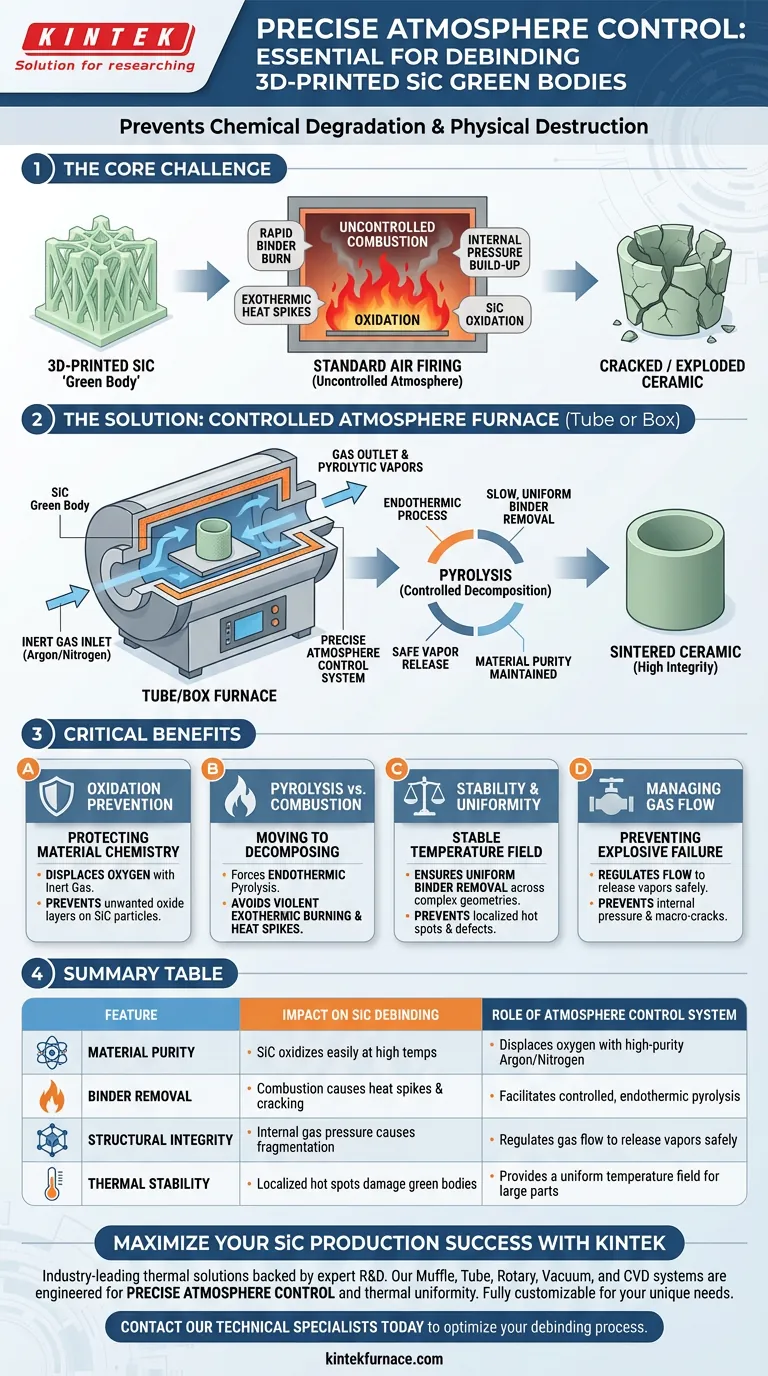
Precise atmosphere control is non-negotiable for debinding 3D-printed Silicon Carbide (SiC) because it prevents chemical degradation and physical destruction of the green body. Standard air firing causes SiC to oxidize and binders to burn uncontrollably; a specialized tube or box furnace utilizes an inert environment (such as high-purity Argon) to maintain material purity and ensure binders decompose at a safe, uniform rate.
The core challenge in debinding SiC is managing the transition from a fragile "green" part to a sintered ceramic. Without a controlled atmosphere, the rapid combustion of binders creates internal pressure and exothermic heat that will crack or explode the ceramic skeleton before it is fully formed.
The Critical Role of Oxidation Prevention
Protecting the Material Chemistry
Silicon Carbide is highly susceptible to oxidation at the elevated temperatures required for debinding and sintering.
If exposed to oxygen during this phase, the surface of the SiC particles will react, forming unwanted oxide layers.
The Necessity of an Inert Environment
To prevent this, tube and box furnaces are designed to replace the standard air atmosphere with inert gases like high-purity Argon or Nitrogen.
