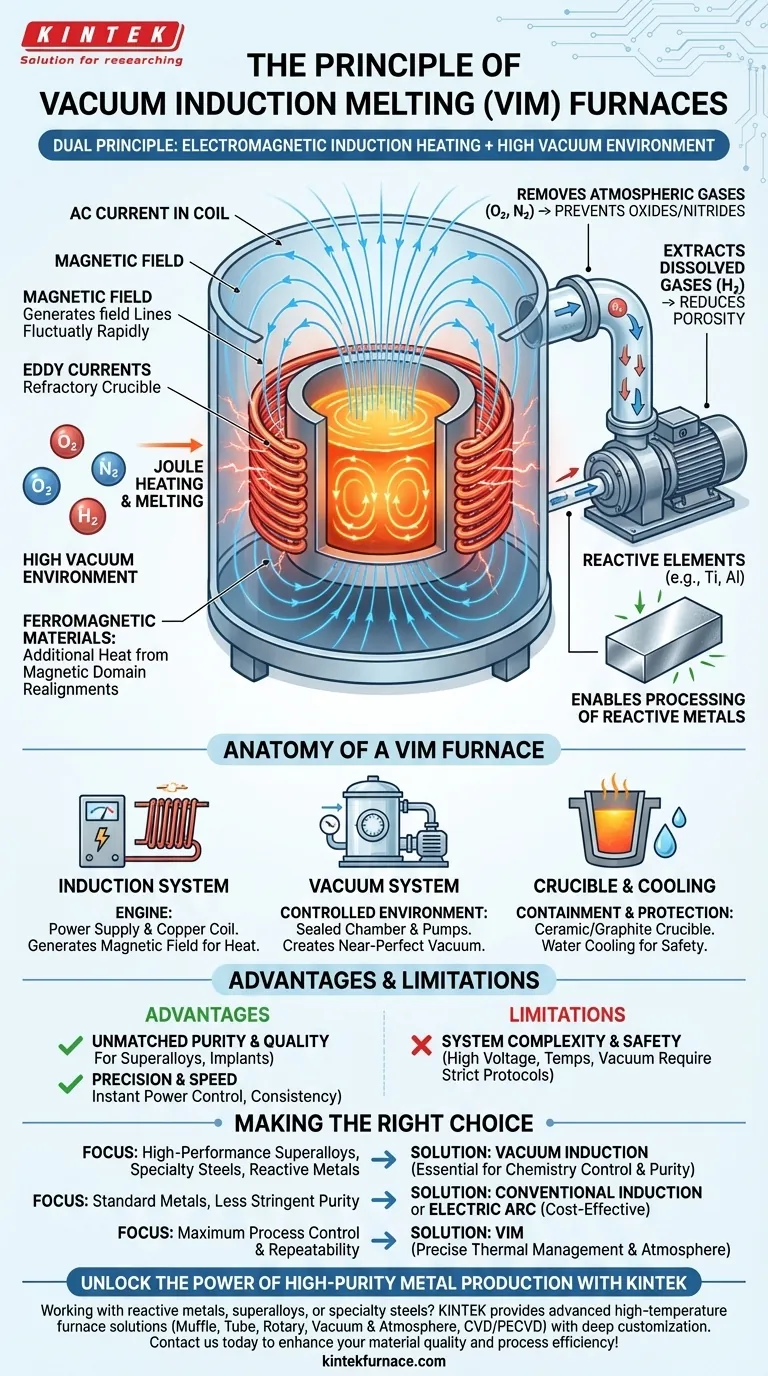
At its core, a vacuum induction melting (VIM) furnace operates on a dual principle: it combines the efficient, contactless heating of electromagnetic induction with the purifying environment of a high vacuum. This combination is not just for melting metal; it's a sophisticated refining process designed to produce alloys with the highest possible purity and performance characteristics.
The essential takeaway is that induction heating provides the energy to melt the metal, while the vacuum provides the controlled environment to purify it. This synergy is what allows for the creation of advanced materials that are impossible to produce in open-air conditions.
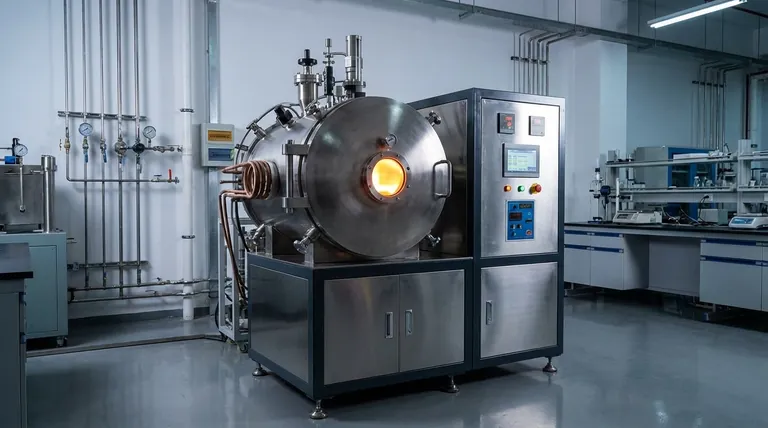

The Dual Principles: Heating and Purification
To understand a VIM furnace, you must appreciate its two foundational technologies working in concert. One is responsible for heat, the other for quality.
