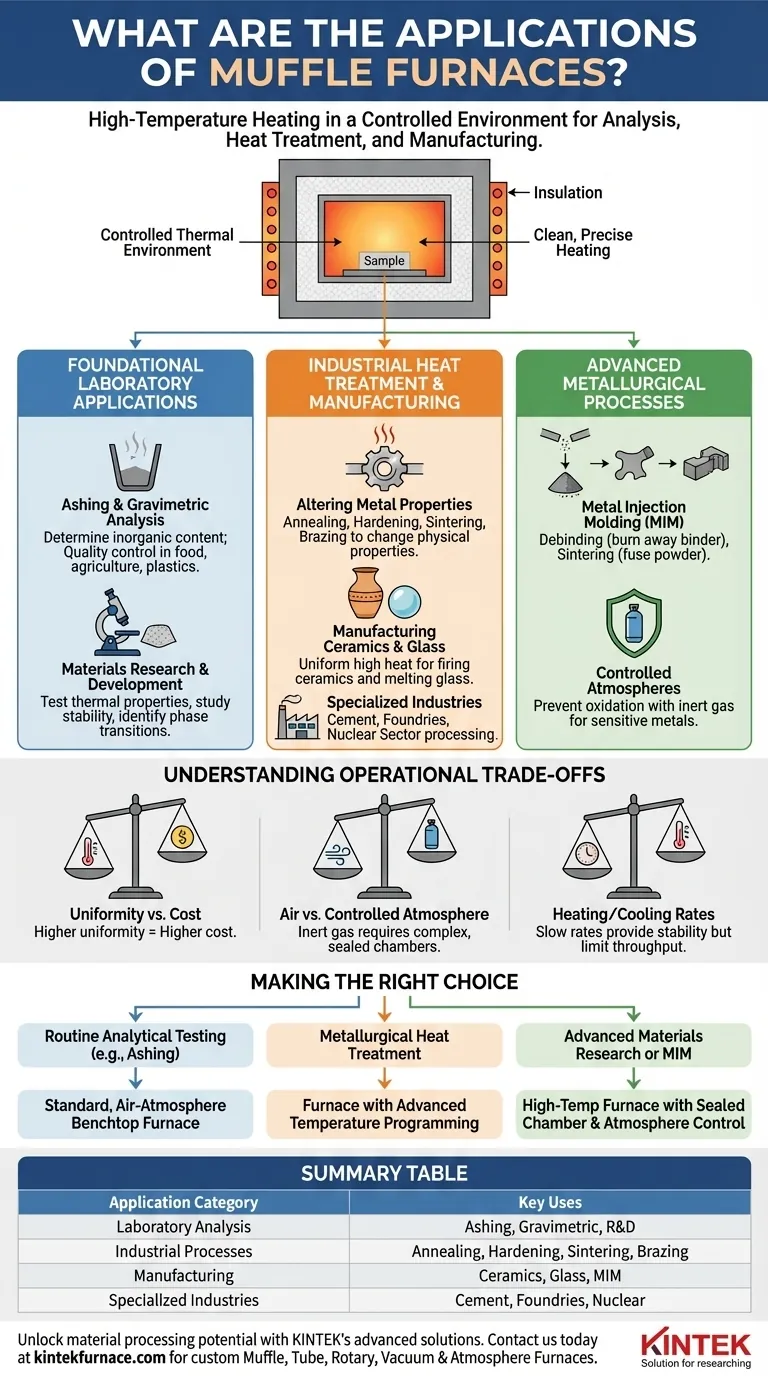
At their core, muffle furnaces are used for any process requiring high-temperature heating in a controlled environment. Their primary applications fall into three main categories: performing chemical analysis like ashing, executing metallurgical heat treatments to alter material properties, and manufacturing materials like ceramics, glass, and sintered metal parts.
A muffle furnace's unique value comes from its design, which separates the material being heated from the heating elements and any combustion byproducts. This creates a clean, precisely controlled thermal environment, making it an indispensable tool for processes where sample purity and predictable results are critical.

Foundational Laboratory Applications
The most common use for muffle furnaces is in analytical and research laboratories, where sample integrity is paramount.
Ashing and Gravimetric Analysis
Ashing is a process used to determine the inorganic, non-combustible content of a sample. The furnace heats the material to a high temperature, completely burning off all organic matter and leaving only the ash (inorganic residue) behind for weighing and analysis.
