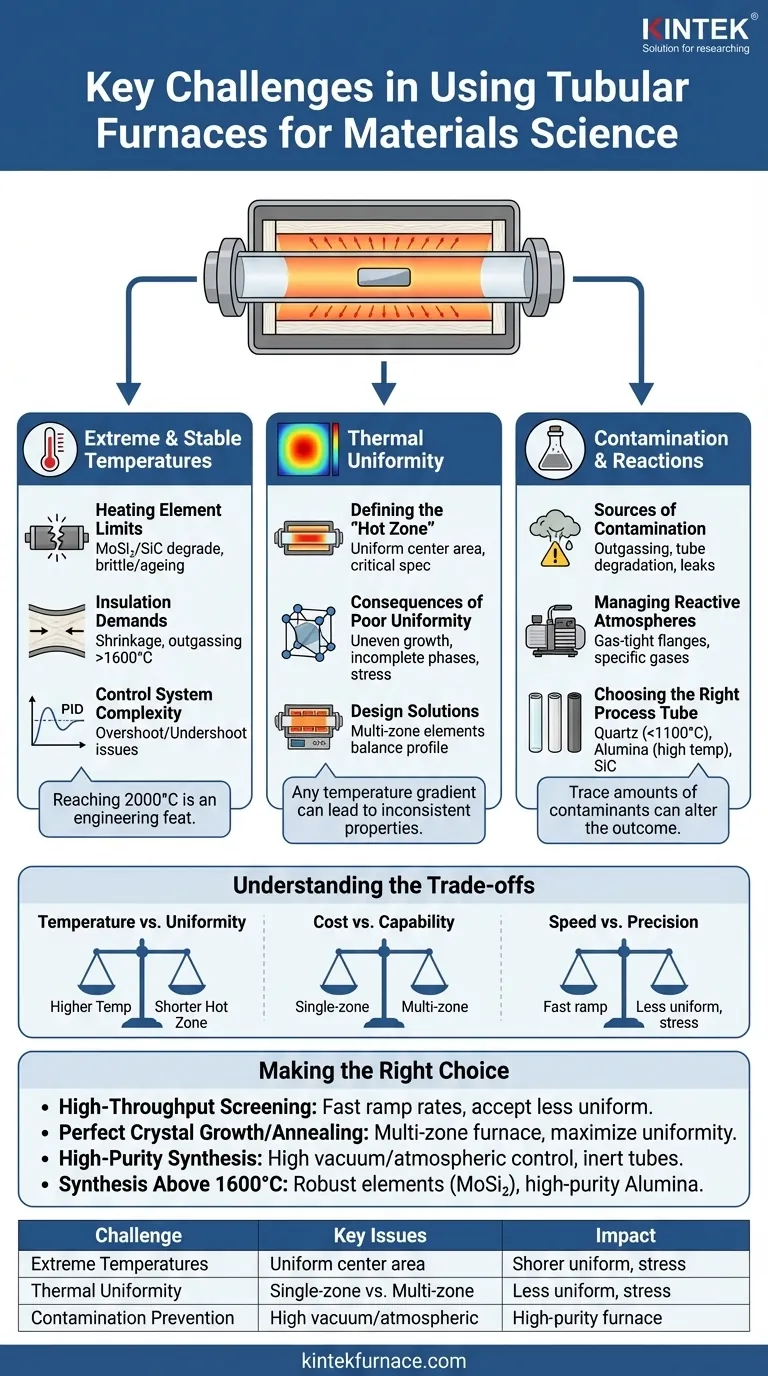
The primary challenges in using tubular furnaces for materials science revolve around achieving extreme temperatures, ensuring absolute thermal uniformity across the sample, and preventing contamination. These are not isolated equipment issues; they directly impact the integrity and reproducibility of experimental results by influencing the final properties of the material being processed.
A tubular furnace is more than a simple heater; it's a precision instrument for creating new materials. The central challenge lies not just in reaching high temperatures, but in creating an environment of perfect uniformity and purity to ensure the material's properties are exactly as intended.

The Pursuit of Extreme and Stable Temperatures
Reaching temperatures up to 2000°C is a significant engineering feat that pushes materials to their operational limits. The challenge is not just getting hot, but staying stable and reliable over many cycles.
The Material Limits of Heating Elements
Heating elements are the heart of the furnace, but they degrade over time, especially at extreme temperatures. Elements like Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) can provide high heat but become brittle, while Silicon Carbide (SiC) elements can "age," changing their resistance and affecting temperature accuracy.
