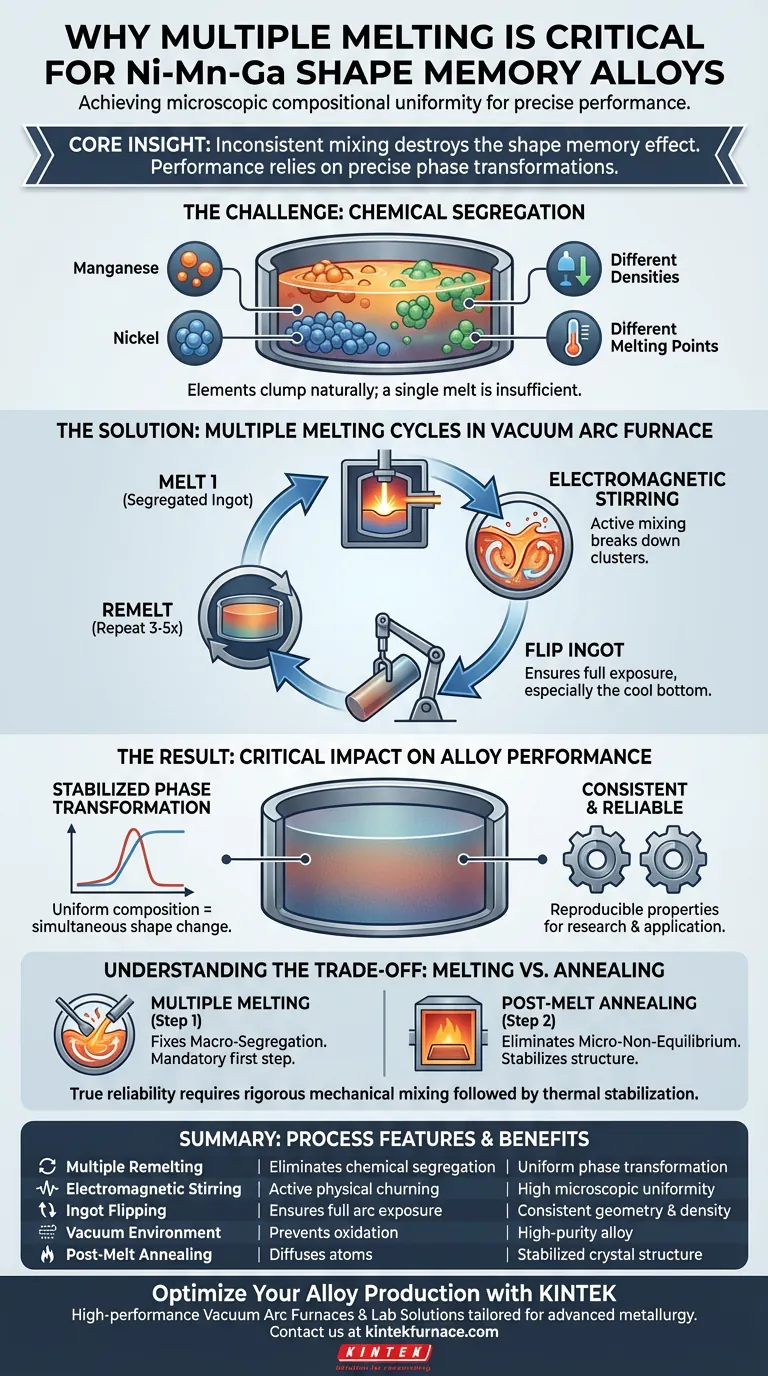
Achieving microscopic compositional uniformity is the decisive factor in preparing high-quality Ni-Mn-Ga shape memory alloys. You must perform multiple melting cycles in a vacuum arc furnace to overcome chemical segregation, ensuring that the nickel, manganese, and gallium are evenly distributed throughout the ingot to guarantee precise alloy performance.
The Core Insight In shape memory alloys, performance relies entirely on precise phase transformations. If an ingot is not remelted multiple times, chemical segregation causes different regions of the material to transform at different temperatures, effectively destroying the consistency of the shape memory effect.

The Physics of Homogeneity
Overcoming Chemical Segregation
When you melt distinct elements like nickel, manganese, and gallium, they do not naturally mix into a perfect solid solution immediately.
The primary reference indicates that without intervention, chemical segregation occurs. This means the elements clump together based on their chemical nature rather than dispersing defined by the target atomic ratio.
The Role of Physical Properties
Supplementary data suggests that segregation often stems from differences in the density and melting points of the constituent metals.
When the arc melts the raw materials, heavier elements may sink while lighter ones float, or those with higher melting points may not fully integrate into the melt pool initially. A single melt cycle is rarely sufficient to overcome these physical barriers to mixing.
