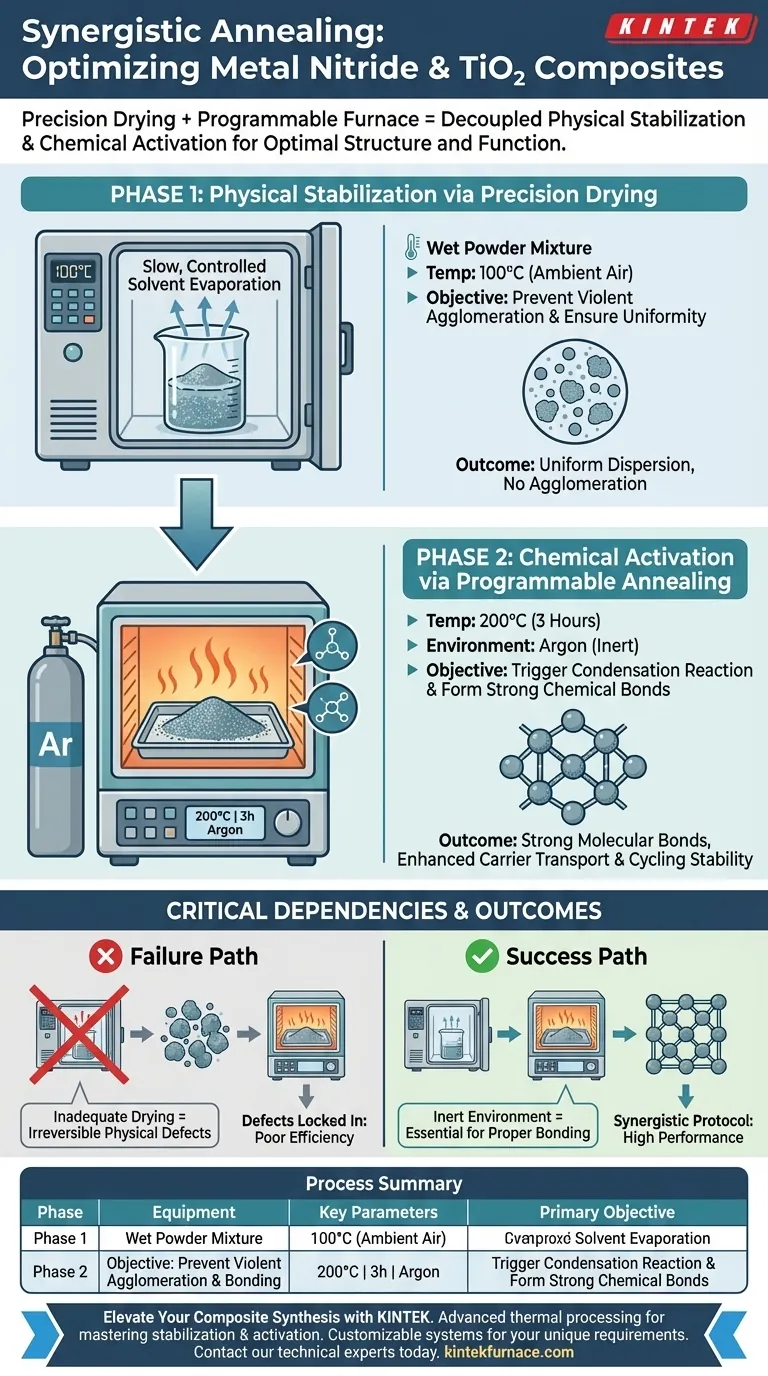
The synergy between precision drying ovens and programmable furnaces serves to decouple physical stabilization from chemical activation, ensuring the composite material achieves optimal structure and function.
The drying oven operates at 100°C to slowly evaporate solvents, preventing the structural damage caused by rapid moisture loss. This prepares the material for the programmable furnace, which executes a 200°C annealing cycle in an argon environment to forge strong chemical bonds, directly enhancing carrier transport efficiency and cycling stability.
To achieve high-performance composites, you must first preserve particle dispersion and then activate surface chemistry. The drying oven prevents the physical defect of agglomeration, creating the necessary foundation for the furnace to trigger the chemical condensation reactions that drive electrical performance.

Phase 1: Physical Stabilization via Precision Drying
The first stage of the process focuses entirely on the physical morphology of the metal nitride and titanium dioxide mixture.
Controlled Solvent Evaporation
A precision drying oven is set to a constant 100°C.
This moderate temperature ensures that solvents within the mixture are evaporated slowly and consistently.
