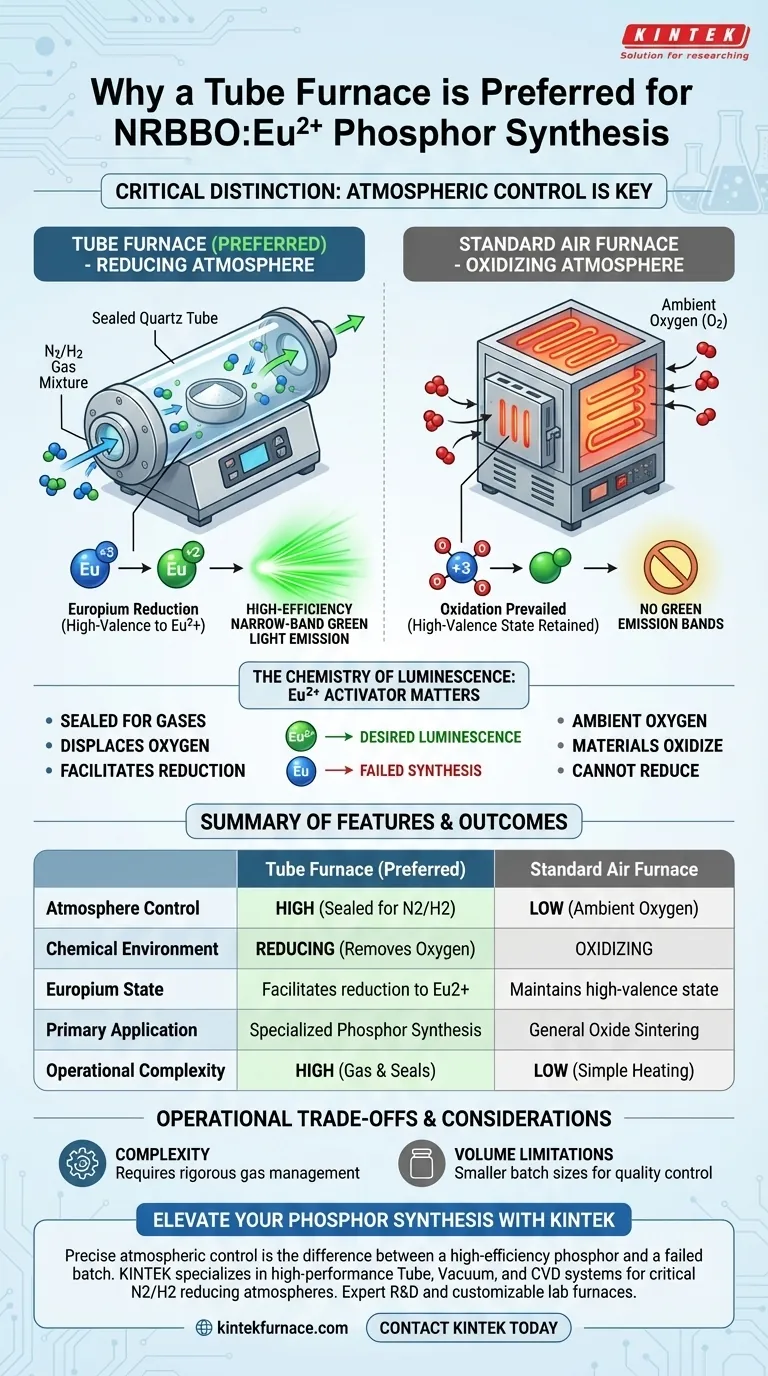
The critical distinction lies in atmospheric control. A tube furnace is preferred over a standard air furnace because it facilitates a strictly controlled reducing atmosphere, typically utilizing a nitrogen/hydrogen (N2/H2) gas mixture. This specific environment is non-negotiable for reducing the europium activator to its divalent state (Eu2+), which is the engine behind the phosphor's high-efficiency narrow-band green light emission.
While standard air furnaces provide heat, they cannot exclude oxygen effectively; the synthesis of NRBBO:Eu2+ requires a specialized reducing environment to stabilize the Europium ion, ensuring the material achieves its specific luminescent properties.

The Chemistry of Luminescence
The Role of the Europium Activator
In the synthesis of NRBBO:Eu2+ phosphors, Europium serves as the activator. This means it is the specific element responsible for the material's ability to emit light.
