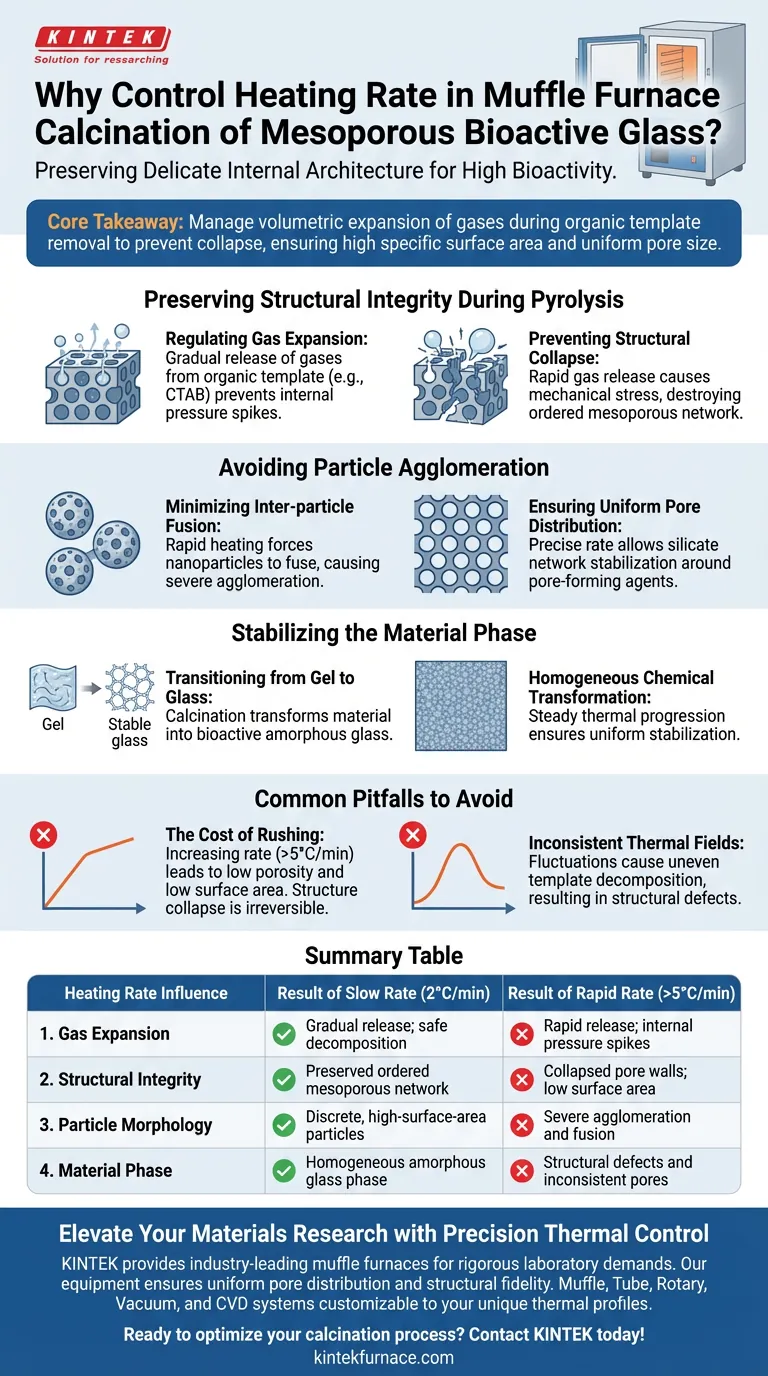
Strict control of the heating rate is required to preserve the delicate internal architecture of mesoporous bioactive glass. By maintaining a slow rate, typically 2 °C/min, you ensure that organic templates decompose gently rather than violently, preventing the destruction of the material's porous framework.
Core Takeaway: The primary goal of a controlled heating rate is to manage the volumetric expansion of gases during organic template removal. This prevents the collapse of the mesoporous structure, ensuring the final material retains the high specific surface area and uniform pore size required for bioactivity.

Preserving Structural Integrity During Pyrolysis
Regulating Gas Expansion
During calcination, the furnace is burning off organic template molecules, such as CTAB (cetyltrimethylammonium bromide).
As these molecules decompose via high-temperature pyrolysis, they release gases.
A controlled heating rate ensures this gas is released gradually, preventing internal pressure spikes that would rupture the delicate pore walls.
