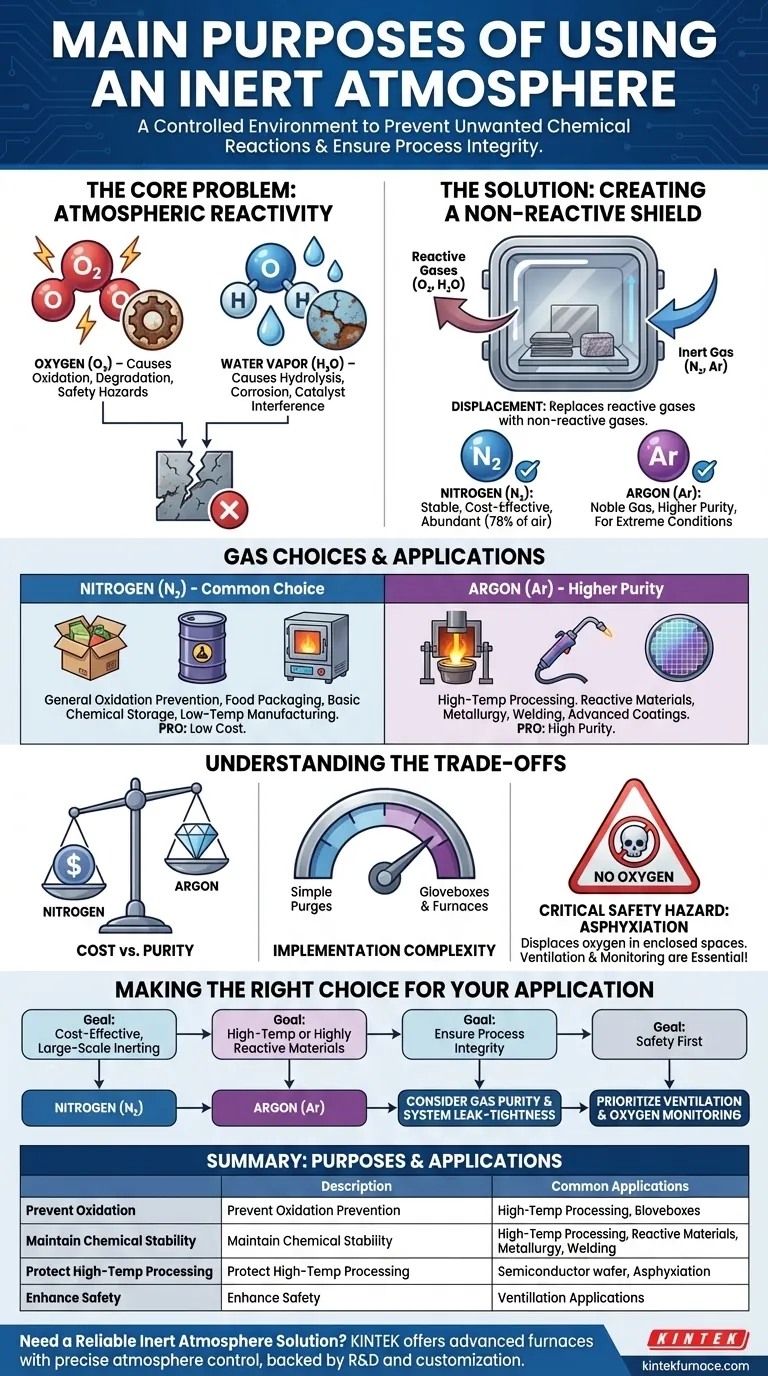
At its core, an inert atmosphere is a controlled environment designed to prevent unwanted chemical reactions. Its primary purposes are to stop degradation from oxidation, maintain the chemical stability of sensitive materials, and protect substances during high-temperature processing. By replacing reactive gases like oxygen and water vapor with a non-reactive gas, it creates a safe space for processes that would otherwise fail.
The fundamental goal of an inert atmosphere is to eliminate the variables of atmospheric chemistry. By removing reactive gases, you ensure that the only chemical changes occurring are the ones you intend, protecting your materials and the integrity of your process.

The Core Problem: Atmospheric Reactivity
To understand the solution, we must first define the problem. The standard air we exist in is a mixture of gases, but two components are responsible for the vast majority of unwanted chemical reactions.
The Role of Oxygen
Oxygen is highly electronegative and seeks to react with other elements in a process called oxidation. This is the same reaction that causes iron to rust, cut apples to brown, and fires to burn.
