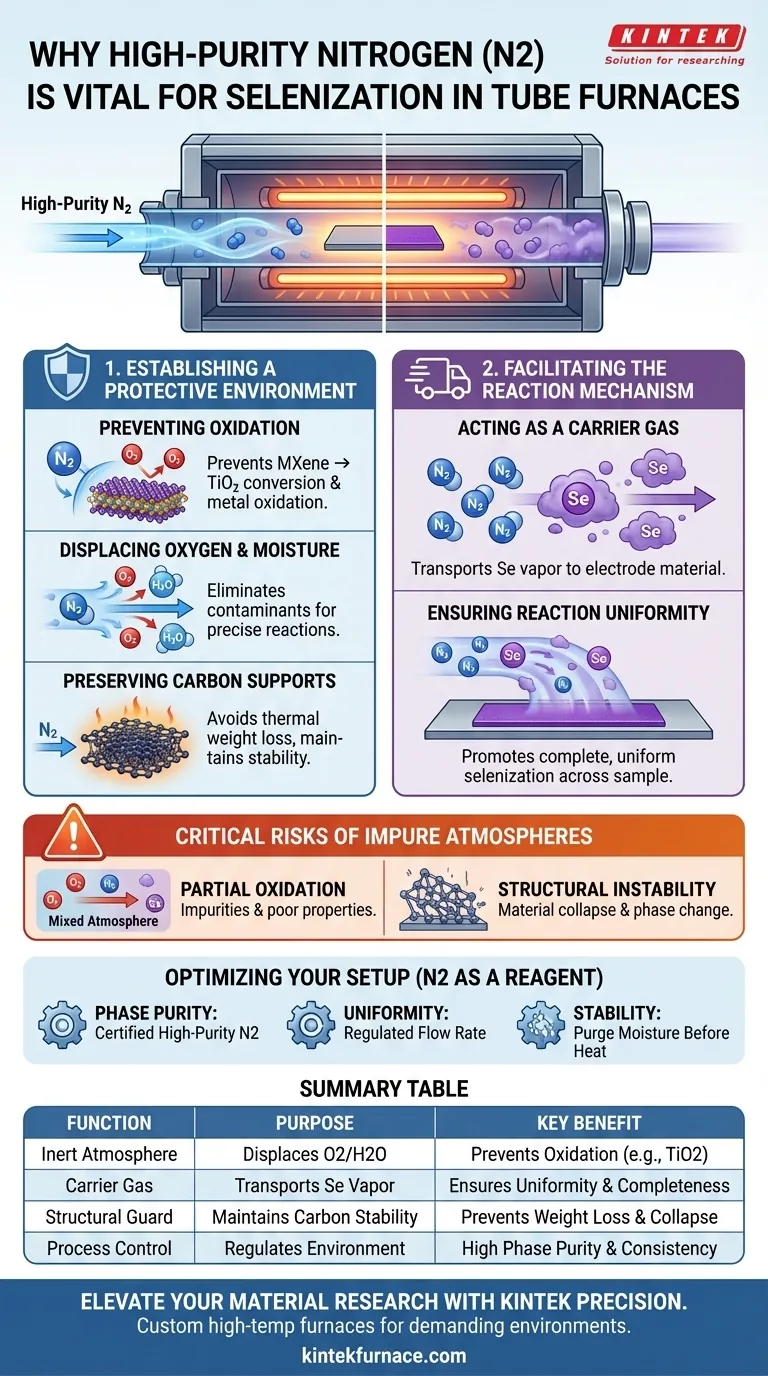
The use of high-purity nitrogen (N2) is mandatory during selenization to simultaneously protect the electrode material and facilitate the chemical reaction. Its primary function is to establish an oxygen-free, reductive environment that prevents sensitive materials, such as MXene layers, from oxidizing into unwanted byproducts like TiO2. Additionally, acts as a critical carrier gas, physically transporting selenium vapor to the sample to ensure a uniform and complete reaction.
The presence of high-purity nitrogen transforms the tube furnace from a simple heating element into a controlled reactor. It prevents the chemical degradation of precursors while physically driving the selenium vapor necessary for a complete and uniform reaction.

Establishing a Protective Environment
Preventing Chemical Oxidation
The most immediate risk during high-temperature selenization is the degradation of the active material.
Without an inert atmosphere, materials like MXene layers are susceptible to oxidation, converting them into Titanium Dioxide (TiO2). Similarly, metallic components like nickel will oxidize if exposed to air. High-purity nitrogen eliminates this risk by creating a reductive or neutral environment.
