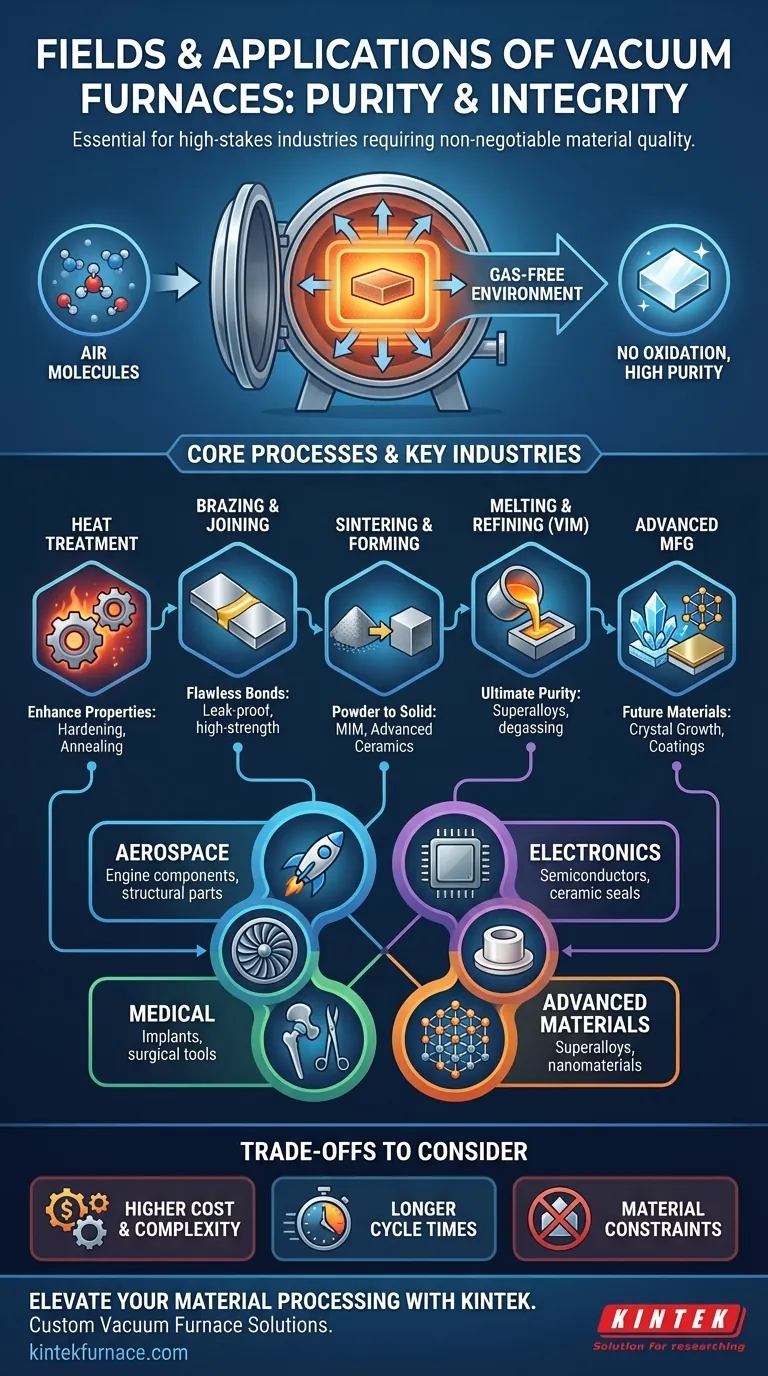
At their core, vacuum furnaces are used wherever material purity and structural integrity are non-negotiable. They are essential tools in high-stakes fields like aerospace, electronics, medical manufacturing, and advanced materials research. These industries rely on vacuum furnaces to perform critical thermal processes—such as heat treatment, brazing, and sintering—in a controlled, gas-free environment that prevents contamination and enables the creation of superior components.
The fundamental value of a vacuum furnace is not just the heat it provides, but the atmosphere it removes. By eliminating reactive gases like oxygen, it prevents oxidation and contamination, allowing for the creation of exceptionally pure, strong, and reliable materials that are impossible to produce in a conventional furnace.

Why Use a Vacuum? The Fundamental Advantage
The defining feature of a vacuum furnace is its ability to pump out the air and other gases from its heating chamber before or during the heating process. This seemingly simple step provides profound benefits.
Preventing Oxidation and Contamination
Most materials, especially metals, react with oxygen at high temperatures. This reaction, known as oxidation, creates a brittle, undesirable layer on the material's surface.
A vacuum environment removes nearly all oxygen, ensuring the part emerges from the furnace clean, bright, and free of scale. This is critical for parts that require a pristine surface finish or will undergo further processing like brazing or coating.
Achieving High Purity
A vacuum can also remove trapped or dissolved gases from within a material, a process called degassing.
Furthermore, it can boil off and remove volatile impurities with low melting points from a metal melt. This refining capability is essential for producing the high-purity alloys required for aerospace engine components and medical implants.
