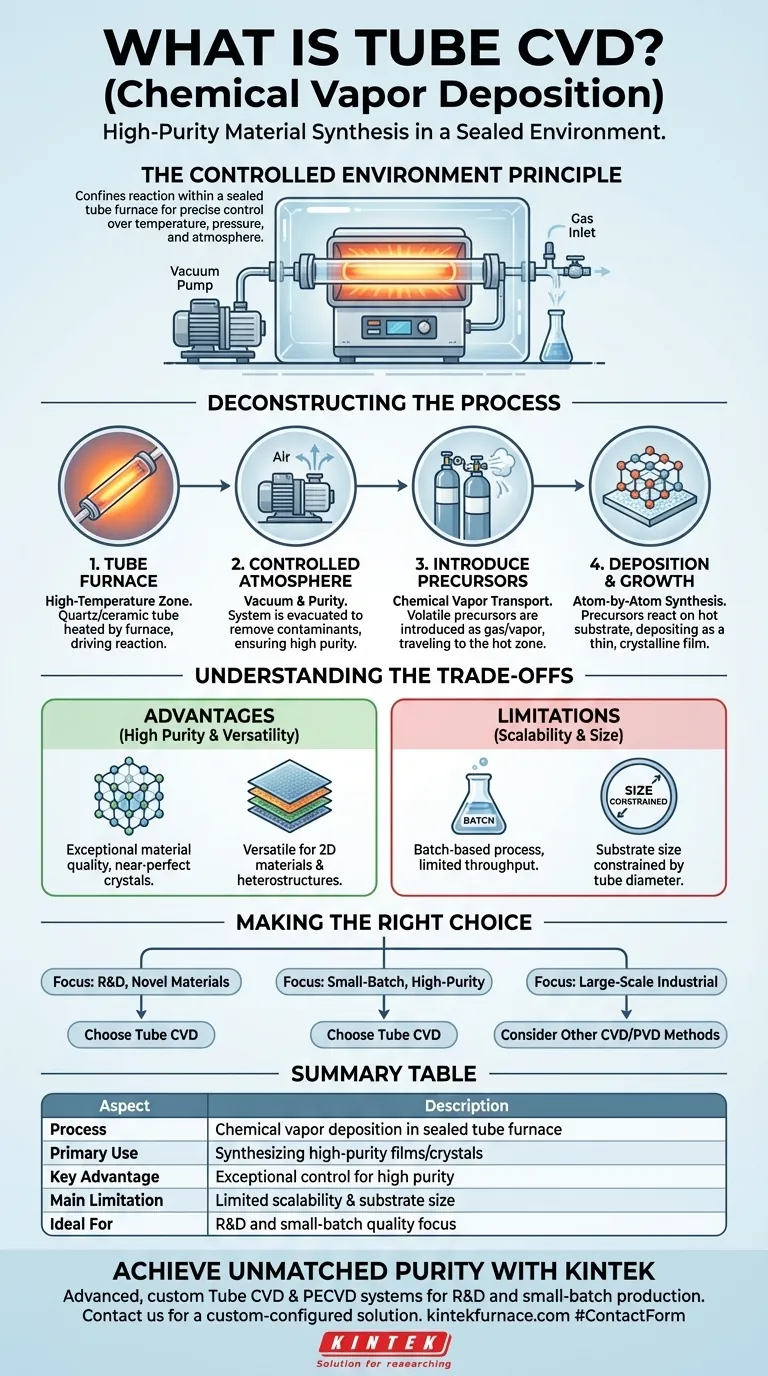
In materials science, tube CVD is a specific method of Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) that is performed inside a sealed tube furnace. This technique is used to synthesize high-purity thin films and crystalline materials, such as two-dimensional (2D) materials, on a substrate. The process involves introducing chemical precursors into the heated tube under vacuum, where they react and deposit onto the substrate surface atom-by-atom.
Tube CVD is best understood not just as a process, but as a controlled environment. By confining the chemical reaction within a sealed tube furnace, this method provides the exceptional control over temperature, pressure, and atmosphere required to grow highly pure, uniform thin films and crystals.

Deconstructing the Tube CVD Process
Tube CVD systems are designed around a central principle: creating a pristine, high-temperature reaction zone isolated from the outside world. Each component plays a critical role in achieving this controlled environment.
