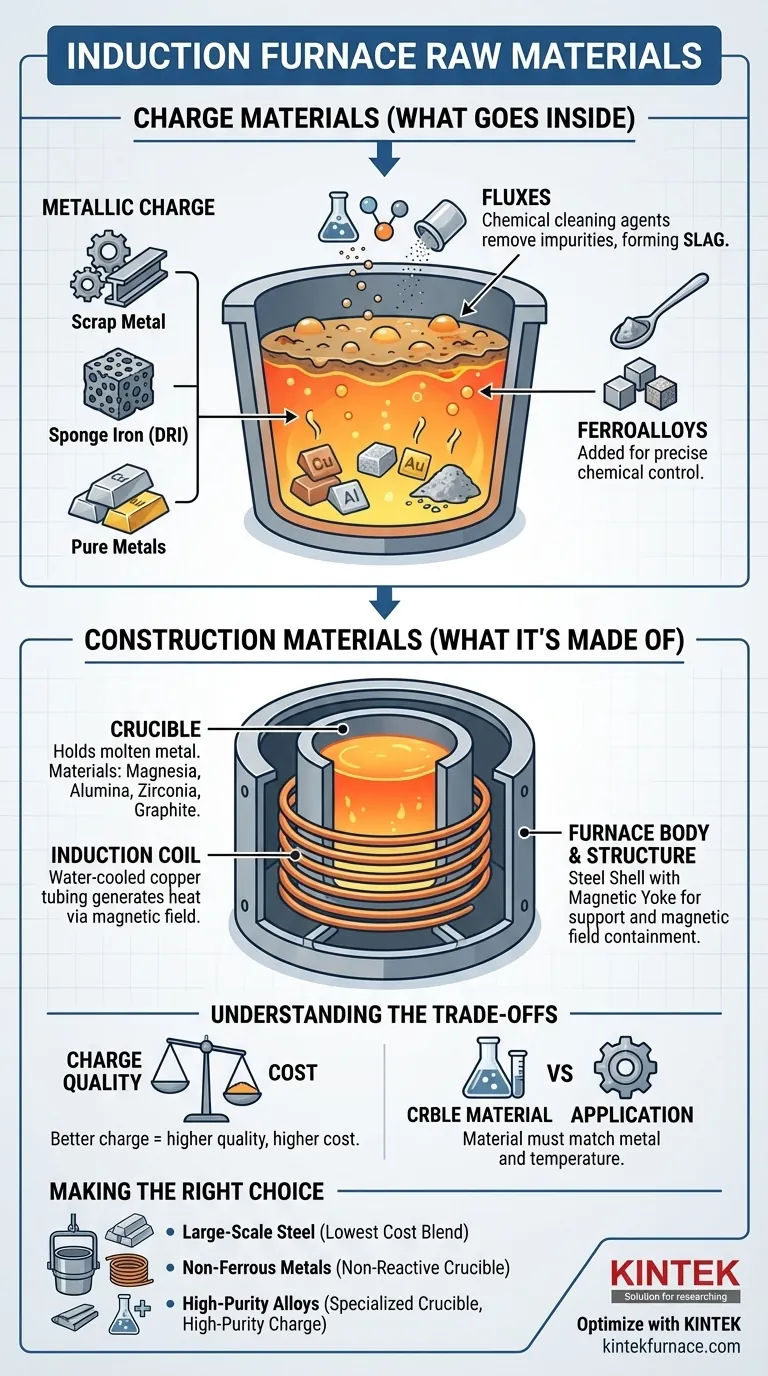
The primary raw materials for an induction furnace process are the metallic charge, such as steel scrap or sponge iron, which is melted down. This charge is supplemented with fluxes to remove impurities and ferroalloys to adjust the final chemical composition of the metal. These materials work together to produce a refined final product.
The term "raw materials" for an induction furnace has two distinct meanings: the charge materials that are melted and the construction materials from which the furnace itself is built. Understanding the role of both is essential for controlling the quality, efficiency, and cost of any melting operation.

The Charge: What Goes Inside the Furnace
The charge is the combination of ingredients placed into the crucible for melting. The specific blend is determined by the desired output metal and its required purity.
The Metallic Charge
This is the main component to be melted. The choice of metallic charge is the primary driver of cost and final quality.
Common options include:
- Scrap Metal: This is the most common charge, especially for steel and iron. It can range from recycled industrial offcuts to post-consumer products.
- Sponge Iron (DRI): A form of pure iron, it can be blended with or substitute scrap metal, often up to 50%, to dilute impurities.
