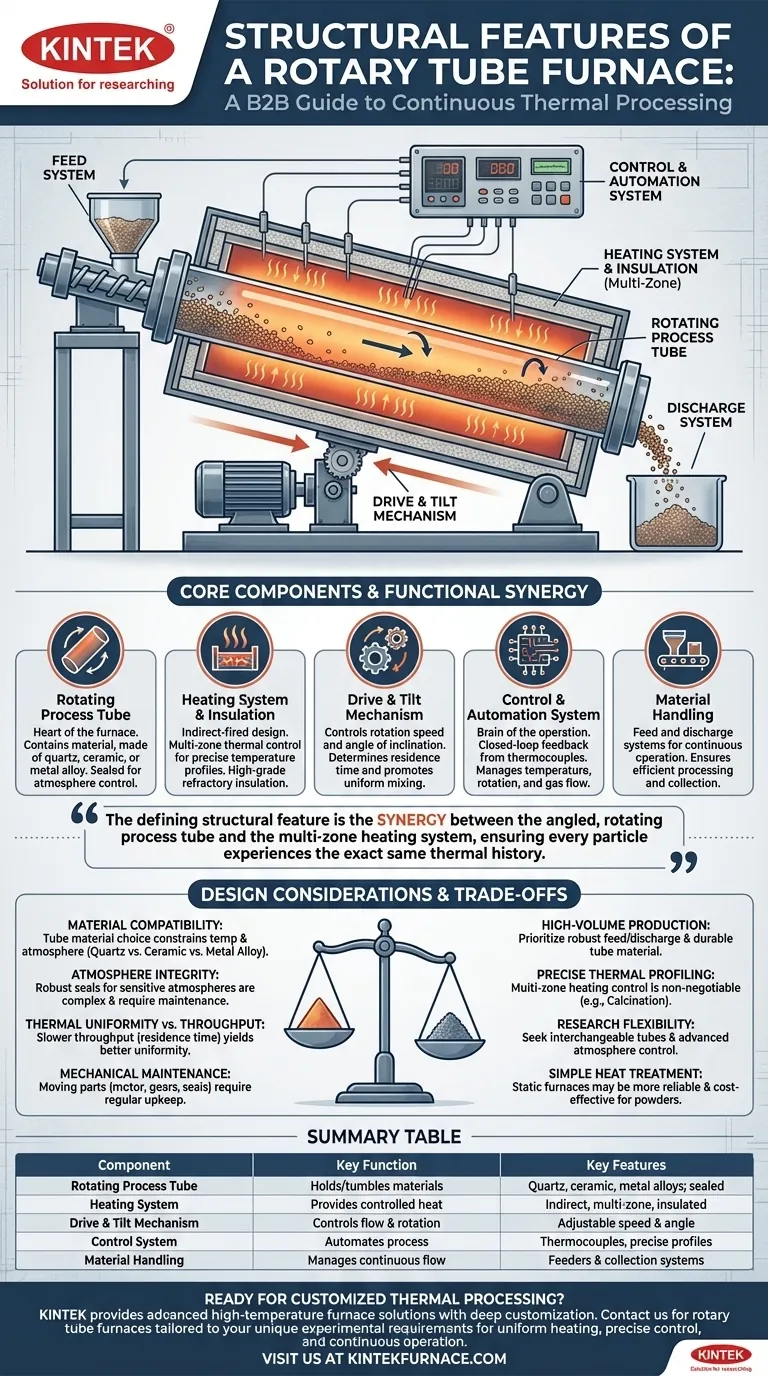
At its core, a rotary tube furnace is an integrated system designed for continuous, uniform thermal processing of materials. Its fundamental structure consists of a rotating cylindrical tube housed within a heating chamber, a drive mechanism to control rotation, and a sophisticated system to manage temperature and atmosphere.
The defining structural feature is not any single component, but the synergy between the angled, rotating process tube and the multi-zone heating system. This combination is engineered to continuously tumble and transport material, ensuring every particle experiences the exact same thermal history.
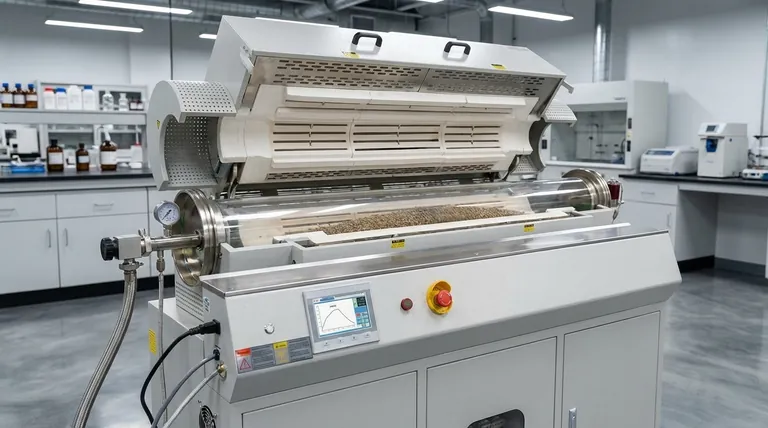

The Core Components: A Functional Breakdown
To understand a rotary tube furnace, you must look at how each part contributes to the primary goal of uniform, dynamic heating. The design is a direct reflection of its function.