This is a fundamental quality control step in industries ranging from food science and agriculture to plastics and petroleum.
Materials Research and Development
Researchers use muffle furnaces to test the thermal properties of materials. By subjecting samples to precise temperature cycles, they can study thermal stability, identify phase transition points, and simulate high-temperature operating conditions.
This is crucial for developing new alloys, polymers, composites, and ceramics with specific performance characteristics.
Industrial Heat Treatment and Manufacturing
In industrial settings, muffle furnaces are workhorses for modifying and creating materials on a larger scale.
Altering Metal Properties
Heat treatment changes the physical and mechanical properties of metals. The controlled environment of a muffle furnace is ideal for processes like:
- Annealing: Softening a metal to improve ductility and reduce internal stresses.
- Hardening: Heating and rapidly cooling a metal to increase its hardness and strength.
- Sintering: Fusing metallic powders together below their melting point to create solid parts.
- Brazing: Joining two or more metal items by melting and flowing a filler metal into the joint.
Manufacturing Ceramics and Glass
The production of technical ceramics and specialty glass requires extremely high, uniform temperatures. A muffle furnace provides the stable thermal environment needed to fire ceramics or melt and form glass components without introducing contaminants.
Processing in Specialized Industries
Muffle furnaces are essential in sectors with demanding material requirements. Industries like cement production, foundries, and the nuclear sector rely on them to process samples and treat materials under high heat.
Advanced Metallurgical Processes
Modern muffle furnaces enable sophisticated applications that are central to advanced manufacturing.
Metal Injection Molding (MIM)
MIM is a multi-step process for creating complex, high-volume metal parts. A muffle furnace is used for two critical stages:
- Debinding: Gently heating the "green" part to burn away the polymer binder mixed with the metal powder.
- Sintering: Heating the now-porous "brown" part to a higher temperature to fuse the metal particles into a dense, solid final product.
Use in Controlled Atmospheres
While many applications run in ambient air, the "muffle" design is perfect for creating a controlled atmosphere. By purging the chamber and introducing an inert gas like nitrogen or argon, oxidation of the sample can be prevented.
This capability is non-negotiable for heat-treating oxygen-sensitive metals or conducting specific types of chemical analysis.
Understanding the Operational Trade-offs
While incredibly versatile, a muffle furnace is a specialized tool with specific considerations.
Temperature Uniformity vs. Cost
Achieving perfect temperature uniformity across the entire chamber is a significant engineering challenge. Higher-end models offer superior uniformity and more precise controllers but at a substantially higher cost.
Air Atmosphere vs. Controlled Atmosphere
A standard muffle furnace operates with an air atmosphere. To run processes under an inert gas or a reactive gas, you need a furnace specifically designed with sealed chambers and gas inlet/outlet ports, which adds complexity and expense.
Heating and Cooling Rates
Due to their significant thermal insulation and mass, muffle furnaces heat up and cool down slowly. This provides thermal stability but can limit sample throughput in a high-volume production environment. Cycle times must be factored into any process planning.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the right approach, you must align the furnace's capabilities with your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is routine analytical testing (e.g., ashing): A standard, air-atmosphere benchtop furnace with a reliable temperature controller will be effective and economical.
- If your primary focus is metallurgical heat treatment: Prioritize a furnace with advanced temperature programming to execute precise heating, soaking, and cooling profiles, and consider if atmosphere control is needed to prevent oxidation.
- If your primary focus is advanced materials research or MIM: You will require a high-temperature furnace with excellent uniformity and a fully sealed chamber for robust atmosphere control.
Ultimately, the muffle furnace is an essential tool for precisely manipulating and analyzing materials at their thermal limits.
Summary Table:
| Application Category | Key Uses |
|---|---|
| Laboratory Analysis | Ashing, Gravimetric Analysis, Materials R&D |
| Industrial Processes | Annealing, Hardening, Sintering, Brazing |
| Manufacturing | Ceramics, Glass, Metal Injection Molding (MIM) |
| Specialized Industries | Cement, Foundries, Nuclear Sector |
Unlock the full potential of your material processing with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with reliable tools like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental needs, enhancing efficiency and accuracy. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your specific applications and drive innovation in your projects!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production



















