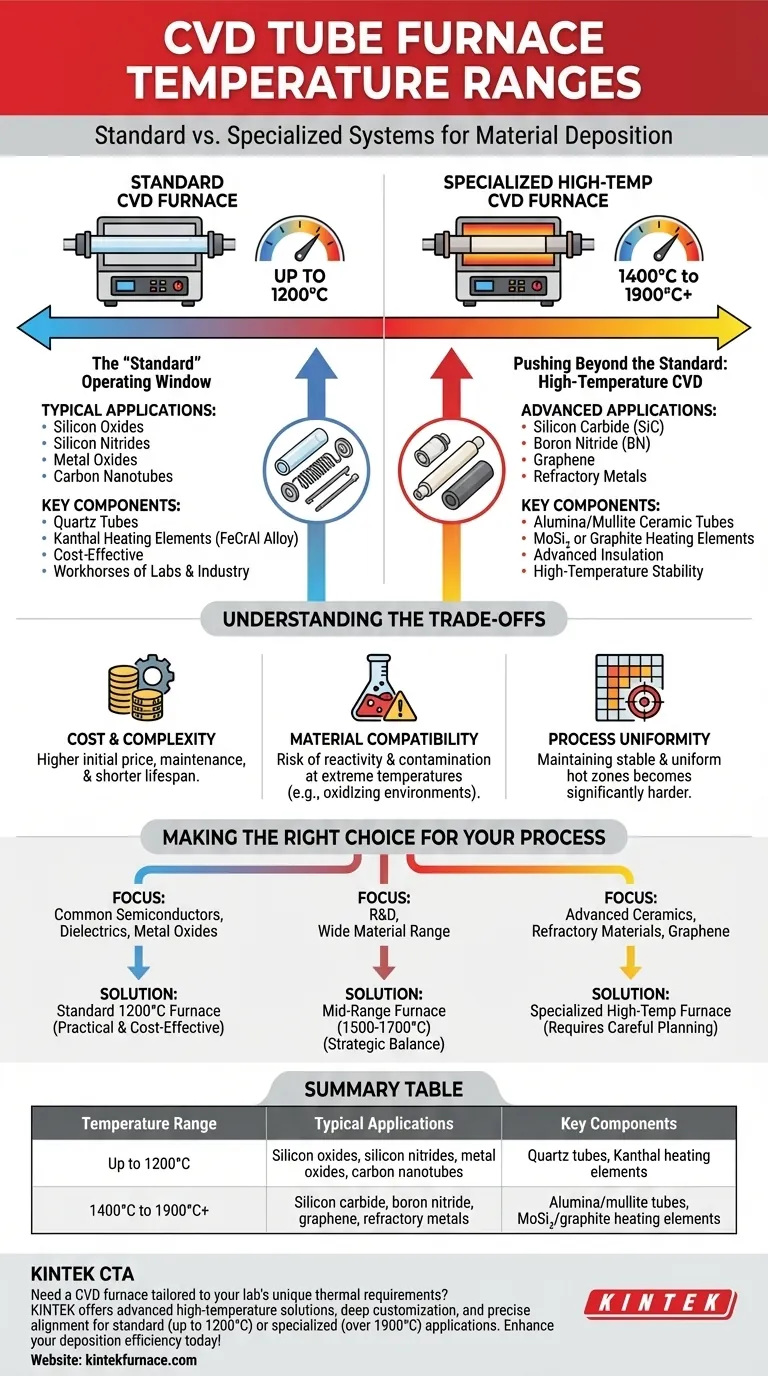
In short, a standard CVD tube furnace typically operates at temperatures up to 1200°C. This range accommodates a wide variety of common material deposition processes. However, the full operational scope of CVD technology extends far higher, with specialized systems capable of exceeding 1900°C for advanced applications.
The key takeaway is that "standard" and "specialized" define two distinct classes of CVD furnaces. Understanding your material's specific thermal requirements is the critical first step in selecting the correct equipment, as capabilities and costs vary dramatically between these classes.

The "Standard" Operating Window
A majority of chemical vapor deposition processes are performed in furnaces that are considered standard in the industry. This operational window is defined by common materials and cost-effective engineering.
