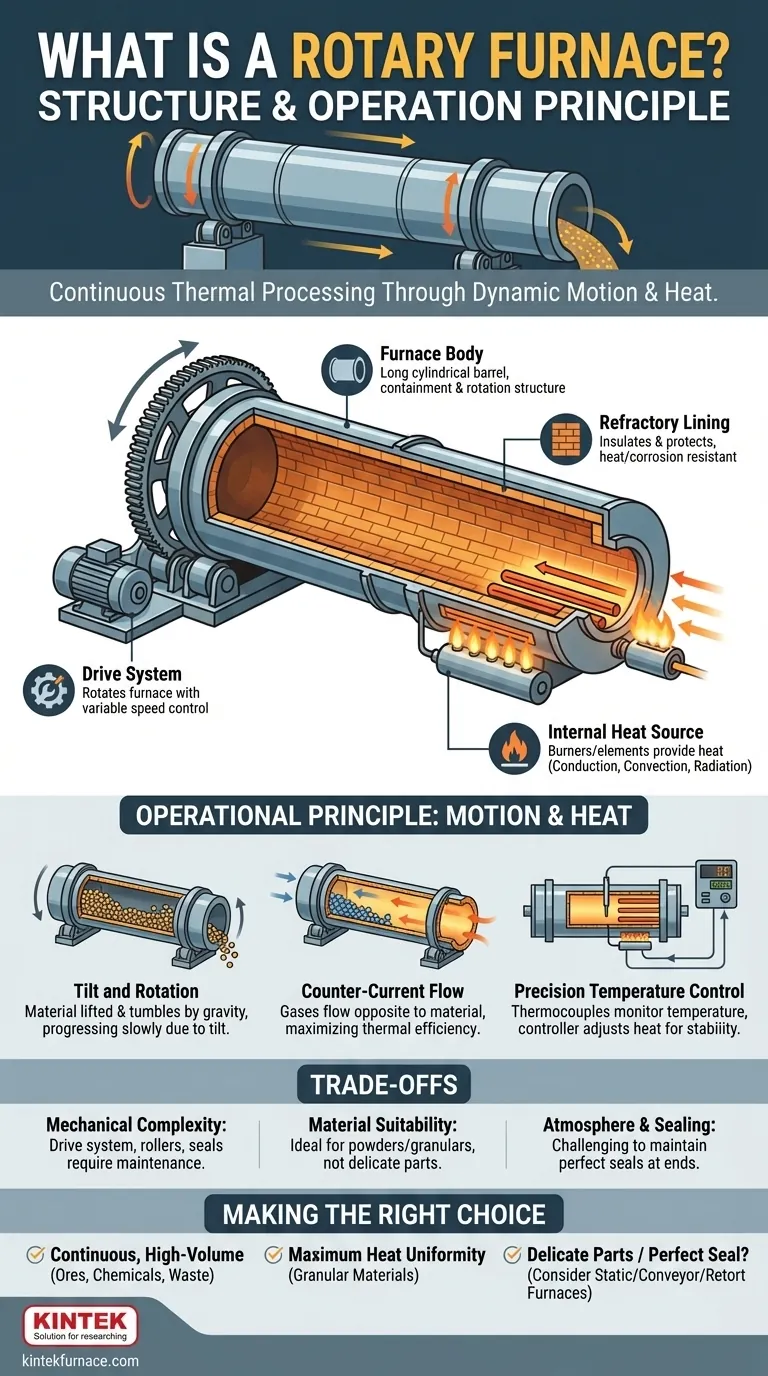
At its core, a rotary furnace is a cylindrical thermal processing unit designed to tumble and mix materials as they are heated. It consists of a barrel-shaped chamber, tilted at a slight angle, that rotates on its axis. This combination of tilt and rotation ensures materials move continuously from the higher entry point to the lower exit point while being uniformly exposed to heat.
The fundamental principle of a rotary furnace is to use mechanical motion—rotation and tumbling—to overcome the primary challenge of static heating: uneven temperature distribution. This design transforms heat treatment from a stationary batch process into a dynamic, continuous flow, ensuring every particle receives consistent thermal exposure.
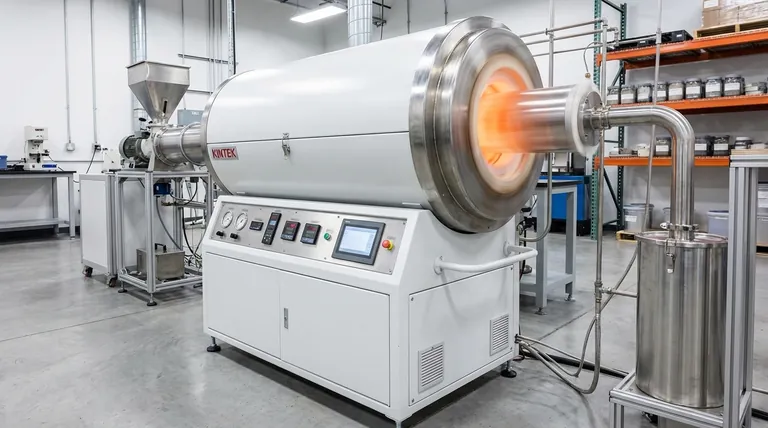

Deconstructing the Rotary Furnace: Key Components
A rotary furnace's effectiveness stems from the interplay of four primary components. Each is engineered for a specific function, from structural integrity to thermal control.