The Role of the Tube Furnace
The core of the system is the tube furnace, which provides the high temperatures necessary to drive the chemical reaction. This furnace heats a quartz or ceramic tube that contains the substrate material.
Precise temperature control is critical, as it directly influences the growth rate and quality of the final material.
Establishing a Controlled Atmosphere
The process is performed under vacuum, well below atmospheric pressure. A vacuum system removes air and other contaminants from the tube before the reaction begins.
This ensures that the deposited film is made only from the intended precursor chemicals, resulting in very high purity.
Introducing the Precursor Gases
Precursors are the volatile chemical compounds that contain the atoms needed to build the new material. They are introduced into the heated tube as a gas or vapor.
These precursors travel through the tube until they reach the hot zone where the substrate is located. This process is sometimes referred to as chemical vapor transport.
Deposition and Material Growth
On the hot substrate surface, the precursors decompose or react with each other. This chemical reaction results in the desired material being deposited as a solid, durable thin film.
The deposition occurs molecule-by-molecule, allowing for the formation of highly ordered crystalline structures, including single-layer 2D materials.
Advanced Process Control
Modern tube CVD systems can be highly sophisticated. Some incorporate features like plasma sources to assist the reaction or sliding stages to allow for rapid heating and cooling of the substrate.
These additions provide even greater control over the material's final properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs of Tube CVD
While powerful, tube CVD is not the solution for every application. Understanding its inherent advantages and limitations is key to using it effectively.
Advantage: High Purity and Crystallinity
The primary advantage of tube CVD is the extremely high quality of the materials it can produce. The sealed, vacuum environment minimizes contamination, leading to exceptional purity and near-perfect crystal structures.
This makes it the go-to method for cutting-edge research and applications where material perfection is paramount.
Advantage: Versatility in Material Synthesis
Tube CVD is highly versatile. By changing the precursors, temperature, and pressure, a wide variety of materials can be synthesized.
It is particularly well-suited for growing novel materials like 2D sheets (e.g., tantalum disulfide) and complex heterostructures, which involve stacking different material layers on top of each other.
Limitation: Scalability and Batch Processing
The main drawback is scalability. Tube furnaces are inherently batch-based and limited by the tube's physical dimensions.
This makes the process less suitable for large-scale, continuous industrial production compared to other deposition techniques. It is primarily a lab-scale and specialized production tool.
Limitation: Substrate Size Constraints
The diameter of the furnace tube directly limits the maximum size of the substrate that can be processed. This can be a significant constraint for applications requiring large-area coatings.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Deciding whether to use tube CVD depends entirely on your project's priorities. It is a choice that balances material quality against production volume.
- If your primary focus is research and development of novel materials: Tube CVD offers the precision and environmental control necessary for experimenting with 2D materials and complex heterostructures.
- If your primary focus is producing small batches of high-purity crystalline films: This method is ideal due to its excellent isolation from contaminants, ensuring top-tier material quality.
- If your primary focus is large-scale industrial coating: You should explore other CVD configurations or PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) methods that are designed for high throughput and larger substrates.
Ultimately, choosing tube CVD is a decision to prioritize material quality and process control above all else.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Process | Chemical vapor deposition inside a sealed tube furnace. |
| Primary Use | Synthesizing high-purity thin films and crystalline materials (e.g., 2D materials). |
| Key Advantage | Exceptional control for high purity and crystallinity. |
| Main Limitation | Limited scalability and substrate size due to batch processing. |
| Ideal For | R&D and small-batch production where material quality is paramount. |
Ready to Achieve Unmatched Material Purity with a Custom Tube CVD Solution?
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Tube Furnaces and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements for synthesizing 2D materials and high-purity thin films.
Contact us today to discuss how a custom-configured tube CVD system from KINTEK can elevate your research and development.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station CVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
People Also Ask
- What is the working principle of a CVD tube furnace? Achieve Precise Thin Film Deposition for Your Lab
- What makes a CVD Tube Furnace essential for material science and nanotechnology? Unlock Precision in Material Synthesis
- Where is a CVD Tube Furnace commonly used? Essential for High-Tech Materials and Electronics
- Why is the tube design important in CVD furnaces? Ensure Uniform Deposition for High-Quality Films
- Which industries and research fields benefit from CVD tube furnace sintering systems for 2D materials? Unlock Next-Gen Tech Innovations



















