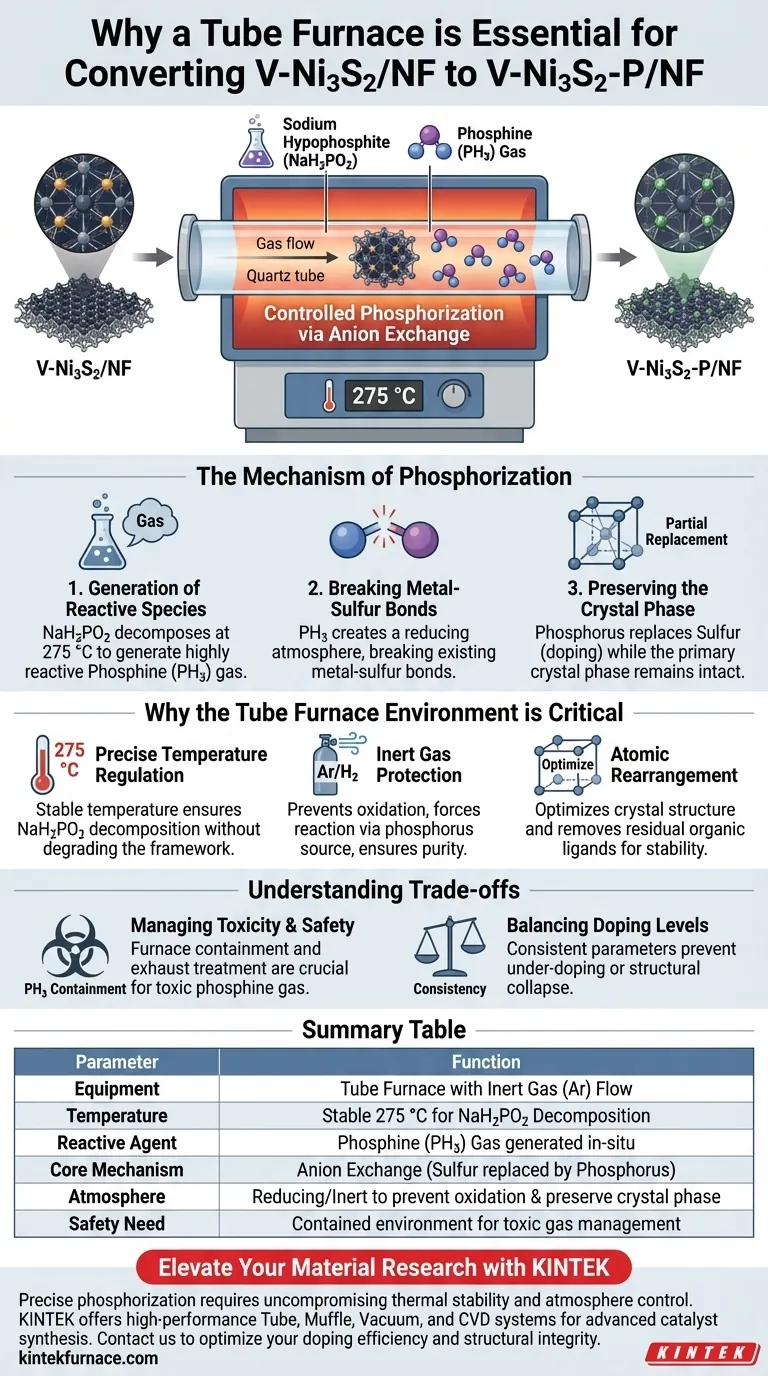
Annealing in a tube furnace is strictly necessary because it creates the precise thermal and chemical environment required to execute the phosphorization reaction safely and effectively. Specifically, this equipment enables the controlled decomposition of sodium hypophosphite at 275 °C to generate reactive phosphine gas, which is the mechanism for doping phosphorus into the material.
The core function of this process is to facilitate anion exchange: replacing a specific portion of sulfur atoms with phosphorus atoms. This is achieved by generating a reducing atmosphere that breaks metal-sulfur bonds without destroying the material's primary crystal structure.

The Mechanism of Phosphorization
Generation of Reactive Species
The conversion relies on a precursor material, typically sodium hypophosphite (NaH2PO2). When heated in the tube furnace, this compound decomposes to generate phosphine (PH3) gas.
Phosphine is a highly active agent. Its generation is the catalyst for the entire doping process, which cannot occur under standard ambient conditions.
Breaking Metal-Sulfur Bonds
Once generated, the phosphine gas interacts with the V-Ni3S2 precursor. In this reducing atmosphere, the high reactivity of PH3 breaks existing metal-sulfur bonds.
