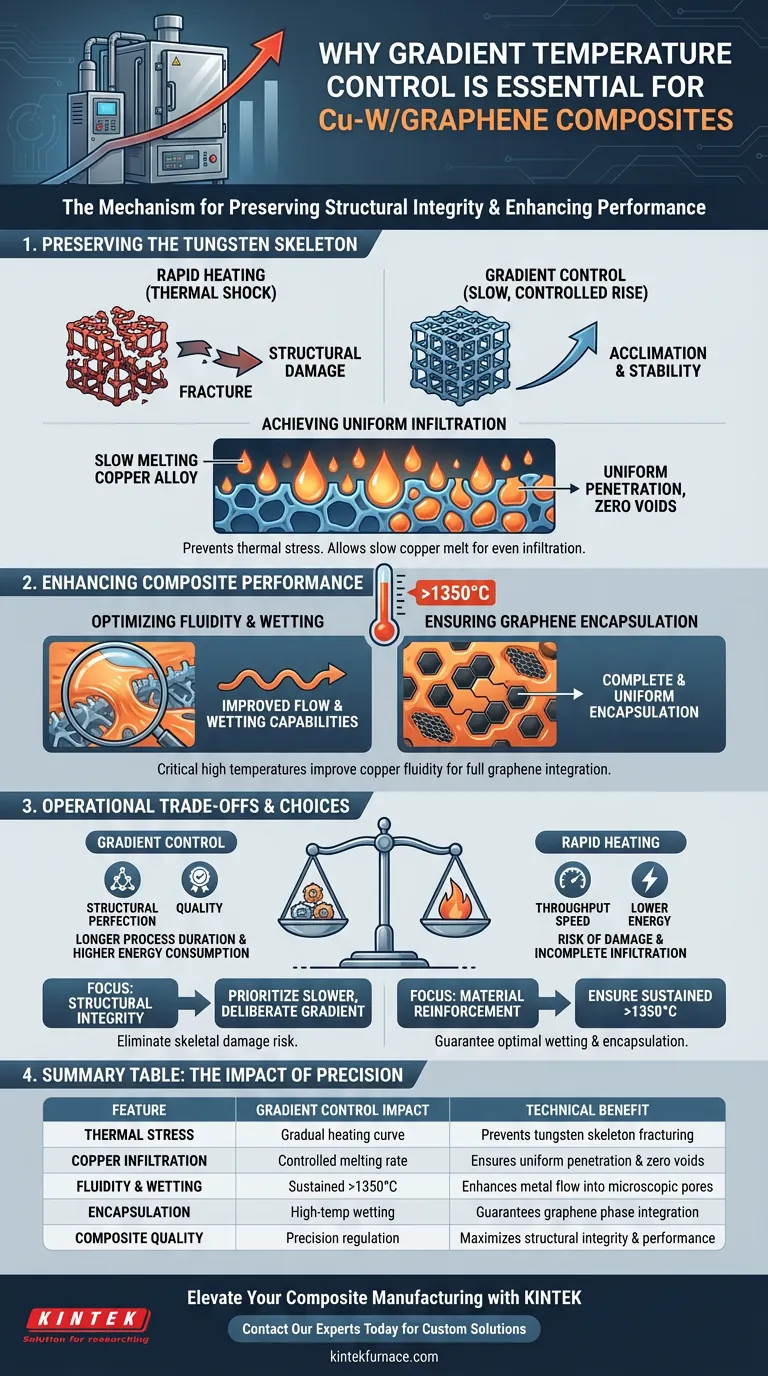
Gradient temperature control is the specific mechanism used to preserve structural integrity during the sintering process. It allows for a controlled, gradual increase in system temperature, which enables copper alloy ingots to melt slowly and infiltrate the tungsten skeleton uniformly. By strictly regulating thermal input, this process prevents the severe thermal stress that would otherwise cause skeletal damage to the composite material.
Gradient control transforms the infiltration process from a chaotic thermal event into a precise operation. It ensures the tungsten skeleton remains intact by minimizing thermal shock, while simultaneously achieving the high temperatures necessary to fully encapsulate the graphene reinforcement phase.
Preserving the Tungsten Skeleton
Preventing Thermal Shock
The primary function of gradient temperature control is the mitigation of severe thermal stress.
If the system heats too rapidly, the differential expansion between materials can fracture the porous tungsten skeleton.
