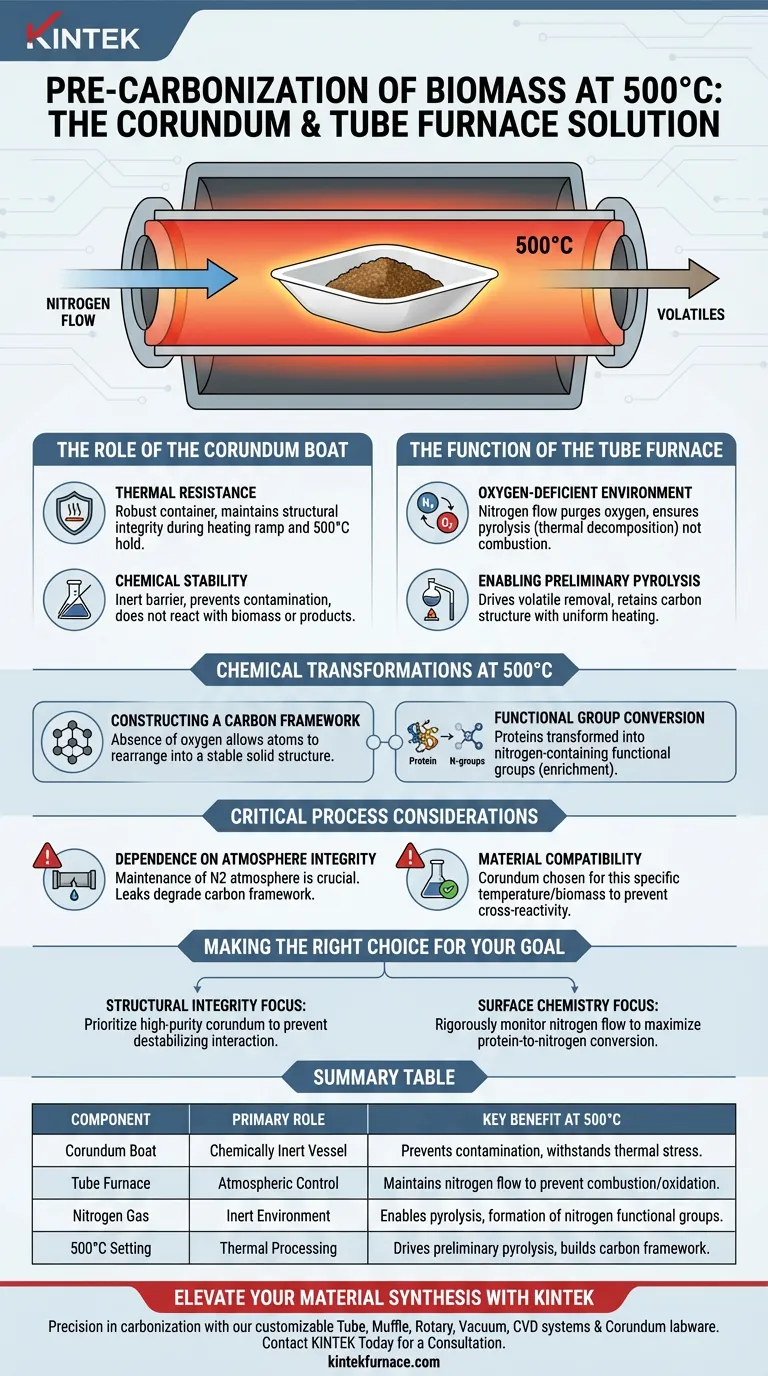
The combination of corundum boats and tube furnaces provides the precise thermal stability and atmospheric control required for the pre-carbonization of biomass. Corundum boats serve as chemically inert vessels that withstand high heat without contaminating the sample, while the tube furnace maintains an oxygen-deficient nitrogen environment to ensure pyrolysis occurs rather than combustion.
By isolating the biomass in a controlled, inert environment at 500°C, you facilitate the creation of a stable carbon framework. This specific setup is essential for converting proteins into nitrogen-containing functional groups without losing material to oxidation.
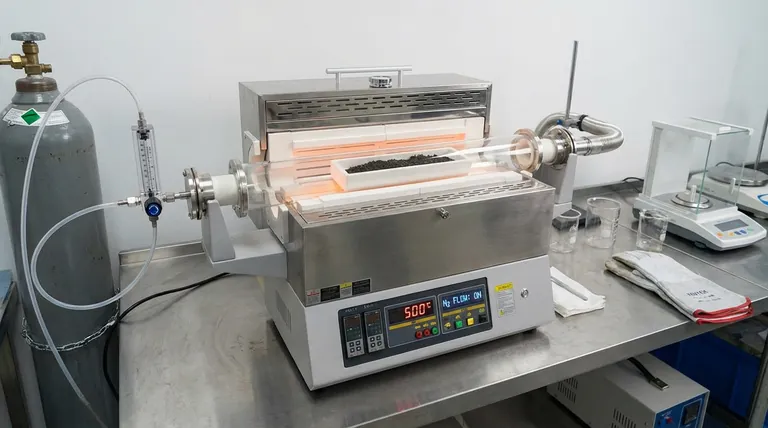

The Role of the Corundum Boat
Thermal Resistance
The primary function of the corundum boat is to provide a container that remains physically robust at 500°C.
