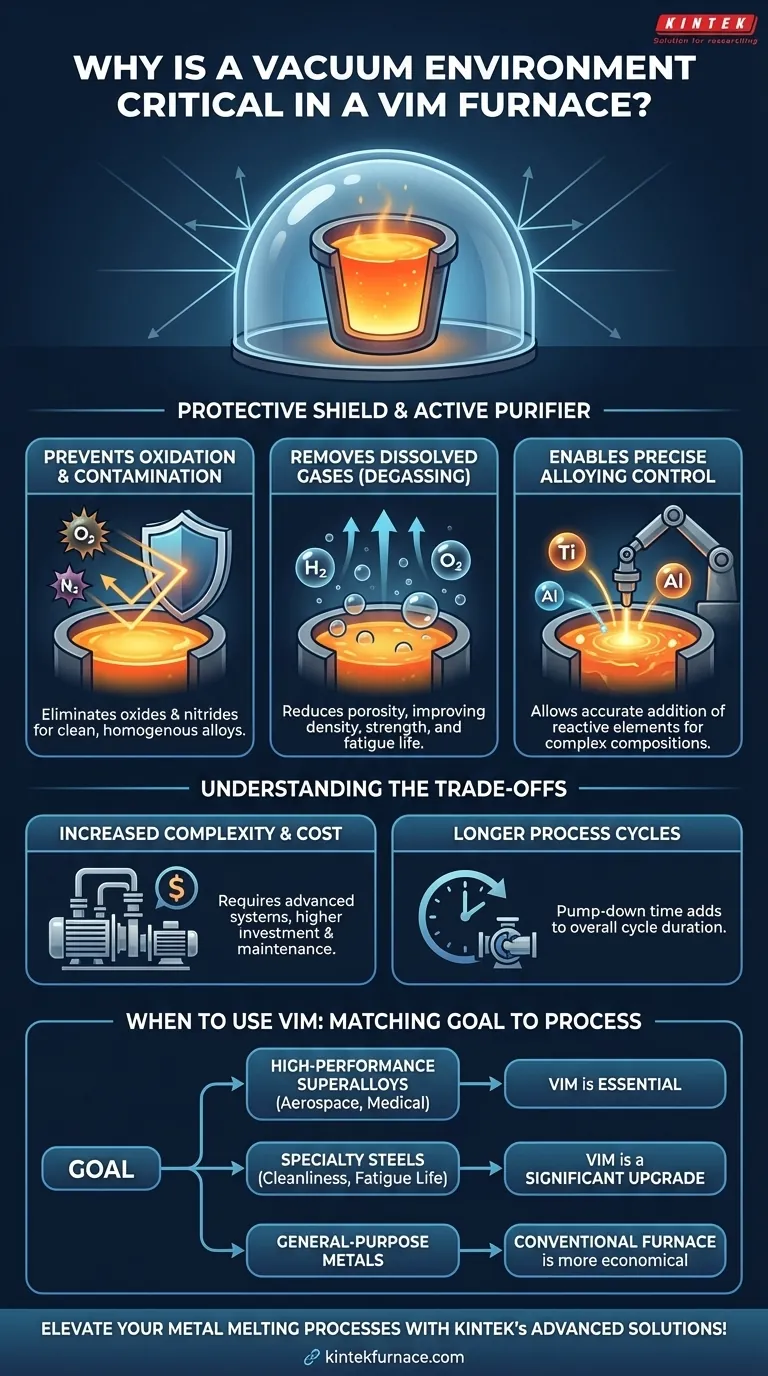
In a Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace, the vacuum environment is essential for two primary reasons. First, it acts as a protective shield, preventing the highly reactive molten metal from being contaminated by atmospheric gases like oxygen and nitrogen. Second, it actively purifies the metal by pulling out dissolved gases, such as hydrogen, that would otherwise compromise the final material's integrity.
The core challenge in high-performance metallurgy is that air, which is essential for life, is a potent contaminant for molten metals. A VIM furnace uses a vacuum to eliminate this threat, enabling the creation of alloys with a purity and performance level that is impossible to achieve in an open atmosphere.

