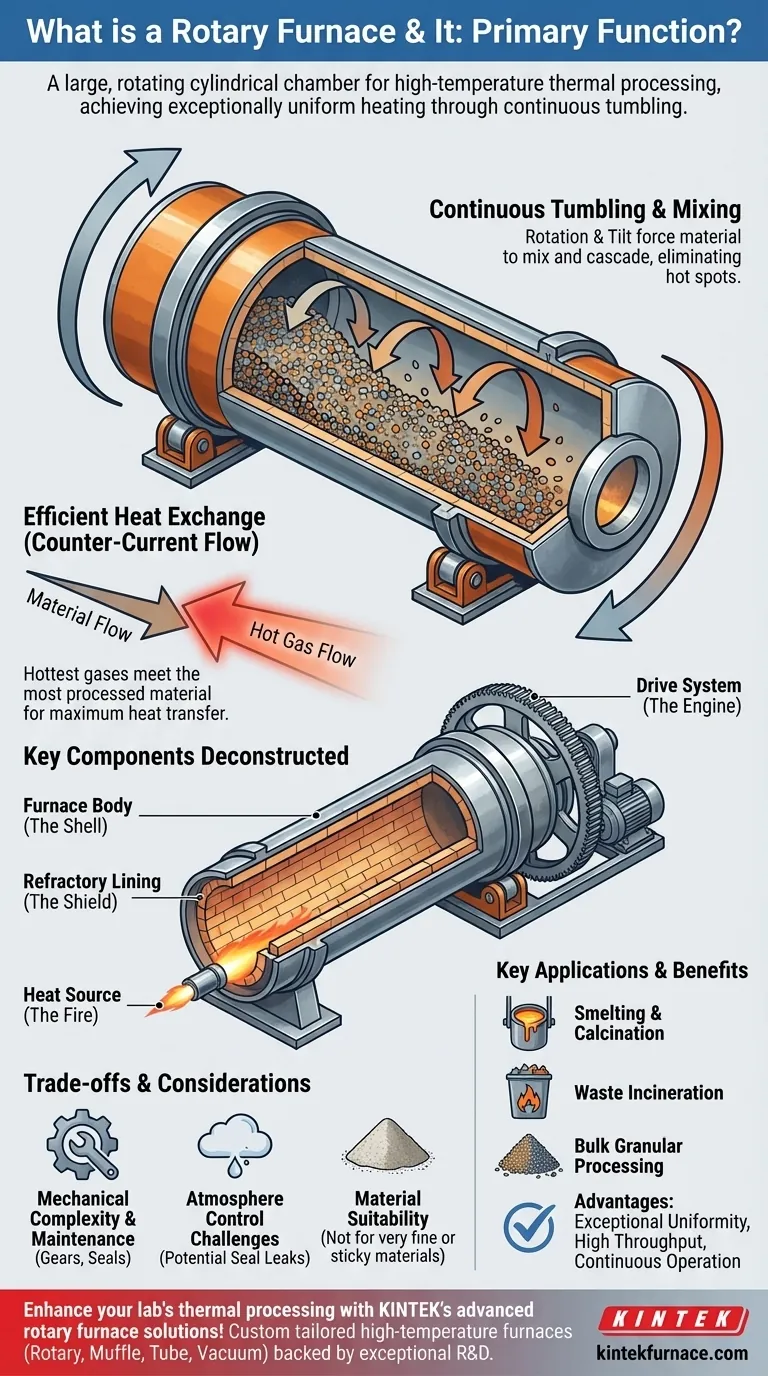
At its core, a rotary furnace is a large, rotating cylindrical chamber designed for high-temperature thermal processing of materials. Its primary function is to achieve exceptionally uniform heating by continuously tumbling the material as it moves from one end of the furnace to the other. This dynamic process makes it indispensable for applications like smelting, calcination, and waste incineration.
The unique value of a rotary furnace is not just its ability to reach high temperatures, but its use of mechanical motion. By combining rotation with a slight tilt, it forces materials to mix and cascade, eliminating hot spots and ensuring every particle undergoes the same consistent thermal treatment.

How a Rotary Furnace Achieves Uniform Processing
The effectiveness of a rotary furnace comes from its simple yet powerful design principles. It leverages gravity and motion to create a processing environment that is impossible to achieve in a static, or stationary, furnace.
The Principle of Rotation and Tilt
A rotary furnace is essentially a long, barrel-shaped drum that rotates slowly on its axis. The entire structure is mounted at a slight angle to the horizontal.