A gradual temperature increase allows the skeleton to acclimate to the heat, maintaining its geometric stability.
Achieving Uniform Infiltration
Successful sintering requires the copper alloy to penetrate the tungsten structure evenly.
Gradient control causes the copper ingots to melt slowly.
This gradual phase change ensures the liquid metal has time to infiltrate the pores of the skeleton uniformly, rather than flooding the surface or leaving void spaces deep within the structure.
Enhancing Composite Performance
Optimizing Fluidity and Wetting
Once the infiltration begins, the furnace must reach and maintain a high-temperature environment, often exceeding 1350 degrees Celsius.
This specific temperature threshold is critical for the physics of the liquid copper.
At these temperatures, the fluidity and wetting capabilities of the copper are significantly improved, allowing it to flow into the microscopic nuances of the composite structure.
Ensuring Graphene Encapsulation
For the composite to function correctly, the graphene reinforcement phase must be fully integrated.
The enhanced fluidity provided by the high heat ensures the graphene is completely and uniformly encapsulated within the metal phase.
Without this high-temperature wetting, the graphene layers might remain isolated, failing to reinforce the metal matrix effectively.
Operational Considerations and Trade-offs
Process Duration vs. Quality
Implementing a gradient temperature control strategy inherently extends the processing time.
Because the temperature must be increased gradually rather than instantly, the total cycle time for sintering increases.
Manufacturers must balance the need for structural perfection against the throughput speed of the production line.
Energy Consumption
Maintaining a precise gradient, particularly when pushing the system above 1350 degrees Celsius, requires significant energy input.
The furnace must work harder to control the rate of the rise, not just the final temperature.
This precision demands robust heating elements and sophisticated control systems, which can increase operational costs compared to simpler heating methods.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To optimize the production of copper-tungsten/graphene composites, you must align your thermal strategy with your specific quality requirements.
- If your primary focus is structural integrity: Prioritize a slower, more deliberate thermal gradient to eliminate the risk of skeletal damage caused by thermal stress.
- If your primary focus is material reinforcement: Ensure your furnace can reliably sustain temperatures exceeding 1350 degrees Celsius to guarantee optimal wetting and graphene encapsulation.
Precision in thermal control is the difference between a mixed aggregate and a true high-performance composite.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Gradient Control Impact | Technical Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Stress | Gradual heating curve | Prevents tungsten skeleton fracturing |
| Copper Infiltration | Controlled melting rate | Ensures uniform penetration & zero voids |
| Fluidity & Wetting | Sustained >1350°C | Enhances metal flow into microscopic pores |
| Encapsulation | High-temp wetting | Guarantees graphene phase integration |
| Composite Quality | Precision regulation | Maximizes structural integrity & performance |
Elevate Your Composite Manufacturing with KINTEK
Achieving the perfect thermal gradient is critical for the structural integrity of high-performance materials. KINTEK provides industry-leading thermal solutions backed by expert R&D and manufacturing. Our diverse range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems are engineered for precision and are fully customizable to meet your specific sintering requirements.
Don't let thermal shock compromise your tungsten/graphene composites. Partner with KINTEK to access lab high-temp furnaces that deliver the exact temperature control your innovation demands.
Contact Our Experts Today to Discuss Your Custom Solution
Visual Guide
References
- Tan Liu, Yi Ding. Graphene-Enhanced CuW Composites for High-Voltage Circuit Breaker Electrical Contacts. DOI: 10.3390/app14072731
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- 9MPa Air Pressure Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace Molybdenum Wire Vacuum Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What core process conditions does an industrial vacuum brazing furnace provide for joining X37CrMoV5-1 tool steel?
- In which fields are vacuum furnaces commonly used? Essential for Aerospace, Electronics, and Medical Manufacturing
- What is a vacuum furnace and what are its main uses? Unlock High-Purity Material Processing
- How does a high vacuum annealing furnace contribute to 2D Bi2Te3-Sb2Te3 superlattices? Precision Thermal Engineering
- What advantages does a vacuum drying oven offer over a standard oven for Fe3Al and CNTs? Protect Your Composites
- What environmental benefits do continuous vacuum furnaces provide? Achieve Zero Emissions and High Efficiency
- What are the disadvantages of vacuum brazing? Understanding the trade-offs for your application
- What are the advantages of vacuum firing? Achieve Ultra-High Vacuum & Magnetic Purity for Sensitive Experiments



