Principle 1: Electromagnetic Induction Heating
The heating process is entirely contactless, relying on fundamental physics.
An alternating current (AC) is passed through a copper induction coil. This generates a powerful and rapidly fluctuating magnetic field inside the furnace.
When a conductive metal is placed within this magnetic field, the field induces strong electrical currents within the metal itself, known as eddy currents.
The metal's natural electrical resistance fights against these eddy currents, generating immense heat through a process called Joule heating. This heat is what melts the material quickly and uniformly.
For ferromagnetic materials like iron and nickel, additional heat is generated as their magnetic domains rapidly realign with the changing field, further increasing heating efficiency.
Principle 2: The Role of the Vacuum Environment
The vacuum is what elevates this process from simple melting to high-purity refining.
The vacuum chamber removes atmospheric gases, primarily oxygen and nitrogen. This prevents the formation of oxides and nitrides, which are impurities that can degrade the metal's mechanical properties.
This is especially critical when working with reactive elements like titanium and aluminum, which would otherwise be lost to oxidation in an air-melt process.
Furthermore, the low-pressure environment helps extract dissolved gases, such as hydrogen, from the molten metal. This degassing process drastically reduces porosity and improves the final alloy's structural integrity.
Anatomy of a Vacuum Induction Furnace
Several key systems must work together seamlessly to execute the VIM process.
The Induction System
This is the furnace's engine. It consists of a power supply that converts standard grid electricity into the high-frequency AC required for induction, and the water-cooled copper coil that generates the magnetic field.
The Vacuum System
This system creates the controlled environment. It includes the sealed vacuum chamber that houses the melt and a series of pumps capable of reducing the internal pressure to a near-perfect vacuum.
The Crucible and Cooling System
The molten metal is held within a high-temperature-resistant crucible, typically made of ceramic or graphite. A robust, closed-loop water cooling system is essential to continuously cool the induction coils and chamber walls, protecting them from the extreme heat.
Understanding the Advantages and Limitations
The complexity of a VIM furnace comes with significant benefits but also requires careful management.
Advantage: Unmatched Purity and Quality
By eliminating atmospheric contamination and removing dissolved gases, VIM furnaces produce the cleanest possible metals. This is non-negotiable for high-performance applications like aerospace superalloys and medical implants.
Advantage: Precision and Speed
The power delivered to the melt can be adjusted instantaneously by controlling the current in the coil. This allows for extremely precise temperature control and rapid heating cycles, leading to greater consistency and productivity.
Limitation: System Complexity and Safety
The integration of high-voltage power, extreme temperatures, and a high-vacuum environment is inherently complex. These systems demand sophisticated control panels and rigorous safety protocols, including automatic shut-offs and thermal protection, to ensure safe and reliable operation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Whether a VIM furnace is the correct tool depends entirely on the desired quality of the final product.
- If your primary focus is producing high-performance superalloys, specialty steels, or reactive metals: Vacuum induction is essential to control chemistry, remove impurities, and achieve the required material properties.
- If your primary focus is melting standard metals with less stringent purity requirements: A conventional, non-vacuum induction furnace or an electric arc furnace may be a more cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is maximum process control and repeatability: The precise thermal management and controlled atmosphere of a VIM furnace offer significant advantages over any open-air melting method.
Ultimately, vacuum induction melting is the enabling technology for creating the advanced materials that power our most demanding industries.
Summary Table:
| Principle Component | Function | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Electromagnetic Induction | Generates heat via eddy currents in metal | Rapid, uniform melting without contact |
| Vacuum Environment | Removes gases and prevents oxidation | Eliminates impurities and degasses metal |
Unlock the Power of High-Purity Metal Production with KINTEK
Are you working with reactive metals, superalloys, or specialty steels that demand the highest purity and performance? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your unique needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your experimental requirements.
Contact us today to discuss how our vacuum induction melting furnaces can enhance your material quality and process efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- What are some common applications of vacuum induction melting and casting (VIM&C)? Essential for Aerospace, Medical, and Nuclear Industries
- How has vacuum smelting impacted the development of superalloys? Unlock Higher Strength and Purity
- How does the Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) process work? Achieve Superior Metal Purity and Control
- What are the common applications of Vacuum Induction Melting? Essential for High-Performance Metals and Alloys
- What are the core functions of the High Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace? Optimize DD5 Superalloy Purification



