This breakage creates vacancies where anion exchange can occur. It allows phosphorus atoms to occupy sites previously held by sulfur, effectively transforming the material into V-Ni3S2-P.
Preserving the Crystal Phase
Crucially, this process is designed to be a partial replacement. The goal is to introduce phosphorus (doping) to modulate electronic properties, not to create an entirely new bulk material.
The annealing process ensures that while the surface chemistry changes, the primary crystal phase of the material remains intact.
Why the Tube Furnace Environment is Critical
Precise Temperature Regulation
The reaction requires a stable temperature of exactly 275 °C.
Tube furnaces provide the thermal stability needed to hold this temperature indefinitely. This specific heat level is sufficient to decompose the phosphorus source but controlled enough to prevent the degradation of the nickel-sulfide framework.
Inert Gas Protection
The process requires a protective, inert gas environment (often involving Argon or a Hydrogen/Argon mix).
This prevents the material from oxidizing (reacting with oxygen in the air) at high temperatures. It forces the reaction to proceed solely via the phosphorus source, ensuring the purity of the doped catalyst.
Atomic Rearrangement
Beyond the chemical reaction, the thermal treatment induces atomic rearrangement.
As noted in broader annealing principles, this heat treatment helps optimize the crystal structure and remove residual organic ligands from synthesis. This stabilizes the catalyst and improves its chemical consistency.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Managing Toxicity and Safety
The generation of phosphine (PH3) is chemically necessary but presents a significant safety hazard due to its high toxicity.
A tube furnace is essential for containment. However, the system must be sealed perfectly, and the exhaust must be treated properly to prevent hazardous exposure.
Balancing Doping Levels
The "partial replacement" of sulfur is a delicate balance.
If the temperature fluctuates or the annealing time is incorrect, you risk either under-doping (insufficient phosphorus) or over-reacting, which could collapse the desired crystal structure. The process relies entirely on the consistency of the furnace parameters.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure the successful conversion of V-Ni3S2/NF into its dual-doped counterpart, consider the following based on your specific objectives:
- If your primary focus is Doping Efficiency: Ensure the precursor (NaH2PO2) is placed upstream in the gas flow to maximize the exposure of the substrate to the generated PH3 gas.
- If your primary focus is Structural Integrity: Strictly verify the temperature calibration at 275 °C; exceeding this may compromise the primary crystal phase essential for catalytic performance.
- If your primary focus is Surface Purity: Utilize the annealing phase to ensure complete removal of residual organic ligands, leveraging the inert atmosphere to prevent re-contamination.
Precise control over the thermal and chemical atmosphere is the only way to achieve effective dual-doping while maintaining the structural stability of your catalyst.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Function in Phosphorization Process |
|---|---|
| Equipment | Tube Furnace with Inert Gas (Ar) Flow |
| Temperature | Stable 275 °C for NaH2PO2 Decomposition |
| Reactive Agent | Phosphine (PH3) Gas generated in-situ |
| Core Mechanism | Anion Exchange (Sulfur replaced by Phosphorus) |
| Atmosphere | Reducing/Inert to prevent oxidation & preserve crystal phase |
| Safety Need | Contained environment for toxic gas management |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK
Precise phosphorization requires uncompromising thermal stability and atmosphere control. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Tube, Muffle, Vacuum, and CVD systems tailored for advanced catalyst synthesis.
Whether you are converting V-Ni3S2/NF or developing custom dual-doped materials, our customizable lab high-temp furnaces ensure the consistency your research demands. Contact KINTEK today to discover how our heating solutions can optimize your doping efficiency and structural integrity.
Visual Guide
References
- Kyeongseok Min, Sung‐Hyeon Baeck. Unveiling the Role of V and P Dual‐Doping in Ni<sub>3</sub>S<sub>2</sub> Nanorods: Enhancing Bifunctional Electrocatalytic Activities for Anion Exchange Membrane Water Electrolysis. DOI: 10.1002/sstr.202500217
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What function does a tube furnace perform in sintering boron duplex stainless steel? Master High-Precision Results
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum tube furnace for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Electrocatalyst Performance
- What is the material of the anode in a vacuum tube? Choosing the Right Metal for Power & Performance
- What is the function of the pre-oxidation process conducted in a tube furnace? Stabilize Lignin for Carbon Fibers.
- How does a multi-tube pyrolysis furnace achieve precise temperature control? Advanced Hardware & PID Logic Explained
- What factors influence the processing time in a rotary tube furnace? Master Control for Efficient Heat Treatment
- How does an atmosphere tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Master Temperature Stability for Your Lab
- When did tube furnaces originate and what drove their development? Discover the Engineered Solution for Precise Heat



















