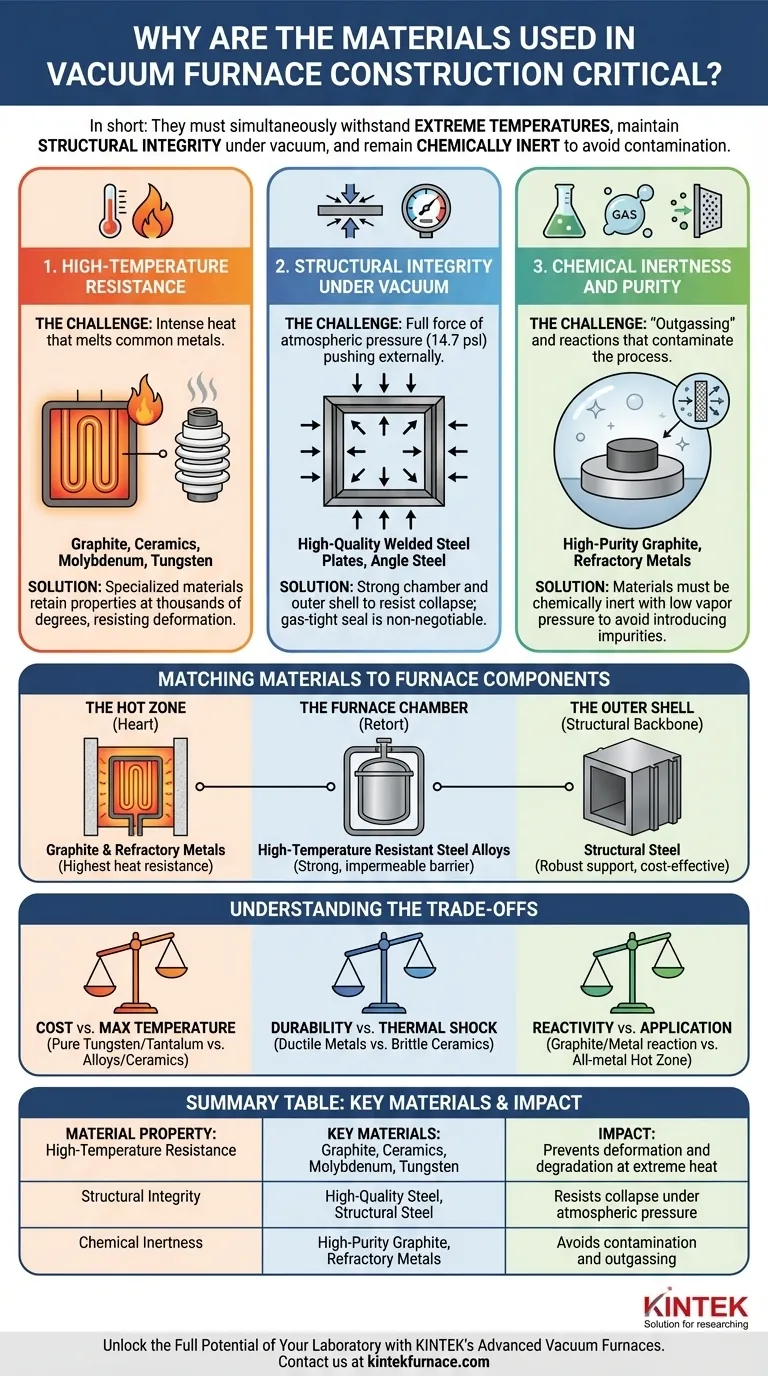
In short, the materials used in a vacuum furnace are critical because they must simultaneously withstand extreme temperatures, maintain structural integrity under a high external pressure, and remain chemically inert to avoid contaminating the process. These three demands—thermal, structural, and chemical—dictate every aspect of the furnace’s design, performance, and reliability.
The selection of vacuum furnace materials is not about finding a single "best" substance. It is a strategic engineering decision, balancing the competing demands of heat resistance, structural strength, and chemical purity to create a controlled environment for highly sensitive processes.

The Three Pillars of Material Selection
A vacuum furnace is an environment of extremes. The materials chosen to build it are not merely passive containers; they are active components that must perform reliably under immense stress. Their selection is guided by three fundamental requirements.
1. High-Temperature Resistance
The most obvious challenge is the intense heat. Materials inside the furnace, particularly in the "hot zone," must operate at temperatures that would melt or vaporize common metals.
These components must resist deformation, melting, and degradation. This is why specialized materials like graphite, ceramics, molybdenum, and tungsten are used for heating elements and insulation, as they retain their properties at thousands of degrees.