The Furnace Body
The main structure is a long, cylindrical barrel or drum, often constructed from heavy-duty welded steel plate. In industrial applications, these bodies can be extremely large, sometimes reaching lengths of over 200 meters.
The Refractory Lining
The interior of the steel body is protected by a refractory lining. This layer, made of materials like specialized bricks, castable cement, or moldable substances, serves two critical purposes: it insulates the steel shell from extreme internal temperatures and protects it from chemical corrosion by the process materials.
The Drive System
The furnace is rotated by a powerful drive system, typically a large gear assembly or a set of driven rollers. Modern systems feature variable speed control, allowing operators to precisely manage the residence time of the material inside the furnace by adjusting the rotation speed.
The Internal Heat Source
Heat is generated either by gas burners or electric heating elements. This thermal energy is transferred to the material through a combination of conduction (contact with the hot furnace wall), convection (contact with hot gases), and radiation (from the walls and flames).
The Operational Principle: A Symphony of Motion and Heat
The operation of a rotary furnace is a continuous, controlled process that leverages physics to achieve its goal.
The Role of Tilt and Rotation
Material is fed into the elevated end of the furnace. As the furnace rotates, the material is lifted up the side of the cylinder wall until gravity causes it to tumble back down. This constant mixing, combined with the gentle slope of the furnace, ensures the material progresses slowly and uniformly toward the discharge end.
The Counter-Current Flow Principle
For maximum thermal efficiency, hot gases are typically passed through the furnace in a counter-current flow. This means the gases enter at the material discharge end and exit at the material feed end. This setup ensures that the hottest gases make contact with the hottest material, creating a steep temperature gradient that maximizes heat transfer along the entire length of the furnace.
Precision Temperature Control
The internal temperature is monitored by thermocouples, which convert heat into electrical signals. These signals are sent to a temperature controller that compares the actual temperature to the desired setpoint. The controller then automatically adjusts the power to the heating elements or the fuel flow to the burners to maintain a stable and precise thermal environment.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, the design of a rotary furnace presents specific trade-offs that must be considered.
Mechanical Complexity
The rotating nature of the furnace introduces significant mechanical complexity compared to a static furnace. The drive system, support rollers, and seals for the rotating shell all require regular maintenance and are potential points of failure.
Material Suitability
The tumbling action, while excellent for powders, granulars, and sludges, is not suitable for all materials. Delicate components or parts that could be damaged by abrasion or impact are not good candidates for this type of processing.
Atmosphere and Sealing
Maintaining a perfectly controlled atmosphere (e.g., inert or reducing) can be more challenging in a rotary furnace. The seals at the feed and discharge ends of a massive rotating cylinder are complex and can be a source of leaks if not properly designed and maintained.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the correct furnace technology depends entirely on your material and processing objectives.
- If your primary focus is continuous, high-volume processing: The rotary furnace is an ideal choice for materials like ores, cements, chemicals, and waste products that benefit from a non-stop workflow.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum heat uniformity: The constant mixing action of a rotary furnace provides a level of thermal consistency for granular materials that is difficult to achieve in a static batch furnace.
- If your primary focus is processing delicate parts or requires a perfect seal: You should consider alternative technologies like a static box furnace, a conveyor belt furnace, or a retort furnace.
Ultimately, understanding the interplay between motion and heat is the key to leveraging the power of a rotary furnace for your application.
Summary Table:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Furnace Body | Cylindrical structure for material containment and rotation |
| Refractory Lining | Insulates and protects from high temperatures and corrosion |
| Drive System | Rotates the furnace with variable speed for control |
| Heat Source | Provides heat via burners or elements for conduction, convection, radiation |
Ready to optimize your thermal processing with a custom rotary furnace? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Rotary Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Tube Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental needs. Whether you're in mining, chemicals, or materials science, we ensure efficient, uniform heating for continuous operations. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your lab's performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How do rotary tube furnaces support real-time monitoring and continuous processing? Boost Efficiency with Continuous Flow & Live Observation
- What are the key features of rotary tube furnaces regarding heat treatment? Achieve Uniform Heating and High Throughput
- What are the main advantages of rotary tube furnaces? Achieve Superior Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- How is the structure of a rotary tube furnace characterized? Discover Its Key Components and Benefits
- What are the key features of a rotary furnace? Achieve Superior Uniformity and Control



















