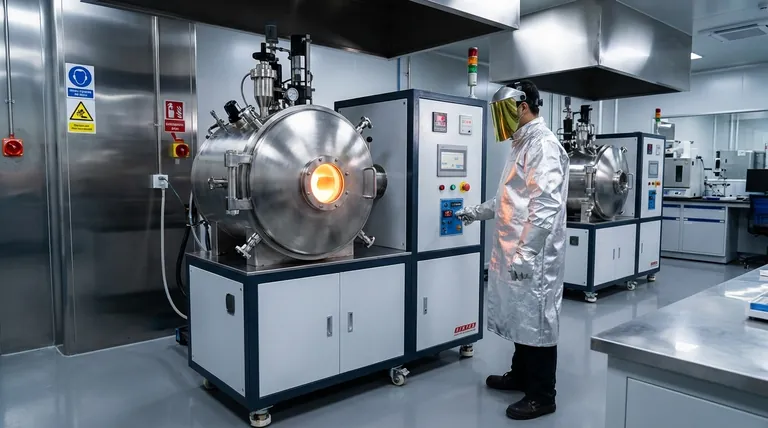
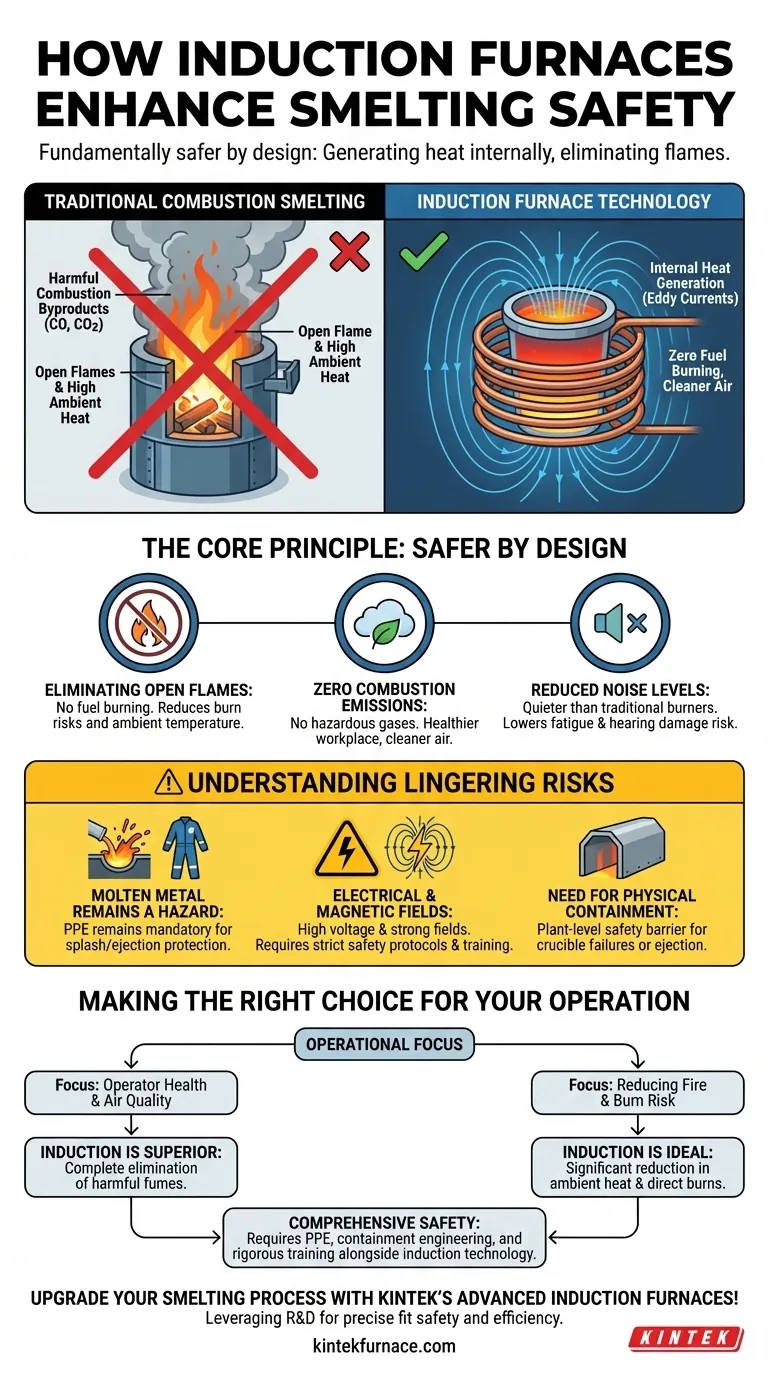
By design, induction furnaces fundamentally enhance safety by changing how heat is generated. Unlike traditional methods that rely on external combustion, induction heating uses electromagnetic fields to generate heat directly within the metal itself. This core principle eliminates open flames and the dangerous byproducts of burning fuel, creating a much safer environment for operators.
