While highly effective, vacuum brazing is not a universal solution. Its primary disadvantages stem from high operational complexity, the metallurgical impact of heating the entire component, and its nature as a batch process. These factors can make it less efficient or unsuitable for certain materials and production environments.
The core challenge of vacuum brazing lies in its demanding and unforgiving nature. The process requires significant upfront investment and strict procedural control, and its thermal effects on the entire workpiece can fundamentally alter pre-existing material properties.

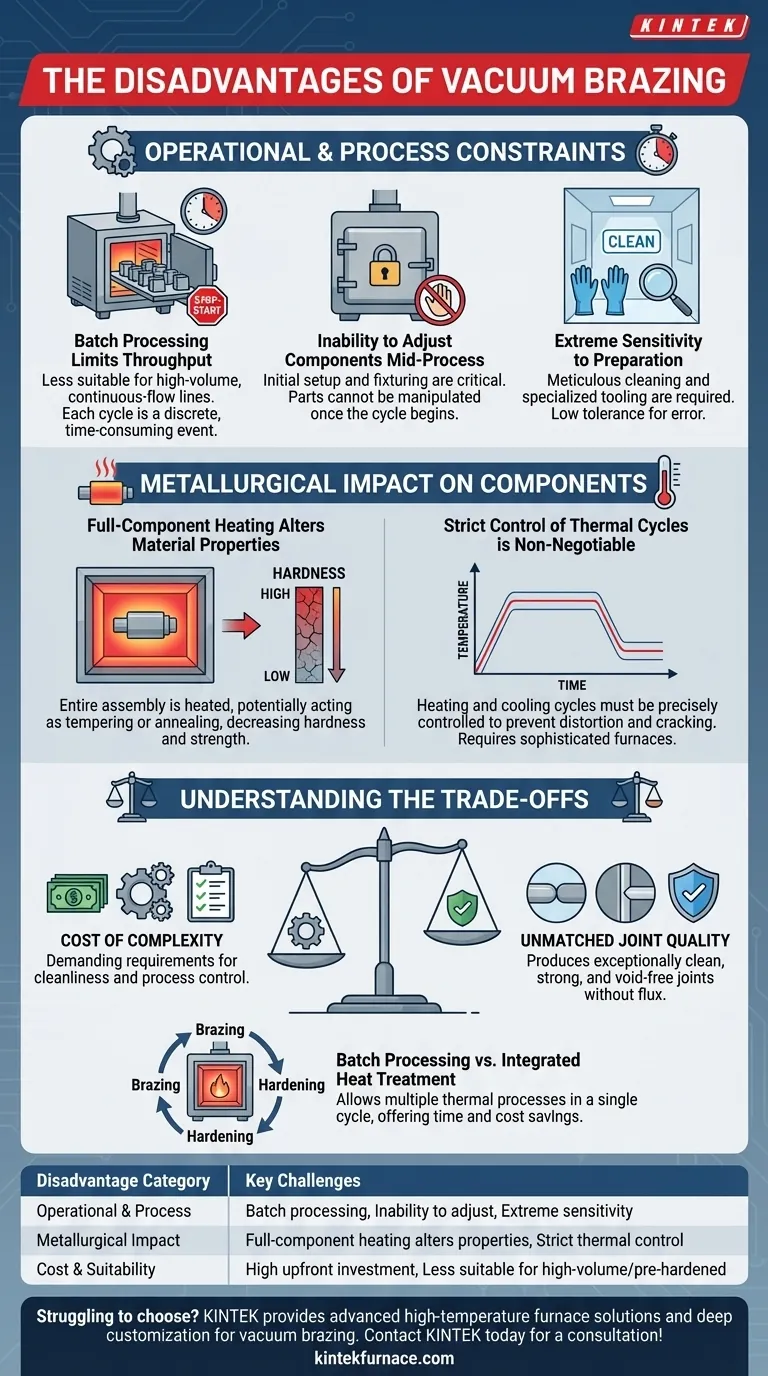
The Operational and Process Constraints
The day-to-day execution of vacuum brazing presents several significant hurdles. These are not just minor inconveniences; they are fundamental constraints that define the process.
