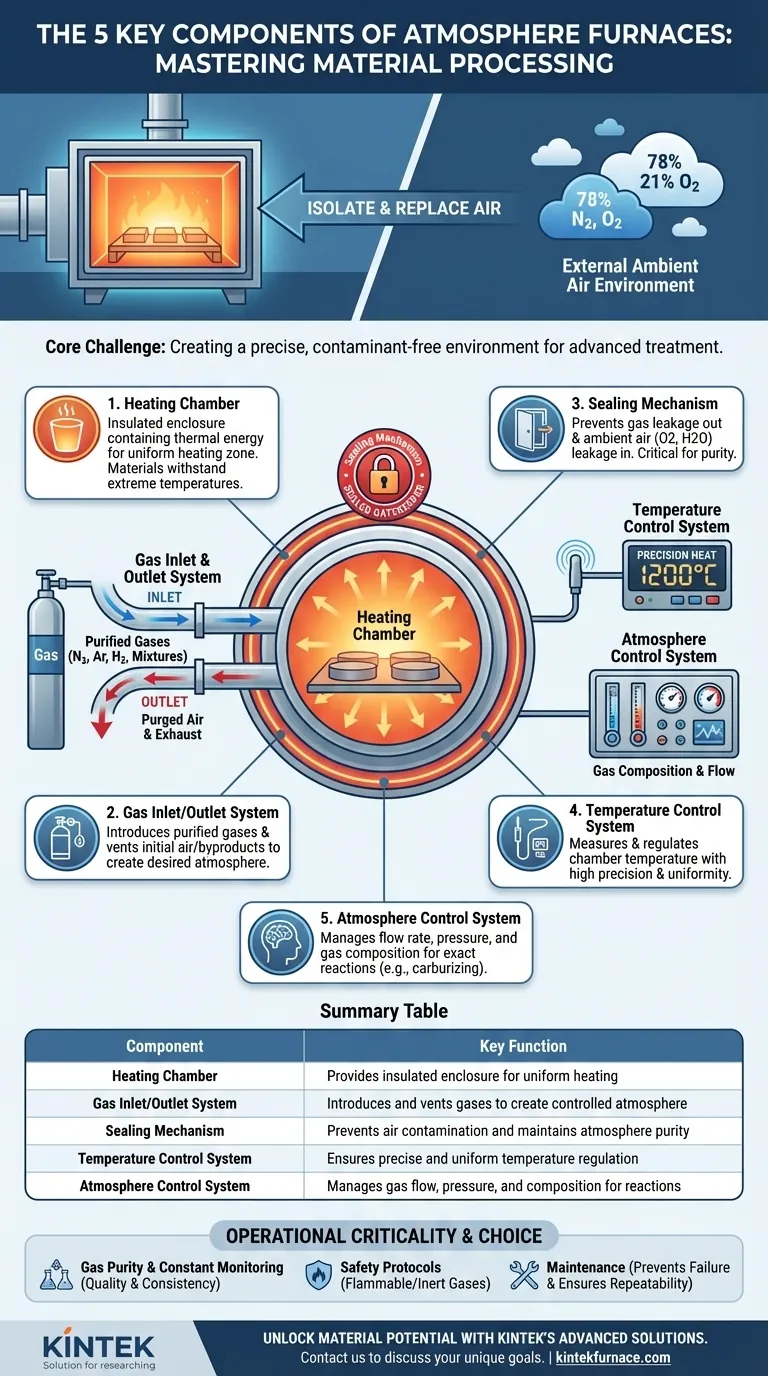
The five key components of an atmosphere furnace are the heating chamber, the gas inlet and outlet system, the sealing mechanism, the temperature control system, and the atmosphere control system. These elements work in concert to create a highly specific, controlled environment, allowing for heat treatment processes that would be impossible in open air.
An atmosphere furnace is not merely an oven; it is a sealed system where every component serves a single purpose: to precisely control both temperature and the chemical composition of the gas surrounding a material. Understanding how these systems interlock is the key to mastering advanced material processing.

The Core Challenge: Isolating the Process from Air
The primary function of an atmosphere furnace is to replace the ambient air—which is roughly 78% nitrogen and 21% oxygen—with a custom, artificially prepared atmosphere.
Oxygen, in particular, is highly reactive at high temperatures and will cause unwanted oxidation (like rust or scale) on most metals. By removing it and introducing a specific gas, you can achieve unique material properties.
Deconstructing the Five Key Components
Each component plays a critical, non-negotiable role in creating and maintaining this isolated, controlled environment.
