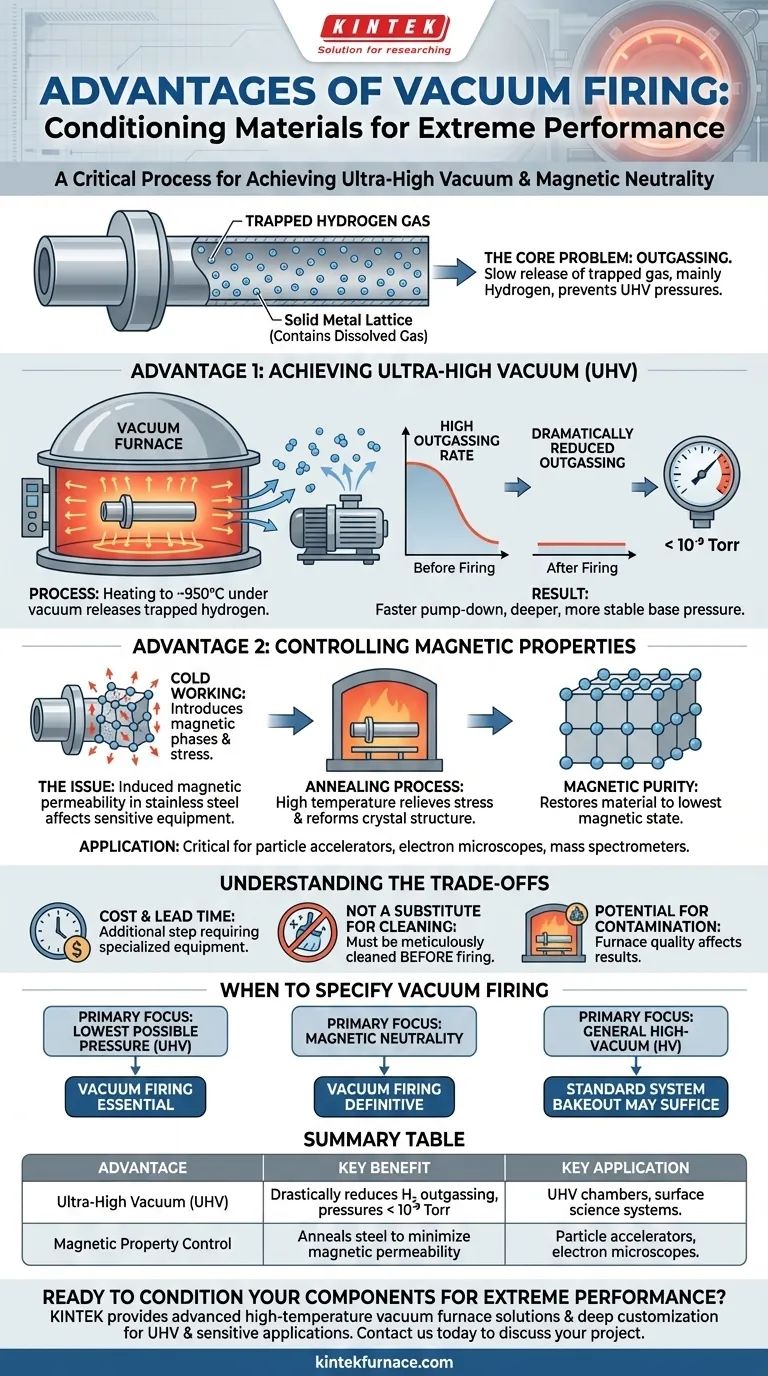
For engineers and scientists working at the limits of performance, vacuum firing is a critical material conditioning process, not merely a cleaning step. It fundamentally alters stainless steel on a molecular level to solve two primary problems: it drastically reduces hydrogen outgassing to enable ultra-high vacuum pressures, and it minimizes the material's magnetic permeability for use in highly sensitive experiments.
Vacuum firing is not about cleaning the surface of a component; it is a thermal process that removes trapped gases from the bulk of the metal itself and resets its magnetic properties, transforming standard stainless steel into a material suitable for extreme environments.

The Core Problem: Gas Trapped in Your Metal
To understand the benefits of vacuum firing, you must first understand that solid metal is not truly solid. It contains vast quantities of dissolved gas atoms, primarily hydrogen, trapped within its crystal lattice during manufacturing.
What is Outgassing?
Outgassing is the slow release of these trapped gas molecules from the bulk of a material into the vacuum environment. This process is the single greatest factor preventing a vacuum chamber from reaching its lowest possible (base) pressure.