Batch Processing Limits Throughput
Vacuum brazing is almost exclusively a batch process. Components are loaded into a furnace, a vacuum is created, the thermal cycle runs, and the parts are cooled before the furnace can be opened.
This inherent start-stop nature makes it less suitable for high-volume, continuous-flow manufacturing lines where speed is the primary driver. Each cycle is a discrete, time-consuming event.
Inability to Adjust Components Mid-Process
Once the furnace door is closed and the cycle begins, the components cannot be manipulated. The initial setup and fixturing are critical and final.
If a part shifts or a joint is misaligned, the entire batch may be compromised. This makes rework difficult and costly, demanding extreme precision during the assembly stage.
Extreme Sensitivity to Preparation and Environment
The success of a vacuum braze is heavily dependent on what happens before the parts ever enter the furnace. The process has a very low tolerance for error.
Key requirements include meticulous part cleaning, the use of dedicated clean assembly rooms, and specialized tooling. Any failure in these preparatory steps can lead to a failed braze, wasting time and resources.
The Metallurgical Impact on Components
Unlike localized welding, vacuum brazing heats the entire assembly to the brazing temperature. This has significant metallurgical consequences that must be managed.
Full-Component Heating Alters Material Properties
The most critical disadvantage is that the entire component is heated, not just the joint area.
For materials that have been previously heat-treated (quenched and tempered) or work-hardened, this thermal cycle can act as a tempering or annealing process. This often results in a decrease in hardness and strength throughout the component, which may be unacceptable for the final application.
Strict Control of Thermal Cycles is Non-Negotiable
To prevent distortion, residual stress, or cracking, the heating and cooling cycles must be precisely controlled. This requires sophisticated, high-quality vacuum furnaces and expert process control.
Factors like joint clearance, which must be held to tight tolerances (typically 0.025 mm to 0.125 mm), and the rate of temperature change are critical variables that add to the overall complexity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The disadvantages of vacuum brazing are the necessary trade-offs for achieving its unique benefits.
The Cost of Complexity vs. Unmatched Joint Quality
The demanding requirements for cleanliness and process control are a direct trade-off for producing exceptionally clean, strong, and void-free joints. Because no flux is used, there is no risk of flux entrapment or post-braze corrosion, which is a major advantage for critical applications.
Batch Processing vs. Integrated Heat Treatment
While it is a batch process, vacuum brazing allows for multiple thermal processes in a single cycle. Brazing, hardening, and age-hardening can often be combined, which can be a significant time and cost saver compared to performing these steps separately.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing your joining method requires balancing process limitations with your final goal.
- If your primary focus is joint integrity and purity for a critical component: Vacuum brazing is often the superior choice, despite its complexity.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production with minimal material alteration: You should investigate alternative, localized heating methods or other joining processes.
- If your components are already heat-treated to a final hardness: Carefully evaluate if the vacuum brazing thermal cycle will negatively impact their required mechanical properties.
Ultimately, you must weigh the demanding process requirements against the exceptional quality of the final joint.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage Category | Key Challenges |
|---|---|
| Operational & Process | Batch processing limits throughput, inability to adjust components mid-process, extreme sensitivity to preparation. |
| Metallurgical Impact | Full-component heating alters material properties (e.g., decreased hardness), requires strict control of thermal cycles. |
| Cost & Suitability | High upfront investment, less suitable for high-volume production or pre-hardened components. |
Struggling to choose the right high-temperature joining process for your critical components? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements like vacuum brazing. Let our experts help you navigate the trade-offs and select or customize the ideal furnace for your application. Contact KINTEK today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of a 1400°C heat treatment for porous tungsten? Essential Steps for Structural Reinforcement
- What are the benefits of using a high-temperature vacuum furnace for the annealing of ZnSeO3 nanocrystals?
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- Why is a vacuum environment essential for sintering Titanium? Ensure High Purity and Eliminate Brittleness
- What tasks does a high-temperature vacuum sintering furnace perform for PEM magnets? Achieve Peak Density



