Preventing Structural Collapse
If the temperature rises too quickly, the sudden release of large gas volumes creates mechanical stress.
This stress causes the nanoparticle structure to collapse, effectively destroying the ordered mesoporous network you are trying to create.
Without this structure, the material loses the specific surface area that defines its quality and utility.
Avoiding Particle Agglomeration
Minimizing Inter-particle Fusion
Rapid heating introduces thermal shock and excessive energy that can force nanoparticles to fuse together.
This phenomenon, known as severe agglomeration, results in large, irregular clusters rather than discrete, high-surface-area particles.
Ensuring Uniform Pore Distribution
For bioactive glass to be effective, pore size must be uniform to allow for consistent biological interaction.
A precise heating rate allows the silicate network to stabilize slowly around the pore-forming agents before they are fully removed.
This creates a stable, ordered lattice that remains intact even after the organic template is gone.
Stabilizing the Material Phase
Transitioning from Gel to Glass
Beyond pore formation, calcination transforms the material from a gel state into a bioactive amorphous glass phase.
This process stabilizes the silicate network structure.
A steady thermal progression ensures this chemical transformation occurs homogeneously throughout the material.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
The Cost of Rushing
The most common error is increasing the heating rate to save time.
While a rate of 5 °C/min or higher might shorten the process, it frequently results in a product with low porosity and low surface area.
Once the structure collapses during calcination, it cannot be recovered; the batch is effectively ruined.
Inconsistent Thermal Fields
Fluctuations in the heating rate can lead to uneven decomposition of the template.
This results in structural defects where some areas have open pores while others are dense or collapsed.
Stability in the temperature rise is just as critical as the target temperature itself.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure the successful synthesis of mesoporous bioactive glass, adhere to the following parameters:
- If your primary focus is Structural Fidelity: Adhere strictly to a heating rate of 2 °C/min to maximize specific surface area and pore uniformity.
- If your primary focus is Material Purity: Ensure the final hold time at 700 °C is sufficient to fully remove all organic residues without compromising the silicate network.
Precise thermal management is the difference between a high-performance bioactive material and a useless, non-porous glass.
Summary Table:
| Heating Rate Influence | Result of Slow Rate (2°C/min) | Result of Rapid Rate (>5°C/min) |
|---|---|---|
| Gas Expansion | Gradual release; safe decomposition | Rapid release; internal pressure spikes |
| Structural Integrity | Preserved ordered mesoporous network | Collapsed pore walls; low surface area |
| Particle Morphology | Discrete, high-surface-area particles | Severe agglomeration and fusion |
| Material Phase | Homogeneous amorphous glass phase | Structural defects and inconsistent pores |
Elevate Your Materials Research with Precision Thermal Control
Precise heating rates are the foundation of high-performance biomaterial synthesis. KINTEK provides industry-leading muffle furnaces designed for the rigorous demands of laboratory research. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, we offer Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all customizable to your unique thermal profiles.
Whether you need to maintain a strict 2°C/min ramp or require specialized atmospheres for organic template removal, our equipment ensures uniform pore distribution and structural fidelity every time.
Ready to optimize your calcination process? Contact KINTEK today to discuss your custom furnace needs!
Visual Guide
References
- Usanee Pantulap, Aldo R. Boccaccini. Hydroxycarbonate apatite formation, cytotoxicity, and antibacterial properties of rubidium-doped mesoporous bioactive glass nanoparticles. DOI: 10.1007/s10934-023-01546-9
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- How does a bench-top high-temperature furnace ensure the quality of the ceramic layer? Master CCT for Ti6242 Alloy
- What are the applications of muffle furnaces? Essential for High-Temperature Material Processing
- How does a muffle furnace control the atmosphere around the sample? Achieve Precise Material Processing
- What is the reputation of box furnaces in terms of quality and reliability? Trusted for Decades in High-Stakes Applications
- What is a muffle furnace and how is it designed? Discover Its Clean, High-Temp Heating for Pure Results
- How are muffle furnaces used in glassmaking? Achieve Clean, Controlled Heat for Superior Glass Quality
- What is the temperature of a sintering oven? Master Material-Specific Thermal Cycles
- What are the research applications of box furnaces? Essential for Material Synthesis and Heat Treatment



















