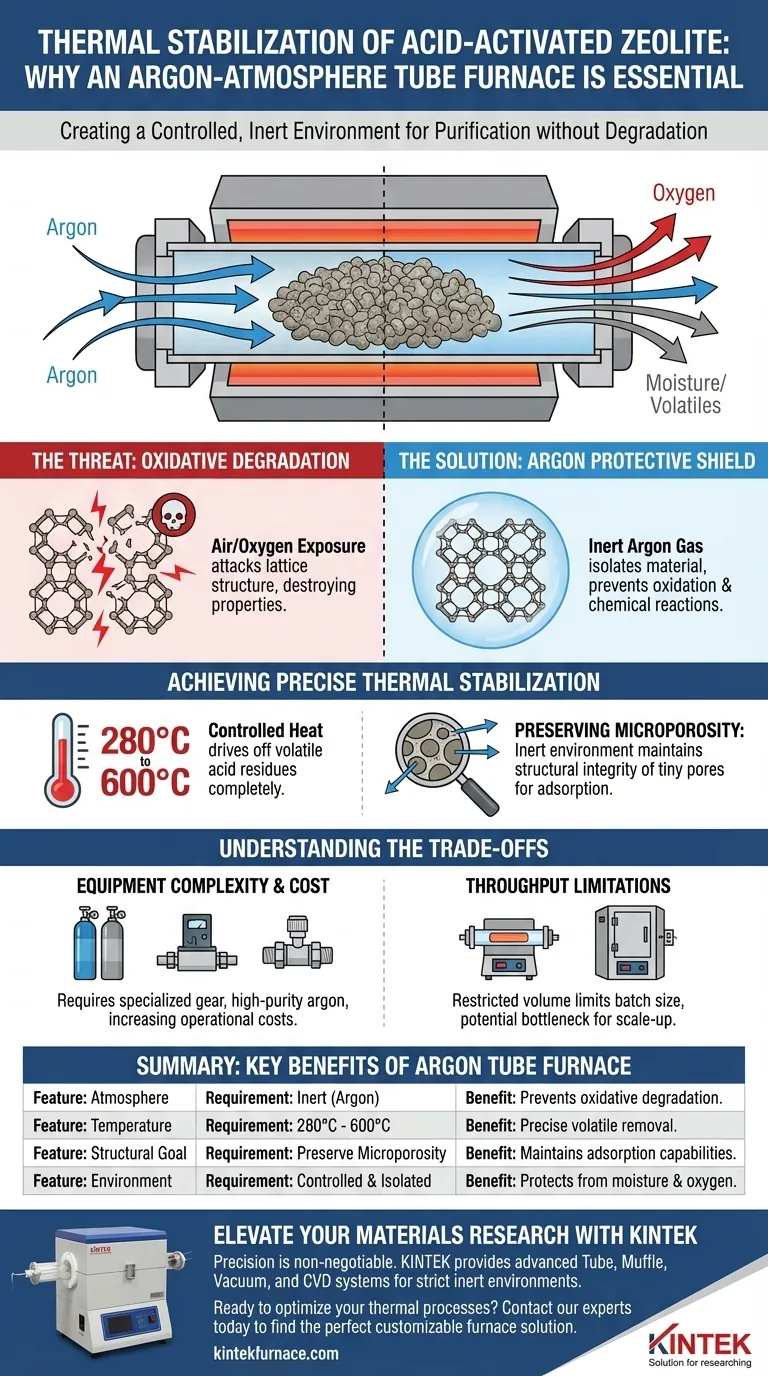
A tube furnace equipped with an argon atmosphere is essential for the thermal stabilization of acid-activated zeolite because it creates a strictly controlled, inert environment. By isolating the material from atmospheric oxygen and moisture, this setup prevents oxidative degradation while effectively removing volatile residues at high temperatures.
The core objective of thermal stabilization is to clean the material without destroying it. Using an argon-filled tube furnace ensures that the zeolite is purified of volatile contaminants while preserving the critical structural framework that defines its utility.

Protecting the Zeolite Framework
The Threat of Oxidative Degradation
When heating acid-activated zeolite (specifically clinoptilolite) to high temperatures, exposure to standard air presents a significant risk. The presence of oxygen can trigger oxidative degradation, which attacks the material's lattice structure.