The Heating Chamber: The Crucible of Transformation
The heating chamber is the insulated enclosure where the workpieces are placed and heated. It is constructed from materials that can withstand extreme temperatures without degrading or contaminating the process.
Its job is to contain the thermal energy and provide a stable, uniform temperature zone for the material being treated.
The Gas System: The Heart of the Atmosphere
This system consists of gas inlets and outlets. The inlets introduce purified gases—such as nitrogen, argon, hydrogen, or specific mixtures—into the chamber to create the desired atmosphere.
The outlets serve to purge the initial air from the chamber and to safely vent any byproducts or exhaust gases generated during the heat treatment process.
The Sealing Mechanism: The Gatekeeper Against Contamination
This is arguably what defines an atmosphere furnace. Seals on doors, feedthroughs, and other joints are critical for preventing two things: the controlled atmosphere from leaking out, and, more importantly, ambient air from leaking in.
Even a small leak can introduce oxygen and moisture, compromising the entire process and leading to failed parts. The integrity of the seal dictates the purity of the atmosphere you can achieve.
The Temperature Control System: Precision is Paramount
This system, typically composed of thermocouples (sensors) and controllers, measures and regulates the temperature inside the chamber.
For processes like annealing or bright quenching, temperature must be incredibly precise and uniform. This system ensures the material reaches and holds the exact temperature required for the desired metallurgical or chemical transformation.
The Atmosphere Control System: The Conductor of the Process
While the gas system introduces the gas, the atmosphere control system is the brain that manages it. This includes mass flow controllers, gas analyzers, and pressure sensors.
It precisely regulates the flow rate, pressure, and composition of the gas mixture throughout the process cycle. For reactive treatments like gas carburizing (adding carbon) or nitriding (adding nitrogen), this system's accuracy directly determines the final properties of the material's surface.
Understanding the Operational Demands
Controlling both heat and chemistry simultaneously introduces significant complexity. Success depends on vigilance and an understanding of the potential failure points.
Gas Purity is Non-Negotiable
The quality of your final product is directly tied to the purity of the gases you introduce. Any impurities in the source gas will end up in your furnace, potentially ruining sensitive processes like those used in semiconductor or solar cell manufacturing.
Constant Monitoring is Essential
An atmosphere furnace cannot be a "set it and forget it" tool. Operators must continuously monitor temperature, chamber pressure, and gas composition to ensure the process remains within its strict parameters. Deviations can lead to inconsistent or failed results.
Safety Protocols are Critical
Many controlled atmospheres use flammable gases like hydrogen or inert gases like nitrogen and argon, which pose an asphyxiation risk. Strict safety protocols for handling, storage, and venting these gases are mandatory to ensure operator safety.
Maintenance Prevents Catastrophic Failure
Seals wear out, thermocouples drift out of calibration, and gas analyzers require periodic servicing. A rigorous preventative maintenance schedule is not just recommended; it is essential for ensuring process repeatability and avoiding costly equipment failures.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The emphasis you place on each component depends entirely on your process objective.
- If your primary focus is high-purity processing (e.g., semiconductors, medical devices): Your most critical components are the sealing mechanism and a high-integrity gas system to prevent even trace amounts of contamination.
- If your primary focus is reactive heat treatment (e.g., carburizing, nitriding): Your success depends on the precision of the atmosphere control system to manage complex gas mixtures and reactions accurately.
- If your primary focus is quality and repeatability (e.g., aerospace, tool steel): You must prioritize a highly accurate temperature control system and robust monitoring to ensure every part is processed identically.
By viewing these five components as an integrated system, you gain control over the fundamental properties of your materials.
Summary Table:
| Component | Key Function |
|---|---|
| Heating Chamber | Provides insulated enclosure for uniform heating |
| Gas Inlet/Outlet System | Introduces and vents gases to create controlled atmosphere |
| Sealing Mechanism | Prevents air contamination and maintains atmosphere purity |
| Temperature Control System | Ensures precise and uniform temperature regulation |
| Atmosphere Control System | Manages gas flow, pressure, and composition for reactions |
Unlock the full potential of your material processing with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with reliable systems like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, enhancing efficiency and results. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your specific goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the use of nitrogen in furnace? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Heat Treatment
- Why is moisture control critical in inert atmosphere heat treating? Prevent Oxidation and Ensure Material Integrity
- What are the two main types of atmosphere furnaces and their characteristics? Choose the Right Furnace for Your Lab
- What is the main purpose of heat treatment? Transform Metal Properties for Superior Performance
- What are the benefits of inert atmosphere heat treating? Prevent Oxidation and Preserve Material Integrity



