Core Applications Across Industries
The controlled environment of a vacuum furnace enables several key manufacturing processes that are central to modern technology.
Heat Treatment: Enhancing Material Properties
Heat treatment modifies a material's internal structure to improve its mechanical properties, such as hardness, strength, and durability.
- Annealing: This process heats and slowly cools a material to relieve internal stresses, soften it, and improve its ductility. A vacuum prevents surface discoloration.
- Hardening & Tempering: Used on steels and other alloys, these processes create a hard, wear-resistant structure. The vacuum ensures uniform heating and prevents decarburization (the loss of carbon from the surface).
- Vacuum Carburizing: This is a case-hardening process where carbon is diffused into the surface of steel parts at high temperatures to create a hard outer layer while maintaining a softer core. The vacuum allows for precise control over the carbon depth.
Brazing & Joining: Creating Flawless Bonds
Brazing is a process that joins two or more metal items by melting and flowing a filler metal into the joint.
Vacuum brazing is the gold standard for high-strength, leak-proof joints. The vacuum removes surface oxides, allowing the brazing alloy to wet and flow perfectly, creating a bond that is often as strong as the parent materials themselves. This is essential for aerospace components and ceramic-to-metal seals in electronic devices.
Sintering & Forming: From Powder to Solid
Sintering is the process of compacting and forming a solid mass of material by heat and pressure without melting it to the point of liquefaction.
- Powder Metallurgy: Vacuum sintering is used to fuse metal powders into dense, high-strength components for automotive, tool and die, and industrial applications.
- Metal Injection Molding (MIM): After a "green" part is formed, it undergoes a debinding process in a vacuum furnace to remove the polymer binder, followed by sintering to create the final, dense metal part.
- Advanced Ceramics: Vacuum furnaces produce advanced ceramics with superior thermal and electrical properties for use in electronics and high-tech industries.
Melting & Refining: Achieving Ultimate Purity
Vacuum induction melting (VIM) furnaces are used to melt and cast metals and alloys in a clean, controlled environment.
This process is critical for producing high-purity superalloys for jet engine turbine blades, medical implants, and even high-end jewelry. The vacuum prevents reactions with air and helps remove gaseous impurities from the molten metal.
Advanced Manufacturing: Building the Future
Vacuum furnaces are indispensable for creating next-generation materials and components.
- Crystal Growth: The ultra-pure environment is necessary for growing large, single crystals used in semiconductors and optical components.
- Deposition Coatings (CVD & PVD): While often done in dedicated chambers, vacuum furnace principles are used to apply thin, hard, or functional coatings to surfaces.
- New Materials: Researchers use vacuum furnaces to synthesize novel materials like superconductors and nanomaterials, where even minute impurities can alter the desired properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, vacuum furnaces are not a universal solution. Their benefits come with clear trade-offs.
Cost and Complexity
Vacuum systems are inherently more expensive to purchase, operate, and maintain than their atmospheric counterparts. They require robust chambers, high-power vacuum pumps, and sophisticated control systems.
Longer Cycle Times
The time required to pump the chamber down to the desired vacuum level and the need for controlled backfilling and cooling cycles often result in longer overall process times compared to conventional furnaces.
Material Constraints
Not all materials are suitable for high-vacuum processing. Materials with high vapor pressure can "outgas" excessively, contaminating the furnace and making it difficult to maintain a deep vacuum.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right thermal process depends entirely on your final objective.
- If your primary focus is mechanical strength and performance: Vacuum heat treatment (hardening, annealing) and vacuum brazing are your key processes for creating robust, reliable components.
- If your primary focus is material purity and composition: Vacuum induction melting, degassing, and crystal growth are essential for applications in aerospace, electronics, and high-purity alloys.
- If your primary focus is creating solid parts from powders: Vacuum sintering and debinding are the go-to methods for powder metallurgy, MIM, and advanced ceramics.
Understanding these core applications allows you to select the precise thermal process required to achieve your material engineering objectives.
Summary Table:
| Field | Common Applications | Key Processes |
|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Engine components, structural parts | Heat treatment, brazing, melting |
| Electronics | Semiconductor devices, ceramic seals | Sintering, crystal growth, brazing |
| Medical | Implants, surgical tools | Degassing, melting, heat treatment |
| Advanced Materials | Superalloys, ceramics, nanomaterials | Sintering, refining, synthesis |
Ready to elevate your material processing with precision? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces and CVD/PECVD Systems. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs in aerospace, electronics, medical, and research fields. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored vacuum furnace solutions can enhance purity, strength, and reliability in your applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- What is the vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Superior Surface Quality and Material Performance
- What are the general operational features of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Material Purity & Precision
- What are the benefits of vacuum heat treatment? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Control
- Why does heating steel rod bundles in a vacuum furnace eliminate heat transfer paths? Enhance Surface Integrity Today



















