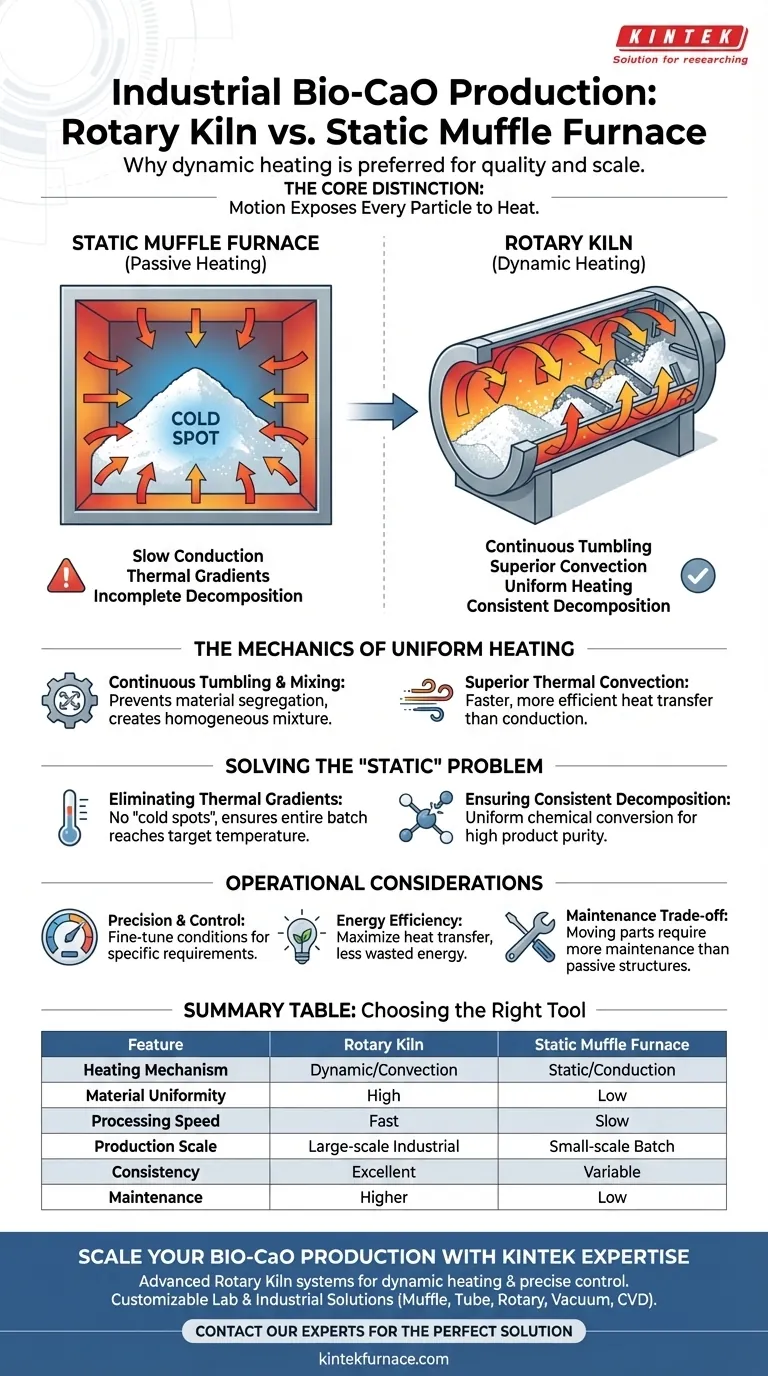
A rotary kiln is the preferred choice for industrial bio-calcium oxide production primarily due to its dynamic heating mechanism. Unlike a static muffle furnace where material remains stationary, a rotary kiln utilizes a rotating, tilted design to continuously tumble and mix the raw materials. This movement facilitates superior thermal convection and heat transfer, ensuring that large batches of powder are heated uniformly and preventing the issue of incomplete decomposition.
The core distinction is that static furnaces rely on slow heat conduction through a stationary pile, while rotary kilns use physical motion to expose every particle to the heat source. This ensures the complete chemical breakdown required for high-quality bio-CaO.
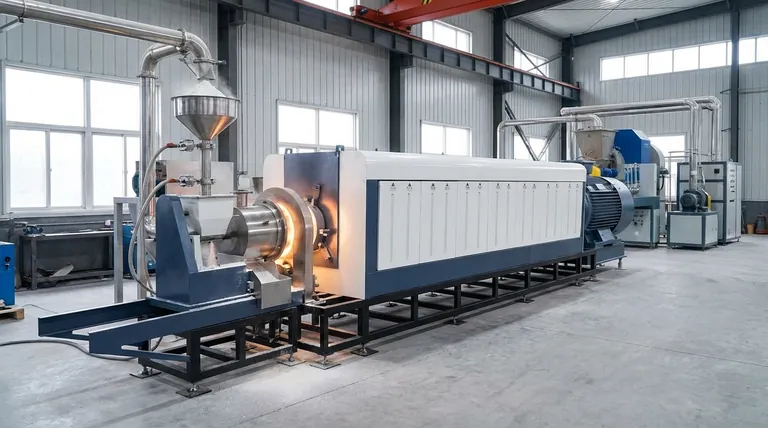

The Mechanics of Uniform Heating
Continuous Tumbling and Mixing
The defining feature of the rotary kiln is its rotating, tilted tube structure. This design forces the raw material to be in constant motion throughout the process.