2. Structural Integrity Under Vacuum
Creating a vacuum means removing the internal pressure, leaving the full force of atmospheric pressure—about 14.7 pounds per square inch—pushing on the outside of the furnace.
The furnace chamber and outer shell must be strong enough to resist this crushing force without collapsing. This is why furnace shells are often constructed from welded, high-quality steel plates and angle steel, providing the necessary rigidity and strength. A gas-tight seal is non-negotiable to maintain the vacuum.
3. Chemical Inertness and Purity
At high temperatures and in a vacuum, materials can "outgas," releasing trapped gases or even vaporizing slightly. This can contaminate the workpiece, ruining sensitive processes like semiconductor manufacturing or the sintering of exotic alloys.
The internal materials must be chemically inert and have extremely low vapor pressure. They cannot react with the material being processed or introduce impurities into the vacuum. This is especially critical in furnaces used for graphite purification, where the furnace itself must be of a higher purity than the product.
Matching Materials to Furnace Components
A furnace is not made of a single material but is an assembly of specialized components, each with its own distinct role and material requirements.
The Hot Zone: Heart of the Furnace
This area contains the heating elements and insulation. It faces the most extreme temperatures and requires materials with the highest heat resistance and specific thermal properties. Graphite and refractory metals are common choices due to their stability and efficient heat transfer.
The Furnace Chamber or Retort
This is the sealed vessel that contains the vacuum. It must be strong, impermeable, and often made from high-temperature resistant steel alloys. The retort acts as the primary barrier, containing the controlled environment and protecting the hot zone.
The Outer Shell: Structural Backbone
The outer shell provides the main structural support against atmospheric pressure. Since it is shielded from the highest temperatures by insulation, it can be built from more conventional but robust materials like structural steel, which offers an excellent balance of strength and cost.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The choice of materials is always a balance of competing factors. Understanding these trade-offs is key to understanding furnace design.
Cost vs. Maximum Temperature
Materials capable of handling the highest temperatures, like pure tungsten or tantalum, are exceptionally expensive. For processes that operate at lower temperatures, more cost-effective alloys or ceramics provide reliable performance without the high price tag.
Durability vs. Thermal Shock
Metals are generally ductile and resistant to physical impact. Ceramics, while offering excellent temperature and chemical resistance, can be brittle and susceptible to cracking if heated or cooled too quickly (thermal shock).
Reactivity vs. Application
While graphite is a popular choice for hot zones, it can react with certain metals to form carbides. In these cases, an all-metal hot zone using molybdenum or tungsten is necessary, even if it is more expensive, to ensure the purity of the final product.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The ideal furnace construction is defined by its intended application, as different processes prioritize different material properties.
- If your primary focus is ultra-high temperatures (e.g., graphitization, ceramic firing): You will need a furnace with a hot zone made of graphite or refractory metals like tungsten to handle the extreme thermal load.
- If your primary focus is preventing any contamination (e.g., medical implants, electronics): The purity of the internal materials, such as high-purity graphite or an all-metal hot zone, becomes the most critical factor to prevent outgassing.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose vacuum brazing or sintering: A furnace with a durable, high-temperature steel retort and a metallic or graphite hot zone offers the best balance of performance, versatility, and cost.
Ultimately, a vacuum furnace's performance is a direct reflection of the thoughtful engineering and material science that form its foundation.
Summary Table:
| Material Property | Key Materials | Impact on Furnace Performance |
|---|---|---|
| High-Temperature Resistance | Graphite, Ceramics, Molybdenum, Tungsten | Prevents deformation and degradation at extreme heat |
| Structural Integrity | High-Quality Steel, Structural Steel | Resists collapse under atmospheric pressure |
| Chemical Inertness | High-Purity Graphite, Refractory Metals | Avoids contamination and outgassing in sensitive processes |
Unlock the Full Potential of Your Laboratory with KINTEK's Advanced Vacuum Furnaces
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you need ultra-high temperatures for graphitization, contamination-free environments for medical implants, or versatile solutions for brazing and sintering, KINTEK delivers reliable performance tailored to your goals.
Contact us today via our contact form to discuss how our expertise can enhance your processes and drive innovation in your lab!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Superior Surface Quality and Material Performance
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in LP-DED? Optimize Alloy Integrity Today
- What are the general operational features of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Material Purity & Precision
- Why does heating steel rod bundles in a vacuum furnace eliminate heat transfer paths? Enhance Surface Integrity Today
- What are the proper procedures for handling the furnace door and samples in a vacuum furnace? Ensure Process Integrity & Safety



