This tilt is critical. It ensures that material fed into the higher end will gradually travel the length of the cylinder and exit at the lower end, enabling continuous processing.
Continuous Tumbling and Mixing
As the furnace rotates, the material inside is lifted up the side of the cylinder before cascading, or tumbling, back down. This constant motion intimately mixes the material.
This tumbling action prevents the formation of a static top layer that would otherwise shield the material underneath. Every particle is repeatedly exposed to the heat source, ensuring a homogenous final product.
Efficient Heat Exchange
Most rotary furnaces employ a counter-current flow system for maximum thermal efficiency.
In this setup, the material moves downhill while the hot gases from the burner or heating elements are directed uphill, flowing in the opposite direction. This ensures that the hottest gases meet the most processed material, maximizing heat transfer throughout the length of the furnace.
Deconstructing the Key Components
A rotary furnace is a system of integrated parts, each with a specific role in containing heat and creating motion.
The Furnace Body (The Shell)
This is the outer cylindrical structure, typically fabricated from heavy-duty welded steel plate. The size can range from small lab-scale units to massive industrial kilns over 200 meters long.
The Refractory Lining (The Shield)
The inside of the steel shell is lined with refractory materials, such as high-temperature bricks or castable cement. This lining serves two purposes: it insulates the steel shell from extreme process temperatures and protects it from chemical corrosion and abrasion.
The Drive System (The Engine)
A large ring gear, known as a girth gear, is typically fixed to the outside of the furnace body. A smaller pinion gear, driven by a motor, engages this ring gear to rotate the entire cylinder.
The speed of rotation is often variable, allowing operators to control how long the material resides in the furnace and the degree of mixing it undergoes.
The Heat Source (The Fire)
Heat is supplied by powerful burners located at one end of the furnace (typically the discharge end in a counter-current system). These can be fueled by gas, oil, or pulverized coal.
Alternatively, some specialized rotary furnaces use electrical heating elements for more precise temperature control or when a clean, combustion-free atmosphere is required.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, the rotary furnace design comes with inherent complexities that must be considered.
Mechanical Complexity and Maintenance
The rotating nature of the furnace involves large moving parts like gears, support rollers (trunnions), and seals. These components require consistent lubrication and maintenance to prevent wear and ensure reliable operation, making them more complex than static furnaces.
Atmosphere Control Challenges
Maintaining a perfectly sealed, controlled atmosphere inside the furnace can be difficult. The dynamic seals at the feed and discharge ends, where the rotating cylinder meets stationary ductwork, are potential points for leaks.
Material Suitability
The tumbling action is not suitable for all materials. Very fine powders can become entrained in the flowing gas and carried out of the furnace, while sticky or agglomerating materials can build up on the refractory lining, reducing efficiency and requiring manual removal.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting a rotary furnace depends entirely on your material characteristics and production goals.
- If your primary focus is bulk processing of granular materials: A rotary furnace is an ideal choice for achieving high throughput and consistent quality in processes like mineral calcination or ore reduction.
- If your primary focus is precise atmosphere control for small, sensitive parts: A static batch furnace or a sealed tube furnace might offer better control and less mechanical complexity for your application.
- If your primary focus is maximum thermal efficiency for very high volumes: The continuous operation and counter-current heat exchange of a large rotary kiln are unmatched in industries like cement manufacturing.
Understanding these core principles allows you to select the right thermal processing technology by aligning its strengths with your specific material and production goals.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Achieves uniform high-temperature processing through continuous tumbling and mixing of materials. |
| Key Applications | Smelting, calcination, waste incineration, and bulk processing of granular materials. |
| Design Principle | Rotating cylindrical chamber with a slight tilt for material movement and counter-current heat flow. |
| Advantages | Exceptional heating uniformity, high throughput, efficient heat exchange, and continuous operation. |
| Limitations | Mechanical complexity, maintenance needs, challenges in atmosphere control, and unsuitability for fine or sticky materials. |
Enhance your lab's thermal processing with KINTEK's advanced rotary furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnaces tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Rotary Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Tube Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can optimize your processes and deliver superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- What are the benefits of continuous sample movement in rotary tube furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency
- How is the structure of a rotary tube furnace characterized? Discover Its Key Components and Benefits
- What are some applications of rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Continuous High-Temperature Material Processing
- What are the main advantages of rotary tube furnaces? Achieve Superior Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- How do rotary tube furnaces support real-time monitoring and continuous processing? Boost Efficiency with Continuous Flow & Live Observation



