The Rotating Process Tube
This is the heart of the furnace. It is a cylindrical tube, often made of quartz, ceramic (like alumina), or a high-temperature metal alloy, that contains the material being processed.
The tube is housed inside the main furnace body and is sealed at both ends to allow for atmosphere control, enabling processes in inert, reducing, or oxidizing environments.
The Heating System and Insulation
The furnace generates heat using either electric resistance heating elements or gas burners positioned around the process tube. This is an indirect-fired design, meaning the heat is applied to the outside of the tube, not directly to the material.
Crucially, many systems feature multiple thermal control zones along the length of the tube. Each zone has its own sensor and controller, allowing you to create a precise temperature profile that the material is exposed to as it travels. The entire assembly is lined with high-grade refractory insulation to ensure thermal efficiency and stable temperatures.
The Drive and Tilt Mechanism
An electric motor and gear system form the drive mechanism, providing precise control over the rotation speed of the process tube. This rotation is what ensures the material inside is constantly mixing and tumbling, preventing hot spots and promoting uniform heat transfer.
The entire furnace is typically mounted on a frame that allows for adjustable tilting. The angle of inclination, combined with the rotation speed, dictates the "residence time"—how long the material spends inside the furnace—a critical process parameter.
The Control and Automation System
This is the brain of the operation. Thermocouples measure the temperature in each heating zone and feed this data back to a central temperature controller.
The controller executes a programmed temperature profile by adjusting the power sent to the heating elements. This closed-loop system also manages the tube's rotation speed and can be integrated with gas flow controllers for full process automation.
Material Handling: Feed and Discharge
For continuous operation, a feed system (like a screw feeder or hopper) introduces raw material into the elevated end of the tube. As the tube rotates, the material tumbles its way down the incline.
At the lower discharge end, the processed material exits the furnace and is collected in a container, ready for the next stage.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Design Considerations
While powerful, the design of a rotary tube furnace presents specific trade-offs that you must consider for any given application.
Material Compatibility and Tube Selection
The choice of process tube material is a critical constraint. A quartz tube offers high purity but has a lower maximum temperature than a ceramic alumina tube. Metal alloy tubes can handle mechanical stress but may react with certain process materials or atmospheres at high temperatures.
Atmosphere Integrity vs. Mechanical Complexity
Achieving a perfectly sealed system for sensitive atmosphere control requires robust, and often complex, rotary seals. These seals are a point of mechanical wear and require more maintenance than the simple end caps on a static tube furnace.
Thermal Uniformity vs. Throughput
There is a direct relationship between residence time and thermal uniformity. Achieving the most uniform heating possible may require slowing down the throughput of the furnace by decreasing the tilt angle or rotation speed.
Maintenance of Mechanical Systems
Unlike a static box or tube furnace, a rotary furnace has moving parts. The drive motor, gears, and rotating seals are all subject to mechanical wear and tear, necessitating a more rigorous preventative maintenance schedule.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal furnace configuration is dictated entirely by your process objectives. By understanding the function of each structural feature, you can make a more informed decision.
- If your primary focus is high-volume continuous production: Prioritize a robust, automated feed and discharge system and a durable, long-life process tube material.
- If your primary focus is precise thermal profiling (e.g., calcination): A furnace with multiple, independently controlled heating zones is non-negotiable.
- If your primary focus is research with diverse materials: Seek a flexible system with interchangeable process tubes (e.g., quartz and alumina) and advanced atmosphere control capabilities.
- If your primary focus is simple heat treatment of powders: The mechanical complexity of a rotary furnace may be unnecessary; a static tube or box furnace could be a more reliable and cost-effective solution.
Understanding these structural principles empowers you to select and operate a furnace that perfectly aligns with your material processing objectives.
Summary Table:
| Component | Key Function | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Rotating Process Tube | Holds and tumbles materials for uniform heating | Made of quartz, ceramic, or metal alloys; sealed for atmosphere control |
| Heating System | Provides controlled heat to the tube | Indirect-fired design; multi-zone temperature control; refractory insulation |
| Drive and Tilt Mechanism | Controls rotation and material flow | Adjustable rotation speed and tilt angle for residence time management |
| Control System | Automates temperature and process parameters | Uses thermocouples and controllers for precise profiles and integration |
| Material Handling | Manages feed and discharge for continuous operation | Includes feeders and collection systems for efficient processing |
Ready to enhance your lab's thermal processing with a customized rotary tube furnace? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements for uniform heating, precise temperature control, and continuous operation. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can optimize your material processing and boost efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the basic construction of a rotary tube furnace? Key Components for Uniform Heating
- What are the main structural components of a rotary furnace? Explore Key Parts for Efficient Material Processing
- What factors should be considered when selecting a tube for a rotary tube furnace? Ensure Optimal Performance and Longevity
- What materials can be used to make the rotating tube assembly of these furnaces? Choose the Best for Your High-Temp Needs
- What supplementary features can enhance rotary tube furnace performance? Boost Efficiency with Precision Control



