The Mechanism of Multiple Melting
Utilizing Electromagnetic Stirring
The vacuum arc furnace offers a distinct advantage described as the electromagnetic stirring effect.
By remelting the alloy, you utilize the high-energy arc and the convection currents within the liquid metal to physically churn the mixture. This active mixing eliminates macro-segregation, breaking down large clusters of unmixed elements.
The Importance of Flipping
A standard protocol often involves not just remelting, but flipping the ingot between cycles.
While the primary reference focuses on the outcome, supplementary contexts regarding similar alloys (like High-Entropy Alloys and Ti-based alloys) confirm that flipping ensures the bottom of the ingot—which is often cooled against the crucible—is brought to the top and exposed to the direct energy of the arc. This creates a consistent baseline across the entire geometry of the ingot.
Critical Impact on Alloy Performance
Stabilizing Phase Transformation
For Ni-Mn-Ga alloys specifically, the "shape memory" capability is dictated by the temperature at which the crystal structure changes (phase transformation).
The primary reference explicitly states that uniformity prevents phase transformation temperature fluctuations. If the composition varies even microscopically from one end of the ingot to the other, the alloy will not trigger its shape change simultaneously, leading to unpredictable mechanical behavior.
Ensuring Reproducibility
Multiple melting ensures that the microstructure is consistent from batch to batch.
By eliminating segregation, you ensure that the material properties—such as corrosion resistance or mechanical strength mentioned in broader alloy contexts—remain uniform. This makes the material reliable for research into microstructural evolution or practical application.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Melting vs. Heat Treatment
It is a common pitfall to assume that multiple melting solves all microstructural problems.
While melting fixes macro-segregation (large-scale mixing), it may not achieve perfect equilibrium on its own. As noted in supplementary data regarding vacuum tube furnaces, a subsequent heat treatment (annealing) at stable high temperatures is often required to allow atoms to diffuse and eliminate non-equilibrium structures.
The trade-off: Multiple melting is the mandatory first step to homogenize the chemistry, but it must often be paired with post-melt annealing to stabilize the crystal phase. Relying on melting alone may leave residual stresses or unstable phases.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine the rigor of your process, consider the precision required by your application:
- If your primary focus is fundamental research: You must prioritize 4-5 remelting cycles with flipping to eliminate all variables that could skew microstructural analysis.
- If your primary focus is rapid prototyping: You may reduce cycles to 3, but you must accept the risk of slight variations in phase transformation temperatures across the part.
True reliability in shape memory alloys is not found in the chemistry alone, but in the rigorous mechanical mixing of the melt.
Summary Table:
| Process Feature | Benefit for Ni-Mn-Ga Alloys | Impact on Performance |
|---|---|---|
| Multiple Remelting | Eliminates chemical segregation and macro-clusters | Uniform phase transformation temperatures |
| Electromagnetic Stirring | Active physical churning of the melt pool | High microscopic compositional uniformity |
| Ingot Flipping | Ensures full arc exposure for crucible-cooled areas | Consistent material geometry and density |
| Vacuum Environment | Prevents oxidation and atmospheric contamination | High-purity alloy with reliable properties |
| Post-Melt Annealing | Diffuses atoms to eliminate non-equilibrium phases | Stabilized crystal structure and memory effect |
Optimize Your Alloy Production with KINTEK
Precision in Ni-Mn-Ga shape memory alloys starts with the right equipment. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Vacuum Arc Furnaces, Muffle, Tube, and CVD systems tailored for advanced metallurgy. Whether you are conducting fundamental research or high-precision manufacturing, our customizable lab solutions ensure the thermal stability and mixing efficiency required for your unique needs.
Ready to achieve superior compositional uniformity?
Contact our specialists today to find your custom solution.
Visual Guide
References
- Xinyue Li, Jie Zhu. Mechanical and Magnetic Properties of Porous Ni50Mn28Ga22 Shape Memory Alloy. DOI: 10.3390/met14030291
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace Molybdenum Wire Vacuum Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using an induction melting furnace? Enhance High-Entropy Alloy Homogeneity and Purity
- What critical role does a vacuum arc furnace play in the melting of Ti-Zr-Nb alloys? Ensure Peak Purity and Homogeneity
- What is the function of a Vacuum Induction Heating Furnace in research? Synthesis and Purity of Copper-Bearing Steel
- What are the benefits of using induction furnaces for copper melting? Boost Quality, Efficiency & Safety
- What are the benefits of miniaturization in IGBT induction melting furnaces? Maximize Efficiency & Save Space
- Why are induction gold melting furnaces considered cost-effective in the long run? A Smart Investment for Higher Profits
- What is the principle of a vacuum induction melting furnace based on? Achieve High-Purity Metal Melting
- What are the raw materials for induction furnace? The Essential Guide to Charge & Construction Materials



