Displacing Oxygen and Moisture
A tube furnace is not naturally void of contaminants.
Nitrogen flow is required to actively displace residual oxygen and moisture present within the tube. This displacement is vital to prevent the over-oxidation of metallic nanoparticles. It ensures the environment remains stable for precise reduction and doping reactions.
Preserving Carbon Supports
Many electrode materials rely on carbon supports for conductivity and structure.
In the presence of oxygen, these supports can suffer from unnecessary thermal weight loss during pyrolysis. A continuous nitrogen flow creates the stability needed to maintain the chemical stability of the carbon support throughout the process.
Facilitating the Reaction Mechanism
Acting as a Carrier Gas
Selenium vaporizes at high temperatures, but it cannot effectively reach the sample area on its own.
Nitrogen serves as the vehicle for this transport. It acts as a carrier gas, picking up the selenium vapor and steadily driving it toward the electrode material positioned downstream in the furnace.
Ensuring Reaction Uniformity
The quality of the final electrode depends on how evenly the selenium is applied.
A steady, continuous flow of nitrogen ensures the selenium vapor is distributed evenly across the sample. This promotes the completeness of the selenization reaction, ensuring the entire sample is doped or coated uniformly rather than leaving untreated patches.
Critical Risks of Impure Atmospheres
The Danger of Partial Oxidation
Even a small reduction in nitrogen purity or a breach in the furnace seal can compromise the process.
If oxygen is not fully displaced, you risk creating a "mixed" atmosphere. This can lead to the formation of impurities effectively destroying the electrochemical properties of the material before the selenization is even complete.
Structural Instability
The integrity of the material's structure is linked to the atmosphere.
Failing to maintain a strictly inert environment can lead to the collapse of the material's architecture. For example, the structural integrity of active materials (like MXene) relies heavily on preventing the phase change that occurs during oxidation.
Optimizing Your Selenization Setup
To ensure high-performance electrode materials, you must view the nitrogen supply as a reagent, not just a utility.
- If your primary focus is Phase Purity: Ensure your nitrogen source is certified high-purity to preventing the conversion of MXene to TiO2 or the oxidation of Nickel.
- If your primary focus is Reaction Uniformity: Regulate the flow rate of the nitrogen to ensure a steady, consistent delivery of selenium vapor to the sample zone.
- If your primary focus is Structural Stability: Verify the system is purged of moisture before heating to prevent thermal weight loss in carbon supports.
Control the atmosphere, and you control the chemistry of your final material.
Summary Table:
| Function of N2 | Purpose in Selenization | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Inert Atmosphere | Displaces oxygen and moisture | Prevents oxidation of MXene/metals (e.g., TiO2 formation) |
| Carrier Gas | Transports selenium vapor downstream | Ensures uniform distribution and reaction completeness |
| Structural Guard | Maintains chemical stability of carbon | Prevents thermal weight loss and structural collapse |
| Process Control | Regulates chemical environment | High phase purity and consistent doping levels |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK Precision
Don't let atmospheric contamination compromise your electrode performance. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed for the most demanding chemical environments. Our lab high-temp furnaces are fully customizable to provide the precise atmosphere and temperature control required for your unique selenization and doping processes.
Ready to optimize your results? Contact us today to find the perfect furnace solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
References
- Hui Li, Min Jae Ko. Selenized Binary Transition Metals‐MXene Composite for High‐Performance Asymmetric Hybrid Capacitors. DOI: 10.1002/smll.202504350
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is the development of high-temperature vacuum equipment and processes increasingly important? Unlock Purity and Performance in Materials
- What components are used in the construction of vacuum graphitizing furnaces? A Guide to High-Temp Performance
- What role does a vacuum heat treatment furnace play in the preparation of SKD6 side dies? Enhance Tool Steel Longevity
- Why do some nonferrous metals require a vacuum furnace for heat treating? To Prevent Oxidation and Ensure Purity
- Why are the materials used in vacuum furnace construction critical? Ensure Peak Performance and Purity
- What is the specific purpose of using a vacuum oven for mesoporous Bi2Se3? Enhance Purity and Pore Access
- What are the benefits of using drop-bottom quench furnaces? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Precision and Rapid Quenching
- What role do the vacuum arc furnace and titanium getter play in refractory medium-entropy alloy production? Mastering Purity & Power



