Preventing Structural Defects
The primary goal of this phase is to avoid violent agglomeration.
If solvents are removed too quickly or unevenly, the powder particles clump together, creating structural inconsistencies.
By slowly removing moisture, the oven prevents moisture retention that would otherwise disrupt the uniformity of the composite.
Phase 2: Chemical Activation via Programmable Annealing
Once the physical structure is stabilized, the material is transferred to a programmable furnace for chemical processing.
Triggering the Condensation Reaction
The furnace performs an annealing treatment at 200°C for 3 hours in an argon environment.
This specific thermal profile triggers a condensation reaction among the surface hydroxyl groups.
Forming Strong Chemical Bonds
This reaction creates strong chemical bonds between the metal nitride and the titanium dioxide surface.
These bonds are the critical mechanism that links the two materials at a molecular level.
Enhancing Performance Metrics
The formation of these bonds directly translates to improved device performance.
Specifically, it significantly enhances carrier transport efficiency, allowing electrons to move more freely through the composite.
It also improves cycling stability, ensuring the material maintains its performance over repeated use.
Critical Process Dependencies
Understanding the relationship between these two steps is vital for consistent results. This is where process failures often occur.
The Consequence of Inadequate Drying
If the drying phase is rushed or the temperature is too high, the powder will agglomerate before it reaches the furnace.
The furnace cannot correct physical agglomeration; it will simply lock the defects in place chemically, resulting in poor transport efficiency.
The Necessity of the Inert Environment
The furnace stage specifically requires an argon environment.
Without this inert atmosphere, the high temperatures required for the condensation reaction could lead to unwanted oxidation, degrading the metal nitride rather than bonding it to the titanium dioxide.
Optimizing Your Annealing Protocol
To ensure your composites achieve the highest possible performance, prioritize your equipment settings based on the specific outcome you need to control.
- If your primary focus is Morphology (Structure): Prioritize the precision drying oven phase to ensure slow, uniform solvent evaporation that prevents particle agglomeration.
- If your primary focus is Conductivity (Performance): Ensure the programmable furnace maintains a strict argon atmosphere at 200°C to maximize the condensation reaction and chemical bonding.
By respecting the distinct role of each thermal stage, you transform a simple mixture into a highly stable, efficient composite material.
Summary Table:
| Process Phase | Equipment Type | Key Parameters | Primary Objective |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phase 1: Physical Stabilization | Precision Drying Oven | 100°C, Ambient Air | Prevent agglomeration & ensure uniform solvent evaporation |
| Phase 2: Chemical Activation | Programmable Furnace | 200°C, 3h, Argon Env. | Trigger condensation reactions & form strong molecular bonds |
| Critical Outcome | Synergistic Protocol | Sequential Processing | High carrier transport efficiency & cycling stability |
Elevate Your Composite Synthesis with KINTEK
Precision in thermal processing is the difference between material failure and high-performance innovation. KINTEK provides the advanced lab equipment necessary to master both physical stabilization and chemical activation.
Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, we offer high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, along with precision drying ovens—all fully customizable to meet your unique annealing requirements. Whether you are optimizing particle dispersion or forging molecular bonds in inert environments, KINTEK ensures your lab has the reliability it deserves.
Ready to optimize your annealing protocol? Contact our technical experts today to find the perfect thermal solution for your research.
Visual Guide
References
- Dreenan Shea, Mita Dasog. Decoding Plasmonic Enhancement Pathways in Group 4 Metal Nitride‐TiO<sub>2</sub> Composites: Rhodamine B Dye Degradation Case Study. DOI: 10.1002/nano.70059
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace Molybdenum Wire Vacuum Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering and Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- Why is a controlled nitrogen atmosphere essential during the high-temperature processing of biomass in a tube furnace?
- What heat treatment processes can a 70mm tube furnace be used for? Essential Guide for Material Processing
- What factors should be considered when purchasing a quartz tube furnace? Ensure Reliable High-Temperature Processing
- What role does a high-temperature tube furnace play in the synthesis of SiC nanofibers? Precision CVD Growth at 1100°C
- What are the specifications for three-zone and three-phase horizontal tube furnace models? Find the Perfect Fit for Your Lab
- Why is a high-precision tube furnace required for PtCln/Fe-N-C catalysts? Ensure Sub-Nanometer Precision
- What Role Does a Tube Reactor Play in Food Waste Pyrolysis? Control Carbonization for High-Quality Biochar
- How do vacuum tube furnaces achieve energy efficiency? Maximize Thermal Performance and Cut Costs



