- Pure Metals: For non-ferrous applications or high-purity alloys, the charge may consist of ingots or blocks of aluminum, copper, gold, silver, and other specific metals.
Fluxes
Fluxes are chemical cleaning agents added to the metallic charge. Their primary purpose is to react with and remove impurities from the molten metal.
These impurities, such as phosphorus and sulfur, float to the surface and combine with the flux to form a layer called slag. The slag is then skimmed off before the molten metal is poured.
Ferroalloys
Ferroalloys are master alloys containing a high proportion of a specific element (like manganese, silicon, or chromium) mixed with iron.
They are added to the molten metal in precise amounts toward the end of the melting process. This allows operators to precisely control the final chemical specification and mechanical properties of the resulting steel or iron alloy.
Furnace Construction: What the Furnace is Made Of
Beyond the materials being melted, the materials used to build the furnace are critical for its operation, safety, and longevity. These are not consumed in the process but form the core equipment.
The Crucible
The crucible is the refractory-lined container that holds the molten metal. Its material must withstand extreme temperatures and be chemically non-reactive with the specific metal being melted.
Common crucible materials include magnesia, alumina, zirconia, and graphite. The choice depends entirely on the application's temperature and chemical requirements.
The Induction Coil
The heating itself is generated by an induction coil, which is a precisely wound assembly of water-cooled copper tubing. An alternating electric current flows through this coil, creating a powerful magnetic field that induces heat directly within the metallic charge.
The Furnace Body and Structure
The furnace body provides the structural support for the coil and crucible. It is typically a steel shell designed to contain the magnetic field and manage operational stresses.
A magnetic yoke, made of laminated steel, is often placed around the coil to concentrate the magnetic field on the charge and prevent the steel shell from overheating.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Material selection involves balancing cost, quality, and operational efficiency. There are no universally "best" materials, only optimal choices for a specific goal.
Charge Quality vs. Cost
Using lower-grade, cheaper scrap metal will reduce initial material costs. However, it often contains higher levels of impurities, requiring more flux, more energy to refine, and potentially leading to a lower-quality final product. High-purity sponge iron or pure metals yield a better product but at a significantly higher cost.
Crucible Material vs. Application
The crucible material directly impacts the purity of the melt and the furnace's lifespan. Using an alumina crucible for a standard iron melt is effective, but melting a highly reactive metal in the wrong crucible can lead to contamination of the final product and rapid degradation of the crucible lining.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your choice of raw materials should be directly guided by your end goal.
- If your primary focus is large-scale steel production: Your key consideration is optimizing the blend of steel scrap, sponge iron, and fluxes to achieve the required grade at the lowest possible cost.
- If your primary focus is melting non-ferrous metals (e.g., aluminum, copper): Your charge material will be scrap or pure metal, and selecting the correct non-reactive crucible is your most critical decision to prevent contamination.
- If your primary focus is high-purity or specialty alloys: You must prioritize high-purity charge materials and a specialized crucible (like graphite or zirconia) to maintain absolute control over the final chemistry.
Ultimately, mastering the raw materials for both the charge and the furnace itself is fundamental to controlling every aspect of the induction melting process.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Key Components | Primary Function |
|---|---|---|
| Charge Materials | Steel scrap, sponge iron, pure metals | Main component to be melted |
| Fluxes | Chemical cleaning agents | Remove impurities to form slag |
| Ferroalloys | Master alloys (e.g., FeMn, FeSi) | Adjust final chemical composition |
| Furnace Materials | Refractory crucible, copper coil, steel shell | Build and enable the furnace operation |
Optimize Your Induction Melting Process with KINTEK
Choosing the right raw materials is fundamental to the quality, efficiency, and cost of your melting operation. KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Induction Furnaces, tailored to your specific needs.
Our deep customization capabilities ensure your furnace and its components—from the crucible material to the coil design—are perfectly matched to your charge materials, whether you are processing steel scrap, non-ferrous metals, or high-purity alloys.
Ready to enhance your melting quality and efficiency? Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can be customized for your unique requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of vacuum melting, casting and re-melting equipment? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- How does the Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) process work? Achieve Superior Metal Purity and Control
- What are the common applications of Vacuum Induction Melting? Essential for High-Performance Metals and Alloys
- How does vacuum melting technology contribute to sustainability? Boost Durability and Recycling Efficiency
- Why is a Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace essential? Unlock Purity for Aerospace and Semiconductors



