Why Hydrogen is the Primary Culprit
In stainless steel, hydrogen is the main offender. Its atoms are incredibly small, allowing them to diffuse through the metal's structure relatively easily. When you pump down a chamber, this trapped hydrogen slowly seeps out, constantly adding gas molecules that your pumps must work to remove.
Advantage 1: Achieving Ultra-High Vacuum (UHV)
The primary reason to vacuum fire components is to combat hydrogen outgassing and achieve pressures in the ultra-high vacuum range (below 10⁻⁹ Torr).
How Vacuum Firing Works
The process involves placing cleaned components into a vacuum furnace, which is then heated to a high temperature (typically ~950°C for austenitic stainless steel) while under vacuum. This heat gives the trapped hydrogen atoms the energy they need to break free from the metal lattice and diffuse to the surface, where the surrounding vacuum whisks them away permanently.
The Result: Dramatically Reduced Outgassing
After cooling, the component contains significantly less dissolved hydrogen. When this part is later installed in your vacuum system, its rate of outgassing will be orders of magnitude lower. This allows your pumps to achieve a much deeper, more stable base pressure than would otherwise be possible.
Advantage 2: Controlling Magnetic Properties
For certain scientific applications, even the tiny amount of magnetism in "non-magnetic" stainless steel can be a major problem. Vacuum firing addresses this by acting as a high-purity annealing process.
The Issue of Magnetic Permeability
Magnetic permeability is a measure of how easily a material can support the formation of a magnetic field. While austenitic stainless steels (like 304L or 316L) are largely non-magnetic, they can become slightly magnetic when subjected to cold working, such as machining, bending, or forming. This introduces stress into the material, creating magnetic phases.
Annealing for Magnetic Purity
The high temperatures of vacuum firing anneal the steel. This process relieves the internal stresses caused by cold working and allows the material's crystal structure to reform. This effectively eliminates the strain-induced magnetic phases, reducing the material's magnetic permeability back to its lowest possible state.
Applications Where This Matters
This is critical for equipment like particle accelerators, electron microscopes, and mass spectrometers, where charged particle beams can be deflected by even minute, stray magnetic fields. Using vacuum-fired components ensures the magnetic environment is as neutral as possible.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Vacuum firing is a powerful solution, but it is not without considerations. It is an specialized and deliberate engineering choice.
Cost and Lead Time
Vacuum firing is an additional manufacturing step that requires specialized equipment and expertise. This adds both cost and lead time to a project compared to using components directly after machining.
Not a Substitute for Proper Cleaning
Vacuum firing is a bulk material treatment, not a surface cleaning process. It will not remove surface oils, particulates, or other contaminants. In fact, parts must be meticulously cleaned before being placed in the furnace to avoid baking contaminants onto the surface.
Potential for Contamination
The process is only as good as the furnace it is performed in. If the vacuum furnace itself is not clean or has leaks, it can potentially introduce contamination to the parts, defeating the purpose of the procedure.
When to Specify Vacuum Firing
Your decision should be driven entirely by the performance requirements of your system.
- If your primary focus is achieving the lowest possible pressure (UHV): Vacuum firing is essential to minimize hydrogen outgassing from your stainless steel components.
- If your primary focus is magnetic neutrality: Vacuum firing is the definitive method for reducing the magnetic permeability of cold-worked austenitic stainless steel for sensitive instruments.
- If your primary focus is general high-vacuum (HV): For less demanding systems (above 10⁻⁸ Torr), a standard in-situ system bakeout may be sufficient to manage outgassing without the need for pre-firing components.
This process is how you take a standard industrial material and condition it for extraordinary scientific and technical applications.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Key Benefit | Key Application |
|---|---|---|
| Ultra-High Vacuum (UHV) | Drastically reduces hydrogen outgassing, enabling pressures below 10⁻⁹ Torr. | UHV chambers, surface science systems. |
| Magnetic Property Control | Anneals steel to minimize magnetic permeability for magnetic neutrality. | Particle accelerators, electron microscopes, mass spectrometers. |
Ready to Condition Your Components for Extreme Performance?
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides advanced high-temperature vacuum furnace solutions for UHV and sensitive applications. Our product line, including Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, such as specialized vacuum firing processes.
Contact us today to discuss how our vacuum furnaces can help you achieve ultra-high vacuum and magnetic purity for your most critical projects.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why does heating steel rod bundles in a vacuum furnace eliminate heat transfer paths? Enhance Surface Integrity Today
- How does a vacuum heat treatment furnace influence Ti-6Al-4V microstructure? Optimize Ductility and Fatigue Resistance
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in LP-DED? Optimize Alloy Integrity Today
- What are the components of a vacuum furnace? Unlock the Secrets of High-Temperature Processing
- What are the benefits of vacuum heat treatment? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Control



