If the framework degrades, the zeolite loses the specific properties that made it valuable in the first place.
Argon as a Protective Shield
To counter this, the process requires an inert gas. Argon is introduced into the tube furnace to displace air and create a protective atmosphere.
Because argon is chemically inert, it does not react with the zeolite. It effectively isolates the material from oxygen and moisture, ensuring that the heating process is purely physical (desorption) rather than chemical (oxidation).
Achieving Precise Thermal Stabilization
Controlled Removal of Volatiles
The thermal stabilization process typically operates between 280 and 600 degrees Celsius.
At these temperatures, the heat drives off volatile residues remaining from the acid activation process. The tube furnace allows for precise temperature regulation to ensure these impurities are vaporized completely.
Preserving Microporosity
The primary value of clinoptilolite lies in its microporosity—its internal network of tiny pores.
The inert argon environment ensures that while impurities are removed, the structural integrity of these pores is maintained. This guarantees that the final product retains its surface area and adsorption capabilities.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Equipment Complexity and Cost
Using a tube furnace with a controlled gas atmosphere is significantly more complex than using a standard drying oven.
It requires gas flow controllers, sealed fittings, and a continuous supply of high-purity argon. This increases both the operational cost and the technical expertise required to run the process.
Throughput Limitations
Tube furnaces typically have a restricted volume compared to large chamber furnaces.
While they offer superior atmospheric control, they may limit the batch size you can process at one time. This creates a bottleneck if you are attempting to scale up production from a laboratory setting to industrial quantities.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
If you are setting up a thermal stabilization protocol, consider your specific requirements:
- If your primary focus is maximizing structural integrity: Use the tube furnace with argon to ensure the micropore structure of the clinoptilolite is perfectly preserved.
- If your primary focus is removing stubborn volatiles: Rely on the high-temperature capability (up to 600°C) of the tube furnace, but ensure the inert atmosphere is maintained to prevent burning or degradation.
The use of an argon-purged tube furnace is the definitive method for ensuring that your acid-activated zeolite remains robust, porous, and chemically stable.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Requirement for Zeolite Stabilization | Benefit of Using Argon Tube Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Atmosphere | Inert (Argon) | Prevents oxidative degradation of the lattice structure. |
| Temperature | 280°C to 600°C | Enables precise removal of volatile acid residues. |
| Structural Goal | Preserve Microporosity | Maintains surface area and adsorption capabilities. |
| Environment | Controlled & Isolated | Protects against moisture and atmospheric oxygen interference. |
Elevate Your Materials Research with KINTEK
Precision is non-negotiable when stabilizing sensitive materials like acid-activated zeolites. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK provides advanced Tube, Muffle, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to maintain the strict inert environments your work demands.
Whether you need to preserve delicate microporosity or ensure complete volatile removal, our customizable high-temperature lab furnaces offer the reliability and atmospheric control essential for superior results.
Ready to optimize your thermal processes? Contact our experts today to find the perfect customizable furnace solution for your laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
References
- Sandugash Tanirbergenova, З. А. Мансуров. Effect of Acid Treatment on the Structure of Natural Zeolite from the Shankhanai Deposit. DOI: 10.3390/pr13092896
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is environmental control in a high-temperature tube furnace necessary during NVP/C synthesis? Key to Success
- What safety precautions should be taken when using a High Temperature Tube Furnace? Essential Tips for Safe Operation
- How do vacuum tube furnaces achieve energy efficiency? Maximize Thermal Performance and Cut Costs
- What kind of reaction environment does a laboratory tube furnace provide? Optimize Na4Fe3(PO4)2(P2O7) Synthesis
- What is the key function of a tube furnace for AHSS austenitization? Precision Testing for High-Strength Steel
- What are the key challenges in using tubular furnaces for materials science? Overcome Temperature, Uniformity, and Contamination Issues
- What is the significance of using a tubular furnace in waste salt pyrolysis research? Precision for High-Fidelity Data
- Why are corundum boats and tube furnaces utilized for biomass pre-carbonization? Optimize Your 500°C Pyrolysis



