The 1200°C Benchmark
Most off-the-shelf CVD tube furnaces are designed with a maximum operating temperature of 1200°C.
This temperature range is sufficient for depositing many of the most widely used thin films, including silicon oxides, silicon nitrides, various metal oxides, and certain carbon-based materials like carbon nanotubes.
Why 1200°C is a Common Limit
This temperature is not arbitrary. It represents a practical engineering and materials science threshold.
Furnaces operating up to 1200°C can use quartz tubes as the reaction chamber and Kanthal (FeCrAl alloy) heating elements. Both are reliable, well-understood, and relatively inexpensive materials, making these furnaces the workhorses of both research labs and industrial production.
Pushing Beyond the Standard: High-Temperature CVD
For materials that require more extreme formation conditions, a different class of furnace is necessary. These systems are engineered specifically for high-temperature stability and control.
The Realm of Specialized Materials
Depositing high-performance materials like silicon carbide (SiC), boron nitride (BN), graphene, and certain refractory metals requires temperatures well above the 1200°C standard.
These processes often demand thermal energy in the range of 1400°C to over 1900°C to achieve the desired chemical reactions and crystal structures.
The Technology for Extreme Heat
Reaching these temperatures requires a fundamental change in furnace design. Quartz tubes are replaced with high-purity alumina or mullite ceramics, and standard heating elements are swapped for materials like molybdenum disilicide (MoSi₂) or graphite.
These systems also demand more advanced insulation, power controllers, and cooling systems to manage the extreme thermal loads safely and precisely.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a high-temperature furnace introduces significant considerations beyond the initial purchase price. These systems are not a universal upgrade but a specialized tool for a specific job.
Cost and Complexity
High-temperature furnaces are significantly more expensive to acquire, operate, and maintain. The specialized components, from heating elements to ceramic tubes, have a higher cost and often a shorter operational lifespan than their standard counterparts.
Material Compatibility and Contamination
At extreme temperatures, the furnace components themselves can become reactive. For example, graphite heating elements may not be suitable for processes in an oxidizing atmosphere. The choice of furnace materials becomes a critical part of the process design to prevent unwanted reactions and contamination of the final film.
Process Uniformity
Maintaining a stable and uniform hot zone becomes exponentially more difficult as temperatures increase. Achieving the precise thermal control necessary for high-quality, uniform film deposition across a large substrate is a significant engineering challenge in high-temperature systems.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your decision must be driven by the specific requirements of the material you intend to deposit.
- If your primary focus is on common semiconductors, dielectrics, or metal oxides: A standard furnace operating up to 1200°C is the most practical and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is on advanced ceramics, refractory materials, or high-quality graphene: You must invest in a specialized high-temperature furnace and carefully plan for the associated operational complexities.
- If your primary focus is R&D with a wide range of potential materials: A mid-range furnace (e.g., up to 1500-1700°C) can offer a strategic balance between expanded capability and manageable cost.
Ultimately, aligning the furnace's thermal capability with your specific process needs is the foundation of successful chemical vapor deposition.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Range | Typical Applications | Key Components |
|---|---|---|
| Up to 1200°C | Silicon oxides, silicon nitrides, metal oxides, carbon nanotubes | Quartz tubes, Kanthal heating elements |
| 1400°C to 1900°C+ | Silicon carbide, boron nitride, graphene, refractory metals | Alumina/mullite tubes, MoSi₂/graphite heating elements |
Need a CVD furnace tailored to your lab's unique thermal requirements? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With strong deep customization capabilities, we ensure precise alignment with your experimental needs—whether for standard processes up to 1200°C or specialized applications exceeding 1900°C. Contact us today to enhance your material deposition efficiency and achieve superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the working principle of a CVD tube furnace? Achieve Precise Thin Film Deposition for Your Lab
- Why are advanced materials and composites important? Unlock Next-Gen Performance in Aerospace, Auto, and More
- What makes a CVD Tube Furnace essential for material science and nanotechnology? Unlock Precision in Material Synthesis
- Which industries and research fields benefit from CVD tube furnace sintering systems for 2D materials? Unlock Next-Gen Tech Innovations
- What temperature ranges can a CVD Tube Furnace achieve with different tube materials? Unlock High-Temp Precision for Your Lab



