The Demands on Insulation
Effective insulation is critical for temperature stability and energy efficiency. However, at temperatures above 1600-1700°C, even high-grade ceramic fiber insulation can shrink, degrade, or outgas, compromising the furnace's performance and potentially contaminating the sample.
The Complexity of Control Systems
Modern furnaces use sophisticated PID controllers (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) to manage temperature. The challenge is tuning these controllers perfectly to avoid temperature overshoot or undershoot, which can ruin sensitive processes like crystal growth or phase transitions.
The Critical Importance of Thermal Uniformity
Perhaps the most significant challenge is achieving a perfectly uniform temperature across the entire sample. Any temperature gradient can lead to inconsistent material properties.
Defining the "Hot Zone"
The uniform hot zone is the area in the center of the furnace tube where the temperature is stable and consistent within a specified tolerance (e.g., ±5°C). The length of this zone is a critical furnace specification.
Consequences of Poor Uniformity
A lack of uniformity can be disastrous for materials processing. It can cause uneven crystal growth, lead to incomplete phase transformations in parts of the sample, or introduce thermal stress that warps or cracks the material.
Design Solutions: Multi-Zone Furnaces
To combat this, advanced furnaces are designed with multiple heating zones. These furnaces use several independent heating elements and thermocouples along the tube, allowing the control system to actively balance the temperature profile and significantly expand the uniform hot zone.
Preventing Contamination and Unwanted Reactions
A furnace must provide a pure environment. At high temperatures, materials become highly reactive, and even trace amounts of contaminants can alter the outcome of an experiment.
Sources of Contamination
Contamination can come from several sources. This includes outgassing from the insulation, degradation of the furnace tube itself, or microscopic leaks that allow oxygen or moisture from the air to enter the system.
Managing Reactive Atmospheres
Many processes require a specific atmosphere, such as a high vacuum, an inert gas (like Argon), or a reactive gas. Ensuring the furnace tube is perfectly sealed with gas-tight flanges is a persistent mechanical challenge, especially with repeated heating and cooling cycles.
Choosing the Right Process Tube
The process tube is the first line of defense. A quartz tube is cost-effective but typically limited to ~1100°C. Alumina tubes are the standard for higher temperatures (up to 1800°C) due to their purity and stability, while materials like Silicon Carbide may be needed for specific chemical environments.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting or operating a tubular furnace always involves balancing competing priorities. Understanding these trade-offs is key to successful experimentation.
Temperature vs. Uniformity
Generally, the higher the maximum operating temperature of a furnace, the shorter its uniform hot zone tends to be. Achieving high uniformity at extreme temperatures requires more sophisticated and expensive designs.
Cost vs. Capability
A simple, single-zone furnace is far less expensive than a three-zone furnace with advanced atmospheric controls. The choice depends entirely on whether the experimental requirements justify the significant investment in precision.
Speed vs. Precision
Rapid heating and cooling rates (ramp rates) can increase experimental throughput. However, these fast rates can compromise thermal uniformity and place immense thermal stress on the heating elements and process tube, potentially shortening their lifespan.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your research goal should dictate your furnace requirements.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput screening: Prioritize furnaces with faster ramp rates and potentially larger tubes, accepting a slightly less uniform hot zone.
- If your primary focus is perfect crystal growth or annealing: Invest in a multi-zone furnace to maximize thermal uniformity, even if it means a slower process.
- If your primary focus is high-purity synthesis: Focus on a furnace with a high-quality vacuum and atmospheric control system, ensuring the process tube material is inert to your sample.
- If your primary focus is synthesis above 1600°C: Ensure the furnace uses robust elements (like MoSi₂ or tungsten) and high-purity alumina tubes, and account for the accelerated degradation of all components.
Mastering these challenges transforms the tubular furnace from a simple tool into a powerful engine for material innovation.
Summary Table:
| Challenge | Key Issues | Impact on Materials Science |
|---|---|---|
| Extreme Temperatures | Heating element degradation, insulation limits, control system complexity | Affects material stability and reproducibility |
| Thermal Uniformity | Hot zone definition, uneven heating, multi-zone design needs | Leads to inconsistent crystal growth and phase transformations |
| Contamination Prevention | Outgassing, tube degradation, atmosphere control | Alters material purity and experimental outcomes |
Struggling with temperature control, uniformity, or contamination in your materials research? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems with strong deep customization capabilities. Whether you're focused on high-throughput screening, perfect crystal growth, or high-purity synthesis, our expertise ensures precise, reliable performance to overcome key challenges and accelerate your innovations. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your laboratory's efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
People Also Ask
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety



