Why the Divalent State (Eu2+) Matters
To achieve the desired narrow-band green light emission, the Europium ion must exist in a divalent state (Eu2+). If the Europium remains in a high-valence state, the phosphor will not exhibit the high-efficiency optical characteristics required for its intended application.
The Limitation of Standard Air Furnaces
The Oxygen Problem
Standard air furnaces operate in an ambient atmosphere rich in oxygen. In this environment, materials are naturally subjected to oxidation during the heating process.
Inability to Reduce
Because air furnaces cannot maintain a reducing atmosphere, they are unable to convert the Europium activator from a high-valence state down to the necessary Eu2+ state. Consequently, synthesis in an air furnace would result in a material that lacks the specific green emission bands targeted in NRBBO synthesis.
The Function of the Tube Furnace
Creating a Reducing Atmosphere
A tube furnace is designed with a sealed work tube that allows for the precise introduction of specific gases. For NRBBO:Eu2+, a mixture of N2/H2 gas is flowed through the tube.
Strictly Controlled Environment
This setup displaces oxygen and introduces hydrogen, creating a chemical environment that actively reduces the Europium ions. This level of atmospheric control is the primary technical reason why a tube furnace is the only viable option for this specific synthesis.
Operational Trade-offs and Considerations
Complexity vs. Necessity
While tube furnaces enable the necessary chemistry, they introduce complexity compared to air furnaces. Managing gas flows, seals, and safety protocols for hydrogen mixtures requires more rigorous operational oversight than a simple box furnace.
Volume Limitations
Tube furnaces often have a smaller working volume than standard air furnaces. This restricts the batch size of the phosphor that can be synthesized at one time, potentially impacting production throughput in favor of quality control.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure you select the correct equipment for your synthesis objectives, consider the following:
- If your primary focus is synthesizing NRBBO:Eu2+: You must use a tube furnace capable of handling an N2/H2 mixture to ensure the Europium activator is properly reduced to Eu2+.
- If your primary focus is general oxide sintering: A standard air furnace is sufficient, as these materials typically do not require valence state reduction to function.
Success in this synthesis relies entirely on your ability to manipulate the chemical state of the activator through precise environmental control.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Tube Furnace (Preferred) | Standard Air Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Atmosphere Control | High (Sealed for N2/H2 mixtures) | Low (Ambient Oxygen) |
| Chemical Environment | Reducing (Removes Oxygen) | Oxidizing |
| Europium State | Facilitates reduction to Eu2+ | Maintains high-valence state |
| Primary Application | Specialized semiconductor/phosphor synthesis | General oxide sintering |
| Operational Complexity | High (Gas management & seals) | Low (Simple heating) |
Elevate Your Phosphor Synthesis with KINTEK
Precise atmospheric control is the difference between a high-efficiency phosphor and a failed batch. At KINTEK, we specialize in high-performance Tube, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to handle critical N2/H2 reducing atmospheres with ease.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, our lab furnaces are fully customizable to meet your unique temperature and gas flow requirements. Ensure the success of your NRBBO:Eu2+ synthesis and other advanced materials—contact KINTEK today to discuss your laboratory's needs.
Visual Guide
References
- Runtian Kang, Yuhua Wang. Chemical Pressure‐Induced FWHM Narrowing in Narrowband Green Phosphors for Laser Displays with Ultra‐High Saturation Thresholds. DOI: 10.1002/advs.202505385
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using a high-temperature tube furnace for rGO sensor fabrication? Precision & Performance
- What role does the gas management system play in a 70mm tube furnace? Essential for Precise Atmosphere Control
- What are the specific calcination requirements for a tubular resistance furnace for NCM622? Expert Synthesis Guide
- How do resistance heating tube furnaces generate heat? Master Precise Temperature Control
- What are the primary functions of a precision gas filtration device? Maximize Data Integrity in Drop Tube Furnaces
- Why must a tube furnace used for the pyrolysis of tungsten-based nanocomposites be equipped with a precision gas flow?
- How can operators prevent contamination in a horizontal electric furnace? Master Systematic Control for Purity
- What is the central design feature of a Quartz Tube Furnace? Unlock Real-Time Visual Monitoring in High-Temp Experiments



















