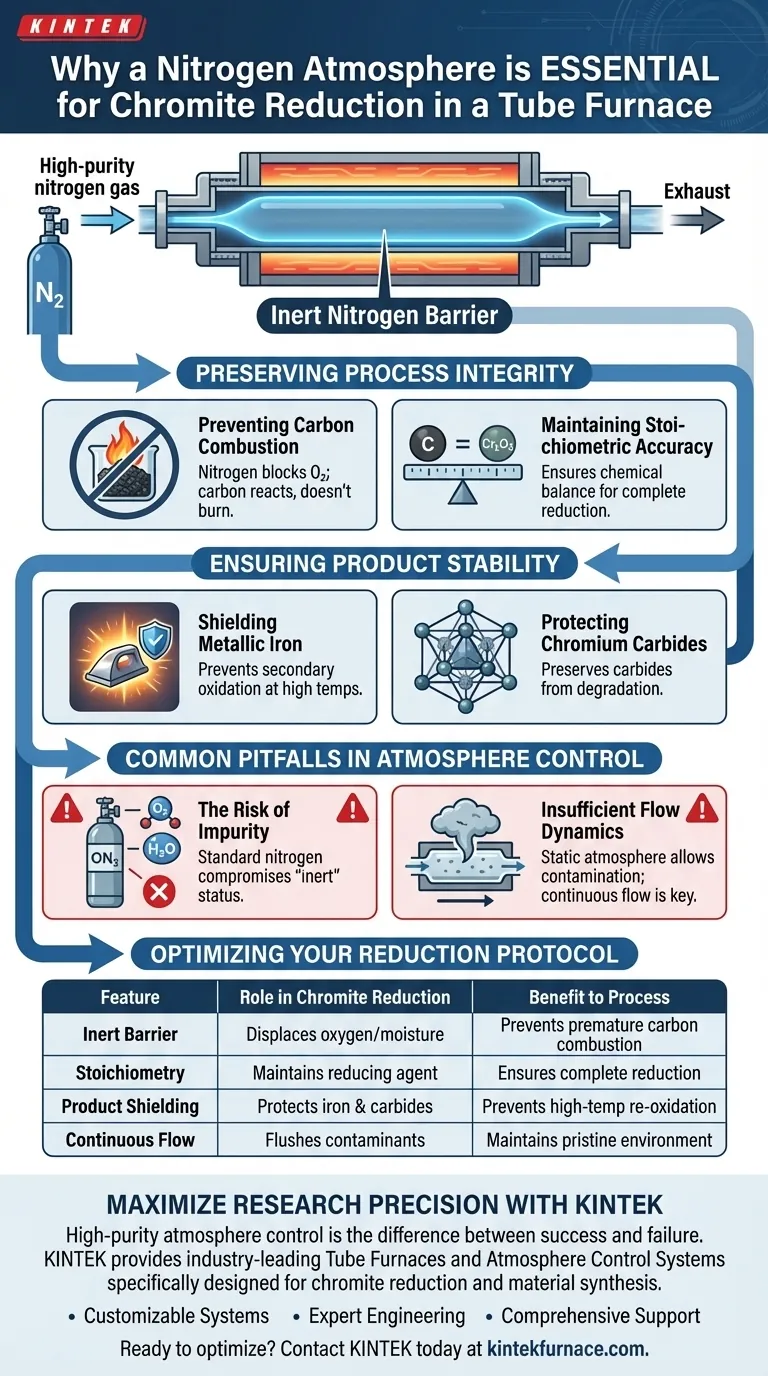
An atmosphere control system utilizing nitrogen is critical for maintaining chemical integrity. During the reduction of chromite, a continuous flow of high-purity nitrogen creates an inert barrier that prevents oxygen from interfering with the reaction. This specific environment is required to stop the carbon reducing agent from burning away prematurely and to protect the final metallic products from re-oxidizing at high temperatures.
By displacing oxygen, a nitrogen atmosphere ensures the reduction process is driven solely by the intended chemical reaction rather than uncontrolled combustion. This preserves the reducing agent and protects the resulting iron and chromium compounds from degradation.

Preserving Process Integrity
To understand why nitrogen is non-negotiable, you must look at the specific chemical vulnerabilities of the materials involved in chromite reduction.
Preventing Carbon Combustion
The reduction process relies heavily on carbon reducing agents to strip oxygen from the chromite ore.
If oxygen is present in the furnace atmosphere, the carbon will combust (burn) uncontrollably. The nitrogen barrier ensures the carbon reacts with the ore as intended, rather than being consumed by the surrounding air.