In a technical context, uncontrolled oxidation can ruin chemical syntheses, degrade product quality, and create significant safety hazards.
The Impact of Water Vapor
Moisture is another pervasive and reactive component of the atmosphere. Water can hydrolyze sensitive compounds, meaning it chemically breaks them down.
Water vapor also acts as a catalyst for corrosion and can interfere with a wide range of surface-sensitive processes, from semiconductor manufacturing to advanced coatings.
The Solution: Creating a Non-Reactive Shield
An inert atmosphere displaces these reactive gases, replacing them with a gas that will not participate in chemical reactions.
What Makes a Gas "Inert"?
True inertness comes from atomic stability. The noble gases (like Argon and Helium) have a full outer shell of electrons, making them extremely non-reactive.
Nitrogen gas (N₂), while not a noble gas, is also very stable due to the powerful triple bond holding its two atoms together. It takes a tremendous amount of energy to break this bond, making it effectively inert for most common applications.
Common Choice: Nitrogen (N₂)
Nitrogen is the workhorse of inert atmospheres. It makes up roughly 78% of our atmosphere, making it abundant and highly cost-effective to isolate and use.
It is sufficient for a vast range of applications, including food packaging, basic chemical storage, and preventing oxidation in many low-temperature manufacturing processes.
Higher Purity Choice: Argon (Ar)
Argon, a true noble gas, is more inert than nitrogen. It is used when conditions are more extreme or materials are exceptionally sensitive.
For example, in high-temperature metallurgy or welding exotic metals, nitrogen can sometimes react to form unwanted nitrides. Argon will not, making it the safer choice for ensuring process purity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing and implementing an inert atmosphere is not without its challenges. It requires a careful balancing of goals and resources.
Cost vs. Purity
The primary trade-off is between cost and the required level of inertness. Nitrogen is significantly cheaper than Argon. For many applications, the marginal benefit of using Argon does not justify the added expense.
Implementation Complexity
Creating an inert environment requires specialized equipment. This can range from simple gas purges in a reaction flask to sophisticated gloveboxes or controlled-atmosphere furnaces. The cost and complexity of this equipment must be factored into the process.
Critical Safety Hazard: Asphyxiation
This is the most important consideration. Inert gases are not toxic, but they displace oxygen. In an enclosed or poorly ventilated space, a leak can quickly reduce oxygen levels to a point that is immediately dangerous to human life. Proper ventilation and oxygen monitoring are non-negotiable safety protocols.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your specific goal dictates the best approach to creating and using an inert atmosphere.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective, large-scale inerting: Nitrogen is almost always the most practical and economical choice for preventing general oxidation.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature processes or highly reactive materials: Argon is the superior choice, as it remains inert under conditions where nitrogen might react.
- If your primary focus is ensuring process integrity: You must consider not just the gas, but the purity of that gas and the leak-tightness of your system.
- If your primary focus is safety: Always prioritize robust ventilation and continuous oxygen monitoring, as all inert gases pose a significant asphyxiation risk.
By understanding these principles, you can select the appropriate inert atmosphere to ensure the integrity, safety, and success of your process.
Summary Table:
| Purpose | Description | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Prevent Oxidation | Shields materials from oxygen to avoid rust, degradation, and unwanted reactions. | Food packaging, chemical storage, metal processing. |
| Maintain Chemical Stability | Preserves sensitive compounds by eliminating reactive gases like water vapor. | Semiconductor manufacturing, advanced coatings, chemical synthesis. |
| Protect During High-Temp Processing | Ensures material integrity in heat treatments by using non-reactive gases. | Metallurgy, welding, furnace operations. |
| Enhance Safety | Reduces risks of asphyxiation and chemical hazards with proper gas handling. | Laboratories, industrial settings with enclosed spaces. |
Need a reliable inert atmosphere solution for your lab? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace systems, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise alignment with your unique experimental requirements, enhancing process integrity and safety. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your specific applications and deliver tailored solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is nitrogen used for in a furnace? Prevent Oxidation and Control Heat Treatment Quality
- How does the inert atmosphere heat treating process work? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Material Quality
- How does nitrogen atmosphere heat treatment improve surface strengthening? Enhance Durability and Performance
- How does a chemically inert atmosphere function in a furnace? Prevent Oxidation and Ensure Material Purity
- What does inert mean in furnace atmospheres? Protect materials from oxidation with inert gases.



















