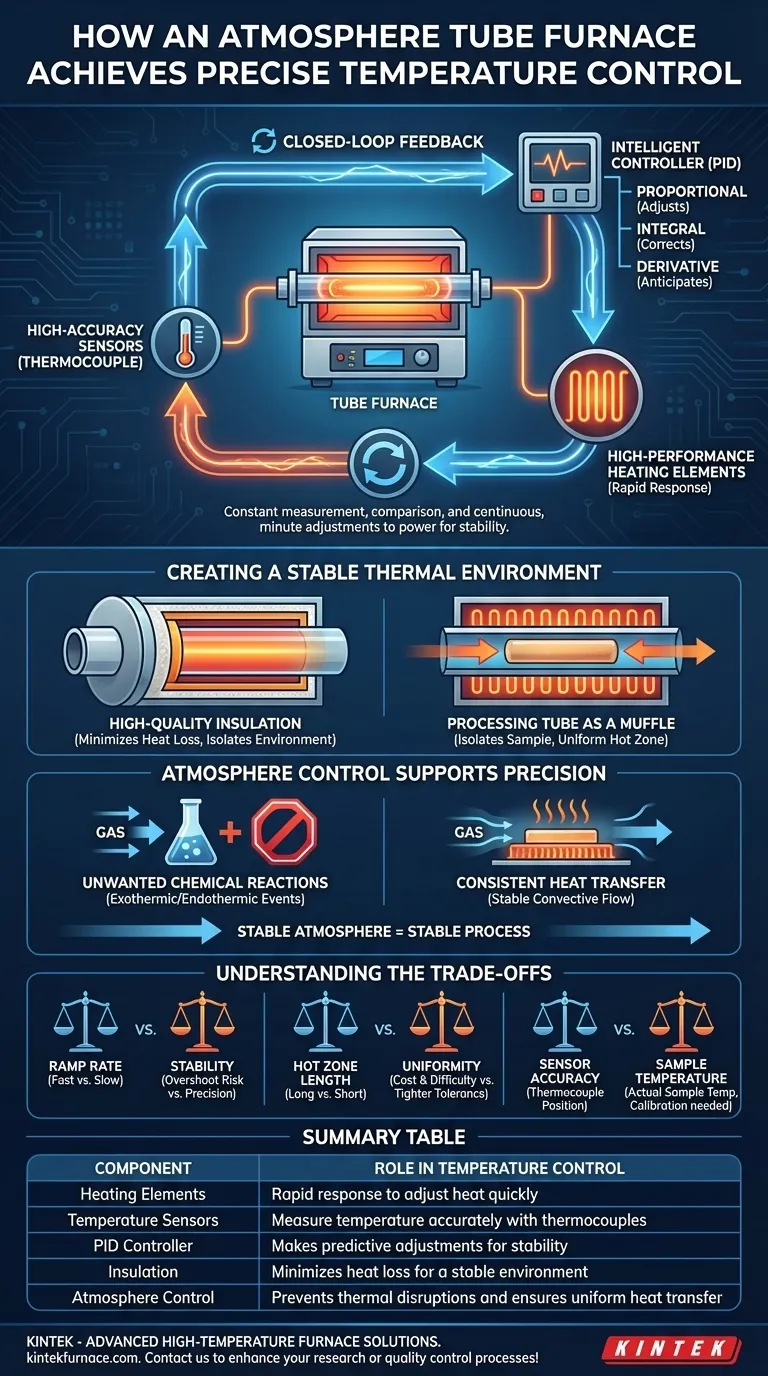
At its core, an atmosphere tube furnace achieves precise temperature control through a sophisticated closed-loop feedback system. This system constantly measures the internal temperature with a high-accuracy sensor, compares it to the desired setpoint, and uses an intelligent controller to make continuous, minute adjustments to the power supplied to the heating elements.
The true precision of a tube furnace comes not from a single component, but from the synergy between rapid-response heating elements, highly accurate sensors, and predictive control algorithms, all operating within a thermally stable and controlled gas environment.
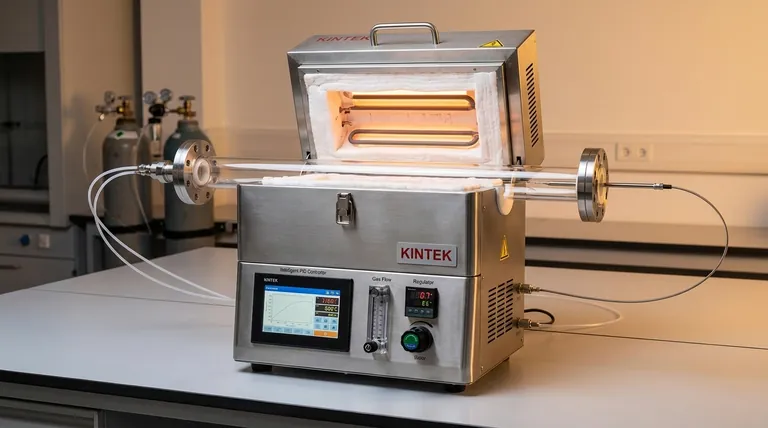

The Core Components of Temperature Control
Precise thermal management is a system-level achievement. Three key components work in a continuous feedback loop to maintain the exact temperature required for your process.