Maintaining Stoichiometric Accuracy
When carbon burns away due to atmospheric oxygen, the chemical balance of the reaction is destroyed.
This loss leads to incomplete reduction because there is insufficient reducing agent left to convert the chromite. Nitrogen preserves the carbon mass, ensuring the stoichiometry remains consistent throughout the experiment.
Ensuring Product Stability
The role of the atmosphere control system extends beyond the reaction itself; it protects the newly formed materials which are highly unstable at elevated temperatures.
Shielding Metallic Iron
As the chromite reduces, metallic iron is produced.
At high temperatures, this fresh metal is chemically active and prone to secondary oxidation. Without a nitrogen shield, the iron would immediately revert to an oxide form, corrupting the results.
Protecting Chromium Carbides
The process also generates specific chromium carbides.
Like metallic iron, these carbides require an oxygen-free environment to maintain their structure. The nitrogen flow prevents these compounds from degrading, ensuring the final product accurately reflects the reduction capabilities of the process.
Common Pitfalls in Atmosphere Control
While the concept of an inert atmosphere is simple, execution often fails due to overlooked details.
The Risk of Impurity
Using standard-grade nitrogen rather than high-purity sources can be detrimental.
Even trace amounts of oxygen or moisture in the gas supply can compromise the "inert" status of the furnace. This can lead to micro-oxidations that skew sensitive chemical analyses.
Insufficient Flow Dynamics
Simply filling the tube is not enough; the system requires a continuous flow.
A static atmosphere allows evolved gases to build up and permits the back-diffusion of air. A steady flow actively flushes contaminants out, maintaining a pristine environment for the duration of the heat treatment.
Optimizing Your Reduction Protocol
To achieve reliable data, the atmosphere control system must be viewed as a precise chemical reagent, not just a passive setting.
- If your primary focus is analytical accuracy: Ensure a continuous flow of high-purity nitrogen to prevent any secondary oxidation that could skew the chemical properties of the final product.
- If your primary focus is reaction efficiency: Strictly monitor the inert barrier to prevent the unintended combustion of carbon, ensuring the maximum amount of reducing agent is available for the ore.
Controlling the atmosphere is not merely a precaution; it is the fundamental baseline required to validate the chemistry of chromite reduction.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Role in Chromite Reduction | Benefit to Process |
|---|---|---|
| Inert Barrier | Displaces oxygen and moisture | Prevents premature carbon combustion |
| Stoichiometry | Maintains carbon reducing agent levels | Ensures complete reduction of the ore |
| Product Shielding | Protects metallic iron and carbides | Prevents re-oxidation at high temperatures |
| Continuous Flow | Flushes evolved gases and contaminants | Maintains a pristine chemical environment |
Maximize Your Research Precision with KINTEK
High-purity atmosphere control is the difference between a successful reduction and a failed experiment. KINTEK provides industry-leading Tube Furnaces and Atmosphere Control Systems specifically designed to handle the rigorous demands of chromite reduction and material synthesis.
Our Value to You:
- Customizable Systems: From Vacuum and CVD to Rotary and Tube furnaces, we tailor solutions to your specific stoichiometric requirements.
- Expert Engineering: Backed by specialized R&D, our furnaces ensure the gas flow dynamics and thermal stability necessary for sensitive lab processes.
- Comprehensive Support: Whether you are a research lab or an industrial manufacturer, we provide the tools to prevent oxidation and ensure analytical accuracy.
Ready to optimize your reduction protocol? Contact KINTEK today for a consultation.
Visual Guide
References
- Xiaohong Jiang, Z. H. Lei. Mechanism of Iron Powder to Enhance Solid-State Reduction of Chromite Ore. DOI: 10.3390/min15060652
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does the pressure range change under vacuum conditions in an atmosphere box furnace? Explore Key Shifts for Material Processing
- What features are important when selecting an inert atmosphere furnace or oven? Ensure Purity and Efficiency for Your Lab
- What is the function of a high-pressure Argon atmosphere? Master Complex Alloy Purity with Precision Melting
- How does an atmosphere furnace benefit the metallurgy industry? Enhance Material Quality and Efficiency
- What are the five key components of atmosphere furnaces? Master Controlled Heat Treatment for Superior Results
- For what purpose is a chemically reactive atmosphere used in a furnace? To Transform Material Surfaces
- What is the relationship between temperature and the furnace atmosphere in material processing? Master the Critical Heat-Environment Balance
- How does the atmosphere differ between tube furnaces and box furnaces? Optimize Your Heat Treatment Process



