The primary safety advantage of induction furnaces stems from containment. The process confines intense heat to the metal inside the crucible, creating a cooler, cleaner, and quieter working environment by removing the need for external flames and eliminating harmful exhaust gases.

The Core Principle: Internal Heat Generation
The safety benefits of induction technology are not added features; they are a direct result of how the furnace operates. It's a foundational shift away from the risks of traditional combustion-based smelting.
Eliminating Open Flames
An induction furnace does not burn fuel. It uses a powerful, alternating magnetic field from a copper coil to induce electrical currents directly within the conductive metal charge.
These internal currents, known as eddy currents, generate intense heat through electrical resistance, melting the metal from the inside out.
This process completely removes the most obvious danger of traditional smelting: a live, open flame. This drastically reduces the risk of accidental burns to operators and lowers the ambient temperature of the workspace.
No Harmful Combustion Byproducts
Traditional furnaces burn fossil fuels like coke, oil, or natural gas, releasing significant amounts of carbon monoxide (CO), carbon dioxide, and other hazardous exhaust gases into the work environment.
Induction furnaces produce zero combustion emissions. By eliminating fuel burning, they provide cleaner air, reduce the need for complex ventilation systems, and create a healthier workplace.
Reduced Noise Levels
While not silent, induction furnaces operate at significantly lower noise levels than the roar of a fuel-fired burner or an arc furnace. This reduction in industrial noise helps prevent long-term hearing damage and reduces operator fatigue.
Understanding the Lingering Risks
While inherently safer, an induction furnace is still a piece of heavy industrial equipment used for melting metal. Understanding the remaining hazards is critical for a complete safety strategy.
Molten Metal Remains a Hazard
The primary risk of any foundry—molten metal splash and ejection—still exists. The method of heating the metal changes, but the danger of handling a liquid at extreme temperatures does not.
Proper personal protective equipment (PPE), including aluminized coats, face shields, and gloves, remains absolutely mandatory for all personnel near the furnace.
Electrical and Magnetic Field Safety
Induction furnaces use very high levels of electrical power and generate strong magnetic fields.
Workers must be trained on high-voltage electrical safety and lockout/tagout procedures. While modern furnace designs contain the magnetic fields, personnel with medical implants (like pacemakers) must adhere to strict safety protocols and exclusion zones.
The Need for Physical Containment
For large-scale industrial operations, the furnace itself is often housed within a protective tunnel or enclosure. This is not a feature of the furnace but a plant-level safety measure.
This containment helps protect the wider facility and workers from the extreme heat and provides a crucial barrier in the rare event of a crucible failure or metal ejection.
Making the Right Choice for Your Operation
Choosing an induction furnace is a major step toward a safer smelting process. The decision should be aligned with your specific operational priorities.
- If your primary focus is operator health and air quality: Induction is the superior choice due to the complete elimination of harmful combustion fumes.
- If your primary focus is reducing fire and burn risk: Induction's lack of an open flame significantly lowers ambient heat and dramatically reduces the chance of direct-contact burns.
- If you are implementing a new system: Remember that the furnace is only one part of a comprehensive safety plan that must include robust PPE policies, containment engineering, and rigorous electrical safety training.
Ultimately, adopting induction technology is a proactive investment in a fundamentally safer and cleaner operational environment.
Summary Table:
| Safety Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| No Open Flames | Reduces burn risks and ambient heat |
| Zero Combustion Emissions | Improves air quality and operator health |
| Lower Noise Levels | Decreases hearing damage and fatigue |
| Internal Heat Generation | Confines heat to metal, enhancing containment |
| Electrical Safety Protocols | Mitigates high-voltage and magnetic field hazards |
Upgrade your smelting process with KINTEK's advanced induction furnaces! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise fit for your unique safety and efficiency needs. Contact us today to enhance your operational safety and performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- What role does a vacuum induction melting furnace play in Fe-5%Mn-C alloys? Ensure Chemical Integrity and High Purity
- What are the common applications of Vacuum Induction Melting? Essential for High-Performance Metals and Alloys
- How does vacuum melting technology contribute to sustainability? Boost Durability and Recycling Efficiency
- What are the core functions of the High Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace? Optimize DD5 Superalloy Purification
- What are some common applications of vacuum induction melting and casting (VIM&C)? Essential for Aerospace, Medical, and Nuclear Industries



















