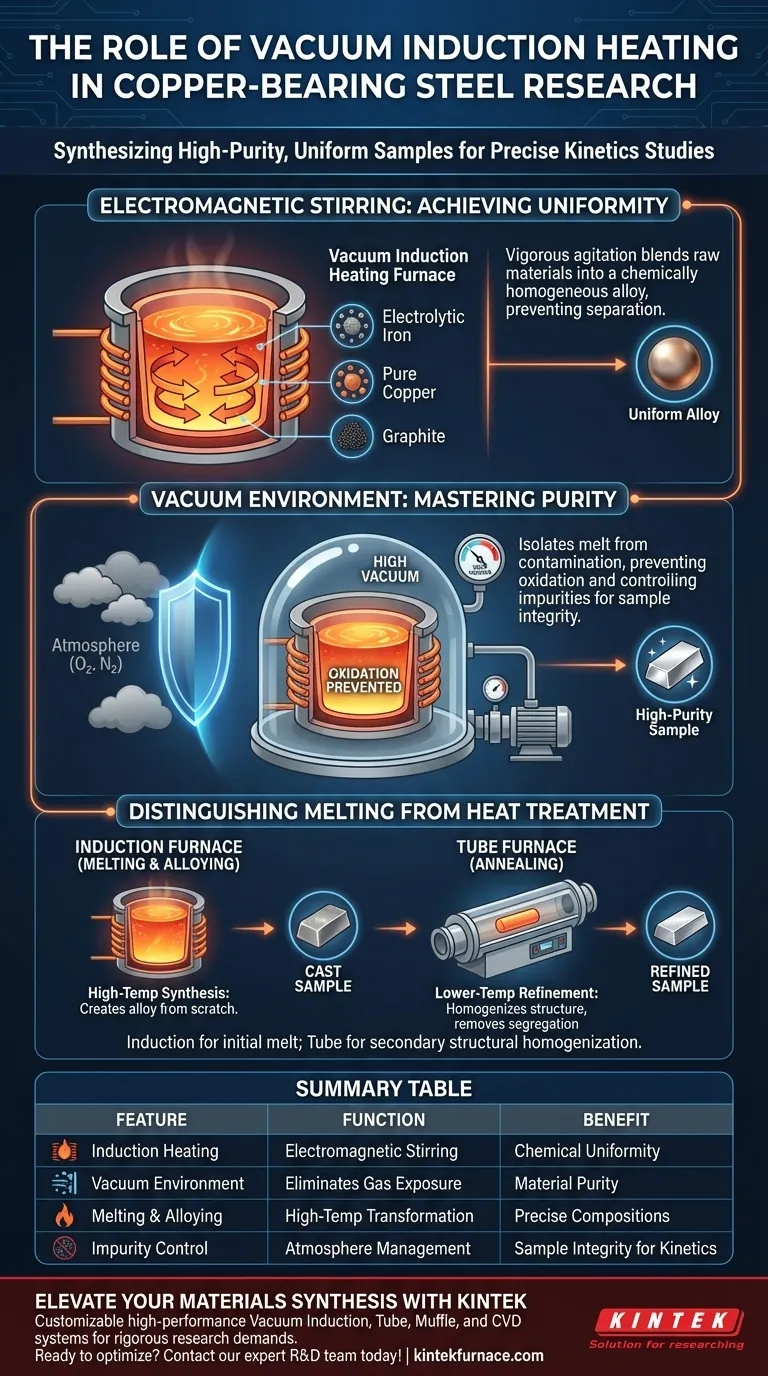
The primary function of a Vacuum Induction Heating Furnace in this context is to synthesize high-purity copper-bearing steel samples by melting and alloying raw materials in a strictly controlled environment. It utilizes electromagnetic forces to vigorously stir the molten mixture, ensuring that constituent elements like electrolytic iron, pure copper, and graphite are blended into a chemically uniform alloy suitable for research.
In materials science, the validity of kinetics studies relies entirely on sample integrity. The Vacuum Induction Heating Furnace serves as the foundational tool for synthesis, creating an isolated, active environment that guarantees the chemical homogeneity and impurity control required for high-precision data.

The Mechanics of High-Quality Synthesis
Electromagnetic Stirring
The defining feature of this furnace is its use of induction heating, which generates powerful electromagnetic forces within the crucible.