High-Performance Heating Elements
The furnace's ability to respond quickly to commands begins with its heating elements. These are typically made of materials like Molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2) or Silicon Carbide (SiC), chosen for their ability to heat up rapidly and withstand extreme temperatures.
This rapid response allows the controller to add or remove heat almost instantly, preventing the temperature from drifting away from the setpoint.
High-Accuracy Temperature Sensors
The "eyes" of the system are the temperature sensors, almost always a thermocouple. A thermocouple is a robust sensor that generates a small voltage directly proportional to the temperature.
Its placement is critical—usually positioned near the center of the heating zone and close to the processing tube. This ensures the temperature being measured is as close as possible to the temperature your sample is experiencing.
The Intelligent Controller (PID)
The "brain" of the operation is the PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) controller. This is far more sophisticated than a simple thermostat that just turns the heat on or off.
- Proportional: Adjusts power based on how far the current temperature is from the setpoint.
- Integral: Corrects for small, steady-state errors by looking at past performance, ensuring the furnace doesn't settle slightly above or below the target.
- Derivative: Anticipates future temperature changes by looking at the rate of change, preventing overshoot or undershoot during heating ramps.
This predictive capability allows the controller to make smooth, precise adjustments, holding the temperature stable within fractions of a degree.
Creating a Stable Thermal Environment
Controlling the heat source is only half the battle. The furnace must also create an exceptionally stable environment to prevent heat loss and ensure the temperature is uniform across your sample.
The Role of High-Quality Insulation
Atmosphere tube furnaces are built with multiple layers of high-purity, low-conductivity ceramic fiber insulation.
This insulation minimizes heat loss to the surrounding environment. This not only improves energy efficiency but, more importantly, isolates the heating chamber from fluctuations in ambient room temperature, creating a highly stable thermal core.
The Processing Tube as a Muffle
The ceramic or quartz tube that holds your sample also acts as a muffle. It isolates the sample from direct radiation from the heating elements.
This creates a more uniform thermal environment inside the tube, where heat is transferred evenly through radiation and convection from the tube walls and the controlled atmosphere gas. This results in a defined "hot zone" with excellent temperature uniformity.
How Atmosphere Control Supports Temperature Precision
In an atmosphere furnace, managing the gas is inseparable from managing the temperature. A stable atmosphere is a prerequisite for a stable thermal process.
Preventing Unwanted Thermal Events
The primary purpose of the controlled atmosphere is to prevent unwanted chemical reactions, like oxidation. These reactions can be exothermic (releasing heat) or endothermic (absorbing heat).
By flooding the tube with a precise, stable flow of inert or reactive gas, the furnace prevents these unpredictable thermal events from occurring, which would otherwise disrupt the controller's efforts to maintain a stable temperature.
Ensuring Consistent Heat Transfer
The gas inside the tube is not just a chemical shield; it is also a medium for heat transfer via convection.
High-precision gas flow meters and regulators ensure that the type, pressure, and flow rate of this gas are constant. A stable gas flow leads to stable and predictable convective heat transfer, which is a key variable the temperature control system relies on.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No system is perfect. Achieving precision requires understanding the inherent limitations and balancing competing factors.
Ramp Rate vs. Stability
Heating the furnace as fast as possible (high ramp rate) can save time, but it makes it much harder for the PID controller to avoid overshooting the target temperature. For maximum precision and stability, slower, more controlled ramps are often necessary.
Hot Zone Length vs. Uniformity
Manufacturers specify a "uniform hot zone," which is the length within the furnace tube where the temperature is held within a tight tolerance (e.g., ±1°C). Creating a very long uniform zone is difficult and expensive. You must ensure your sample fits entirely within this specified zone for repeatable results.
Sensor Accuracy vs. Sample Temperature
The controller can only be as accurate as the thermocouple allows, and it only knows the temperature at the thermocouple's location. There can be a small temperature difference between the sensor and your actual sample. For critical processes, calibration by measuring the true sample temperature is essential.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding these principles empowers you to use the furnace effectively and select the right one for your needs.
- If your primary focus is novel materials research: Prioritize a furnace with excellent temperature uniformity and a flexible PID controller that allows you to program complex, multi-stage thermal cycles.
- If your primary focus is process repeatability and quality control: Emphasize the stability of the atmosphere control system (precision flow meters) and the long-term reliability of the heating elements and thermocouple.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose heat treatment: A balanced system with a decent ramp rate, good stability (e.g., ±2-5°C), and a robust design offers the best value.
By appreciating the interplay of heating, sensing, control, and insulation, you can ensure your thermal processes are both precise and repeatable.
Summary Table:
| Component | Role in Temperature Control |
|---|---|
| Heating Elements | Rapid response to adjust heat quickly |
| Temperature Sensors | Measure temperature accurately with thermocouples |
| PID Controller | Makes predictive adjustments for stability |
| Insulation | Minimizes heat loss for a stable environment |
| Atmosphere Control | Prevents thermal disruptions and ensures uniform heat transfer |
Upgrade your laboratory's precision today! KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With strong deep customization capabilities, we precisely meet your unique experimental needs for superior temperature control and repeatability. Contact us now to discuss how our furnaces can enhance your research or quality control processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents



















