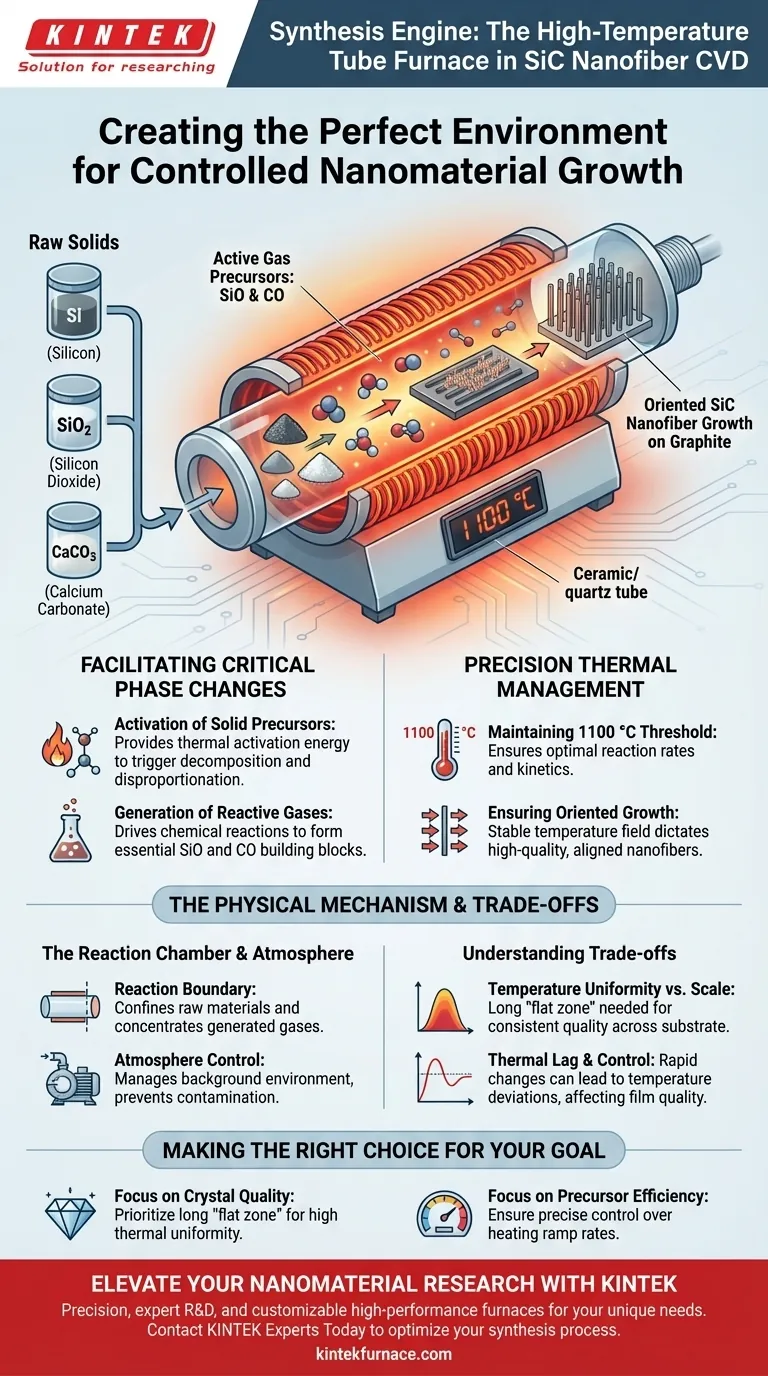
The high-temperature tube furnace functions as the primary reaction engine for synthesizing Silicon Carbide (SiC) nanofibers. It creates a precisely controlled thermal environment at 1100 °C, which is required to convert solid raw materials—specifically Silicon (Si), Silicon Dioxide (SiO2), and Calcium Carbonate (CaCO3)—into the active gas-phase precursors necessary for nanofiber growth.
Core Takeaway The tube furnace is not merely a heat source; it is a chemical reactor that drives the disproportionation and decomposition of solids into gases (SiO and CO). It maintains a stable temperature field that dictates the quality and oriented growth of the resulting nanofibers on graphite substrates.

Facilitating Critical Phase Changes
Activation of Solid Precursors
The primary role of the furnace is to provide the thermal activation energy needed to initiate chemical changes in solid materials. In this specific CVD process, the furnace does not simply melt materials; it triggers the decomposition of Calcium Carbonate (CaCO3) and the disproportionation of Silicon (Si) and Silicon Dioxide (SiO2).