This strictly controlled environment ensures that the chemical composition of the SiC remains pure throughout the heating cycle.
Transforming Combustion into Pyrolysis
Moving from Burning to Decomposing
In an uncontrolled air environment, organic resin binders ignite and combust efficiently.
This combustion is an exothermic process, meaning it releases significant heat, causing temperature spikes within the part.
The Power of Endothermic Reactions
By introducing an inert atmosphere (like Nitrogen), the furnace forces the binders to undergo pyrolysis rather than combustion.
Pyrolysis is generally endothermic (absorbing heat) and much slower, preventing the sudden, violent release of energy associated with burning.
Preventing Explosive Failure
Rapid combustion generates gas faster than it can escape the dense ceramic matrix.
This builds up immense internal pressure, leading to macro-cracks or even the explosive fragmentation of the green body.
Controlled pyrolysis ensures pyrolytic gases are released smoothly, preserving the structural integrity of the part.
Stability and Uniformity
The Stable Temperature Field
Tube and box furnaces with atmosphere control provide a highly stable thermal environment.
This stability allows for a uniform removal rate of binders across the entire geometry of the part, rather than localized hot spots.
Handling Complex Geometries
For large or thick-walled 3D-printed parts, the risk of defect formation is significantly higher.
The precise control over gas flow and pressure ensures that even deep, internal sections of the part debind without creating micro-defects or voids.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
The Risk of "Good Enough" Sealing
Standard furnaces without precise atmosphere capabilities often suffer from leakage.
Even trace amounts of oxygen entering the chamber can compromise the surface quality of SiC, rendering the part useless for high-performance applications.
Flow Rate Mismanagement
It is not enough to simply fill the chamber with gas; the flow must be regulated.
Insufficient flow may fail to clear pyrolytic byproducts, while excessive flow can disturb the thermal uniformity. High-precision flow meters are essential to balance this equation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When selecting a furnace for your SiC application, consider your specific constraints:
- If your primary focus is Material Purity: Prioritize a furnace with vacuum capabilities and high-purity Argon compatibility to strictly eliminate oxidation.
- If your primary focus is Structural Integrity of Thick Parts: Prioritize a system with advanced gas flow regulation to manage the slow release of pyrolytic gases and prevent pressure cracking.
Control the atmosphere, and you control the yield; neglect it, and you are simply burning expensive material.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Impact on SiC Debinding | Role of Atmosphere Control System |
|---|---|---|
| Material Purity | SiC oxidizes easily at high temperatures | Displaces oxygen with high-purity Argon/Nitrogen |
| Binder Removal | Combustion causes heat spikes and cracking | Facilitates controlled, endothermic pyrolysis |
| Structural Integrity | Internal gas pressure causes fragmentation | Regulates gas flow to release pyrolytic vapors safely |
| Thermal Stability | Localized hot spots damage green bodies | Provides a uniform temperature field for large parts |
Maximize Your SiC Production Success with KINTEK
Don't let oxidation or thermal stress ruin your high-performance 3D-printed ceramics. KINTEK provides industry-leading thermal solutions backed by expert R&D and manufacturing. Our Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems are engineered for the precise atmosphere control and thermal uniformity required for complex Silicon Carbide applications. Whether you need to eliminate oxygen contamination or manage delicate pyrolysis cycles, our systems are fully customizable to meet your unique laboratory or production needs.
Ready to optimize your debinding process? Contact our technical specialists today to discover how our high-temperature furnace technology can enhance your material yields.
Visual Guide
References
- Arash Kariminejad, Mart Viljus. Effect of thermal shock treatment parameters on the efficiency of WC-Co cermet recycling. DOI: 10.1063/5.0189330
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the significance of atmosphere control and the heating ramp rate in a reduction furnace for Ni-WOx catalysts?
- What are the main purposes of using an inert atmosphere? Prevent Oxidation and Ensure Process Safety
- How does an inert atmosphere furnace work? Master Controlled Heating for Oxidation-Free Results
- What is the function of a high-temperature pyrolysis furnace in the preparation of magnetic Fe3O4/biochar nanoparticles?
- How do industrial vacuum or atmosphere furnaces improve Inconel 718 after WAAM? Optimize Strength and Microstructure
- How does atmosphere control affect homogenization annealing of low alloy steel? Achieve Precise Chemical Integrity
- What are some key applications of low vacuum atmosphere furnaces? Boost Industrial Efficiency with Cost-Effective Heat Treatment
- What function does a precision annealing furnace serve for molten glass? Prevent Cracking and Ensure Sample Stability



