Unlike static heating methods, these forces create a vigorous, natural stirring action within the molten metal.
Achieving Uniformity
This continuous agitation is critical when alloying raw materials with varying properties, such as electrolytic iron and pure copper particles.
The stirring ensures these components are thoroughly mixed in the liquid state, preventing separation and ensuring the final steel sample has a uniform chemical composition throughout its volume.
Environmental Control and Purity
The Vacuum Advantage
Melting takes place within a vacuum chamber to isolate the molten steel from atmospheric contamination.
This environment prevents the oxidation of the metal and the absorption of unwanted gases, which is vital for maintaining the "cleanliness" of the steel.
Controlling Impurities
By managing the atmosphere and temperature, researchers can precisely control impurity levels in the final sample.
This control is essential for experimental consistency, particularly when the samples are destined for sensitive kinetics studies where impurities could skew results.
Distinguishing Melting from Heat Treatment
Initial Synthesis vs. Structural Refinement
It is crucial to distinguish the role of the Vacuum Induction Heating Furnace from that of a Vacuum Tube Furnace.
The Induction furnace is designed for the high-temperature melting and alloying phase, creating the steel from scratch.
The Role of Annealing
Conversely, a Vacuum Tube Furnace is typically used for secondary processing, such as solid-state annealing at lower temperatures (e.g., 850 °C).
While the Induction furnace ensures chemical mixing, the Tube furnace is used later to eliminate micro-segregation or remove solidification structures through homogenization under inert atmospheres like argon.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure your laboratory process yields valid research data, consider the specific stage of material preparation you are addressing:
- If your primary focus is synthesizing new alloys: Rely on the Vacuum Induction Heating Furnace to melt and mix raw elements into a chemically homogeneous liquid.
- If your primary focus is modifying mechanical properties: Move the cast samples to a Vacuum Tube Furnace for annealing to homogenize the structure and remove segregation.
Success in copper-bearing steel research begins with the precise control of chemical composition during the initial melt.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Function in Synthesis | Benefit to Research |
|---|---|---|
| Induction Heating | Generates vigorous electromagnetic stirring | Ensures chemical uniformity & alloy homogeneity |
| Vacuum Environment | Eliminates atmospheric gas exposure | Prevents oxidation and maintains material purity |
| Melting & Alloying | High-temp transformation of raw materials | Creates precise alloy compositions from scratch |
| Impurity Control | Strict management of the melt atmosphere | Guarantees sample integrity for kinetics studies |
Elevate Your Materials Synthesis with KINTEK
Precision in laboratory research starts with the integrity of your samples. KINTEK provides industry-leading thermal solutions, including high-performance Vacuum Induction, Tube, Muffle, and CVD systems, specifically engineered to meet the rigorous demands of material science. Whether you need to synthesize new copper-bearing alloys or perform high-precision annealing, our customizable furnaces offer the control and reliability your research deserves.
Ready to optimize your lab's heating processes? Contact our expert R&D team today to find your custom solution!
Visual Guide
References
- Hongyan Sun, Z. R. Chen. Copper Removal of Liquid Steel Containing 0.25% Carbon Using Fe<sub>2</sub>O<sub>3</sub>–CaCl<sub>2</sub>–SiO<sub>2</sub> Flux. DOI: 10.2355/isijinternational.isijint-2025-083
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the role of shell mold heating in a vacuum induction furnace? Optimize Casting Flow & Integrity
- How do induction furnaces enhance safety during the smelting process? Achieve Cleaner, Safer Metal Melting
- What are the key application requirements for the vacuum induction furnace? Ensure Safe, High-Purity Metal Processing
- How do induction furnaces generate heat for smelting precious metals? Discover Fast, Pure Melting Solutions
- What are the advantages of using a medium frequency vacuum induction furnace for NAB alloys? Precision & Purity
- What role does a vacuum induction melting furnace play in AHSS research? Master Purity in High-Strength Steel Ingots
- What are the key industries that utilize vacuum induction melting furnaces? Essential for Aerospace, Medical, and Electronics
- What role does a vacuum induction furnace play in smelting AlCoCrFeNi2.1? Master High-Entropy Alloy Precision



