Instead of resting in a static layer, the powder is continuously turned over. This dynamic tumbling creates a homogeneous mixture, preventing material segregation.
Superior Thermal Convection
Because the material is constantly moving, heat is transferred via convection rather than just conduction. This results in a much faster and more efficient heating process compared to static equipment.
In a static muffle furnace, heat must slowly travel from the outside of the pile to the center. The rotary kiln eliminates this barrier by constantly exposing fresh material to the heat source.
Solving the "Static" Problem
Eliminating Thermal Gradients
A major failure point in static muffle furnaces is uneven heat conduction. When processing large industrial batches, the outer layers of the material often reach the target temperature long before the center does.
This leads to "cold spots" within the batch. In the context of bio-CaO, this results in incomplete decomposition, yielding a product that is chemically inconsistent.
Ensuring Consistent Decomposition
The rotary kiln effectively solves the problem of incomplete calcination. By ensuring that every grain of powder experiences the same thermal conditions, the chemical conversion is uniform across the entire batch.
This consistency is critical for industrial applications where product purity and reliability are non-negotiable.
Operational Considerations and Efficiency
Precision and Control
Beyond movement, modern electric rotary kilns offer precise temperature control. They maintain a consistent radial temperature profile, which enhances the overall treatment effect.
This allows operators to fine-tune the processing conditions to the specific requirements of the bio-calcium oxide being produced.
Energy Efficiency
Electric rotary kilns are generally more energy-efficient than traditional combustion methods. By maximizing heat transfer through tumbling, less energy is wasted trying to penetrate static piles of material.
However, it is important to note the trade-off in complexity. A rotary kiln involves moving mechanical parts (motors, gears, seals) that require more maintenance than the passive box structure of a muffle furnace.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
While the rotary kiln is the standard for industrial production, understanding your specific priorities helps clarify the decision.
- If your primary focus is absolute product uniformity: The rotary kiln is essential because its tumbling action eliminates the thermal gradients that cause inconsistent chemical conversion.
- If your primary focus is processing large volumes: The continuous, dynamic nature of the rotary kiln handles bulk powder loads far more effectively than the limited batch capacity of static furnaces.
The rotary kiln transforms calcination from a passive waiting game into an active, controlled process that guarantees industrial-grade quality.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Rotary Kiln | Static Muffle Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Mechanism | Dynamic (Tumbling/Convection) | Static (Conduction) |
| Material Uniformity | High (Homogeneous mixing) | Low (Thermal gradients) |
| Processing Speed | Fast (Efficient heat transfer) | Slow (Passive heating) |
| Production Scale | Large-scale Industrial | Small-scale Batch/Lab |
| Consistency | Excellent (No cold spots) | Variable (Potential incomplete decomposition) |
| Maintenance | Higher (Mechanical parts) | Low (Passive structure) |
Scale Your Bio-CaO Production with KINTEK Expertise
Don't let thermal gradients compromise your product purity. KINTEK’s advanced Rotary Kiln systems are engineered to provide the dynamic heating and precise control necessary for high-quality bio-calcium oxide production.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of lab and industrial high-temperature solutions—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all fully customizable to meet your unique processing needs.
Ready to optimize your calcination process? Contact us today to consult with our experts and find the perfect furnace solution for your application.
Visual Guide
References
- Suwanan Chuakham, Apipong Putkham. Scalable production of bio-calcium oxide via thermal decomposition of solid - hatchery waste in a laboratory-scale rotary kiln. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-84889-w
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the basic structure and operation principle of a rotary furnace? Master Continuous Thermal Processing
- What are the equipment requirements for CO2 activation? Optimize Your Tube & Rotary Furnaces
- What types of materials are suitable for processing in rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Free-Flowing Powders and Granules
- What advantages do indirect-fired rotary kilns offer across industries? Achieve Purity and Precision in Thermal Processing
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of rotary furnace? A Guide to Superior Process Uniformity
- What is a rotary furnace and what is its primary function? Achieve Uniform High-Temperature Processing
- What are the structural features of a rotary tube furnace? Uncover Key Components for Uniform Thermal Processing
- How does customization benefit the use of rotary kilns? Boost Efficiency and Quality with Tailored Solutions



