Biomass mixtures undergo significant physical changes during heating. Corundum ensures the vessel maintains its structural integrity throughout the temperature ramp-up and hold times.
Chemical Stability
Beyond handling heat, corundum offers excellent chemical stability.
It acts as an inert barrier, ensuring that the container does not react with the biomass or its decomposition products. This prevents contamination of the carbon sample during the critical pre-carbonization phase.
The Function of the Tube Furnace
Creating an Oxygen-Deficient Environment
The tube furnace is utilized specifically to facilitate a controlled atmosphere.
By introducing a flow of nitrogen gas, the furnace purges oxygen from the heating chamber. This is the defining factor that distinguishes pyrolysis (thermal decomposition) from combustion (burning).
Enabling Preliminary Pyrolysis
At 500°C, the environment within the furnace drives preliminary pyrolysis.
This process removes volatile components while retaining the carbon structure. The uniform heating provided by the tube furnace ensures that the entire biomass mixture carbonizes evenly.
Chemical Transformations at 500°C
Constructing a Carbon Framework
The specific conditions created by this setup are critical for building a stable carbon framework.
The absence of oxygen allows the carbon atoms to rearrange into a solid structure rather than reacting with air to form carbon dioxide/monoxide gases.
Functional Group Conversion
This temperature and atmosphere are specifically tuned to manage the chemical conversion of proteins found in the biomass.
Under these conditions, proteins are effectively transformed into nitrogen-containing functional groups. This enrichment is often a key goal when synthesizing carbon materials for advanced applications.
Critical Process Considerations
Dependence on Atmosphere Integrity
The success of this method relies entirely on the maintenance of the nitrogen atmosphere.
If the tube furnace leaks or the nitrogen flow is insufficient, oxygen will enter the system. This will immediately degrade the carbon framework and prevent the proper formation of nitrogen functional groups.
Material Compatibility
While corundum is highly stable, it is chosen specifically for this temperature range and biomass type.
Using a vessel with lower chemical stability could lead to cross-reactivity, altering the final composition of the pre-carbonized material.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the quality of your pre-carbonized biomass, ensure your equipment aligns with your specific chemical objectives.
- If your primary focus is Structural Integrity: Prioritize the use of high-purity corundum boats to prevent any chemical interaction that could destabilize the developing carbon framework.
- If your primary focus is Surface Chemistry: rigoroulsy monitor the nitrogen flow in the tube furnace to maximize the conversion of proteins into nitrogen-containing functional groups.
Precision in material handling and atmosphere control is the difference between simple charring and creating high-value functionalized carbon.
Summary Table:
| Component | Primary Role | Key Benefit at 500°C |
|---|---|---|
| Corundum Boat | Chemically Inert Vessel | Prevents sample contamination and withstands thermal stress. |
| Tube Furnace | Atmospheric Control | Maintains nitrogen flow to prevent combustion/oxidation. |
| Nitrogen Gas | Inert Environment | Enables pyrolysis and formation of nitrogen functional groups. |
| 500°C Setting | Thermal Processing | Drives preliminary pyrolysis and builds the carbon framework. |
Elevate Your Material Synthesis with KINTEK
Precision in biomass carbonization starts with the right equipment. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, alongside high-purity Corundum labware. Whether you are synthesizing functionalized carbon or advanced ceramics, our lab high-temp furnaces are fully customizable to meet your unique research needs.
Ready to achieve superior thermal stability and atmospheric control?
Contact KINTEK Today for a Consultation
Visual Guide
References
- Y. Bai, Shicheng Zhang. In Situ, Nitrogen-Doped Porous Carbon Derived from Mixed Biomass as Ultra-High-Performance Supercapacitor. DOI: 10.3390/nano14161368
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role do industrial tube furnaces play in the oxidation of NiCrAl alloys? Precise Stability for Reliable Data
- What are the key advantages of using a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Dynamic, Uniform Heating for Powders
- What is the primary function of a tube furnace? Achieve Precise Atmospheric Control for Material Processing
- How is a Tube Furnace utilized in the color modification process of beryl? Master Deep Blue Aquamarine Transformation
- How do precision drying ovens and programmable furnaces ensure metal nitride/TiO2 composite performance? Expert Guide
- What is the primary function of a tube resistance furnace in g-C3N4 synthesis? Achieve Precise Thermal Condensation
- Why is it important to calibrate the temperature profile of a tube furnace? Ensure Accurate and Repeatable Results
- Why is a tube furnace required for PET carbonization? Achieve High-Surface Area Activated Carbon with Precise Control



