The Core Functions of a Vacuum Environment
To understand the importance of VIM, you must first see the furnace's vacuum not as an empty space, but as an active tool for chemical control. It performs several critical functions that directly impact the quality of the final alloy.
Preventing Oxidation and Contamination
At the extreme temperatures required for melting, metals are highly reactive. Exposing them to air would cause immediate and undesirable chemical reactions.
The vacuum system removes nearly all oxygen and nitrogen from the melting chamber. This prevents the formation of oxides and nitrides, which are brittle, ceramic-like inclusions that act as microscopic weak points within the metal structure.
By eliminating these reactions, the vacuum ensures the final product is a clean, homogenous metal alloy rather than a material contaminated with performance-degrading impurities.
Removing Dissolved Gases (Degassing)
Molten metals can dissolve significant amounts of gases, particularly hydrogen and oxygen. If these gases remain in the melt, they will be forced out of the solution as the metal solidifies.
This outgassing creates microscopic voids and porosity, which severely reduce the material's density, strength, and fatigue life.
The vacuum environment lowers the partial pressure of gases above the melt to near zero. This pressure difference creates a powerful driving force that effectively pulls dissolved gases out of the liquid metal, purifying it in a process known as degassing.
Enabling Precise Alloying Control
Many advanced materials, such as nickel-based superalloys used in jet engines, rely on highly reactive elements like titanium and aluminum for their exceptional properties.
If you were to add these elements in an air-melt process, they would instantly oxidize and be lost as slag instead of becoming part of the alloy.
The inert vacuum environment ensures that every gram of a carefully measured alloying element contributes to the final chemistry. This allows for the precise and repeatable manufacturing of alloys with complex, high-performance compositions.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While the benefits are significant, operating in a vacuum introduces unique challenges and costs. It is a specialized process reserved for applications where material performance is non-negotiable.
Increased Complexity and Cost
VIM furnaces are far more complex and expensive than their air-melt counterparts. They require large, robust vacuum chambers, sophisticated multi-stage pumping systems, and precise instrumentation to maintain and monitor the low-pressure environment.
This inherent complexity translates to higher initial investment, more intensive maintenance, and greater operational costs.
Longer Process Cycles
Achieving the required high vacuum level is not instantaneous. The furnace chamber must be pumped down before melting can begin, and the process must be carefully controlled.
This pump-down time adds to the overall cycle time for each batch, making VIM a less rapid process compared to melting in an open-air induction furnace.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
The decision to use a VIM process is driven entirely by the required quality and performance of the end material.
- If your primary focus is producing high-performance superalloys or reactive metals: VIM is not just beneficial; it is the only viable method for achieving the required purity, strength, and reliability for critical applications like aerospace or medical implants.
- If your primary focus is improving the cleanliness and fatigue life of specialty steels: VIM provides a significant upgrade over air-melting by removing dissolved gases and non-metallic inclusions, resulting in a superior final product.
- If your primary focus is melting common, non-reactive metals for general-purpose applications: The high cost and complexity of VIM are likely unnecessary, and a conventional induction or arc furnace will be more economical.
Ultimately, leveraging a vacuum is a deliberate choice to exert absolute control over the metal's chemistry to achieve peak performance.
Summary Table:
| Function | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Prevents Oxidation and Contamination | Eliminates oxides and nitrides for clean, homogenous alloys |
| Removes Dissolved Gases (Degassing) | Reduces porosity, improving density, strength, and fatigue life |
| Enables Precise Alloying Control | Allows accurate addition of reactive elements for complex compositions |
Elevate your metal melting processes with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored VIM furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Tube Furnaces, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, delivering superior purity, performance, and reliability for critical applications in aerospace, medical, and specialty metals. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your operations and achieve your material goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the common applications of Vacuum Induction Melting? Essential for High-Performance Metals and Alloys
- What are the core functions of the High Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace? Optimize DD5 Superalloy Purification
- What is the purpose of vacuum melting, casting and re-melting equipment? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- What role does a vacuum induction melting furnace play in Fe-5%Mn-C alloys? Ensure Chemical Integrity and High Purity
- What is vacuum induction melting technology and why is it important? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications



