Generation of Reactive Gases
SiC nanofibers cannot be formed directly from the solid raw materials. The furnace heat drives the chemical reactions that generate gas-phase precursors, specifically Silicon Monoxide (SiO) and Carbon Monoxide (CO). These gases are the actual building blocks that will eventually deposit and react to form the final SiC product.
Precision Thermal Management
Maintaining the 1100 °C Threshold
The specific temperature of 1100 °C is critical for this synthesis. Below this threshold, the precursor gases may not generate at sufficient rates; above it, the reaction kinetics may become uncontrollable. The furnace monitors this via internal thermocouples to ensure the reaction remains stable.
Ensuring Oriented Growth
Beyond just reaching the target temperature, the furnace must maintain a stable temperature field. This stability is vital for the oriented growth of the nanofibers. If the temperature fluctuates across the reaction zone, the fibers may grow randomly or suffer from structural defects rather than aligning correctly on the graphite substrate.
The Physical Mechanism
The Reaction Chamber
The "tube" acts as the physical boundary for the reaction, typically made of heat-resistant quartz or ceramic. It holds the graphite substrates and the raw materials in a confined space, allowing the concentration of generated gases (SiO and CO) to reach levels necessary for deposition.
Atmosphere Control
While the primary reference highlights the generation of specific gases, the furnace also allows for the management of the background atmosphere. By controlling the environment (often using vacuum or inert gases), the furnace prevents external contamination that could interfere with the purity of the SiC nanofibers.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Temperature Uniformity vs. Scale
A common challenge in tube furnaces is maintaining temperature uniformity over the entire length of the tube. While a specific zone may be perfectly controlled at 1100 °C, the ends of the tube may be cooler. This can lead to variations in nanofiber quality, where samples in the center achieve perfect crystallinity while those near the edges do not.
Thermal Lag and Control
Electric heating coils have a physical response time. Rapid changes in the desired temperature setpoint can lead to "overshoot" or "undershoot." In CVD processes, even brief deviations from the target temperature can alter the decomposition rates of precursors, leading to inconsistent film thickness or phase impurities.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To optimize your SiC nanofiber synthesis, you must align the furnace capabilities with your specific project requirements.
- If your primary focus is Crystal Quality: Prioritize a furnace with a long "flat zone" (a zone of high thermal uniformity) to ensure the 1100 °C temperature field is consistent across the entire substrate.
- If your primary focus is Precursor Efficiency: Ensure the furnace has precise control over the heating ramp rates to manage the decomposition speed of the CaCO3 and Si/SiO2 mix, preventing gas generation from outpacing the deposition process.
Success in this CVD process relies on viewing the furnace as a dynamic instrument for chemical control, rather than a passive oven.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Role in SiC Nanofiber Synthesis |
|---|---|
| Operating Temperature | Maintains critical 1100 °C threshold for thermal activation |
| Phase Conversion | Drives disproportionation of Si/SiO2 and decomposition of CaCO3 |
| Precursor Generation | Facilitates the formation of reactive SiO and CO gas-phase building blocks |
| Growth Environment | Provides a stable temperature field for oriented growth on graphite |
| Reaction Boundary | Confines gases in a quartz/ceramic tube to ensure proper deposition |
| Atmosphere Control | Prevents contamination and manages inert/vacuum environments |
Elevate Your Nanomaterial Research with KINTEK
Precision is the difference between random growth and high-performance nanofibers. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to meet the rigorous demands of your lab. Whether you need a long thermal 'flat zone' for crystal uniformity or rapid ramp-rate control for precursor efficiency, our furnaces are fully customizable for your unique needs.
Ready to optimize your synthesis process?
Contact KINTEK Experts Today to discover how our high-temperature solutions can enhance your lab's efficiency and material quality.
Visual Guide
References
- Limeng Song, Rui Zhang. Heterointerface‐Engineered SiC@SiO <sub>2</sub> @C Nanofibers for Simultaneous Microwave Absorption and Corrosion Resistance. DOI: 10.1002/advs.202509071
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station CVD Machine
People Also Ask
- What is tube CVD? A Guide to High-Purity Thin Film Synthesis
- How does a CVD tube furnace achieve high purity in gate media preparation? Master Precision Control for Flawless Films
- What temperature range do standard CVD tube furnaces operate at? Unlock Precision for Your Material Deposition
- What customization options are available for CVD tube furnaces? Tailor Your System for Superior Material Synthesis
- How are hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN) films processed using CVD tube furnaces? Optimize Growth for High-Quality 2D Materials



















