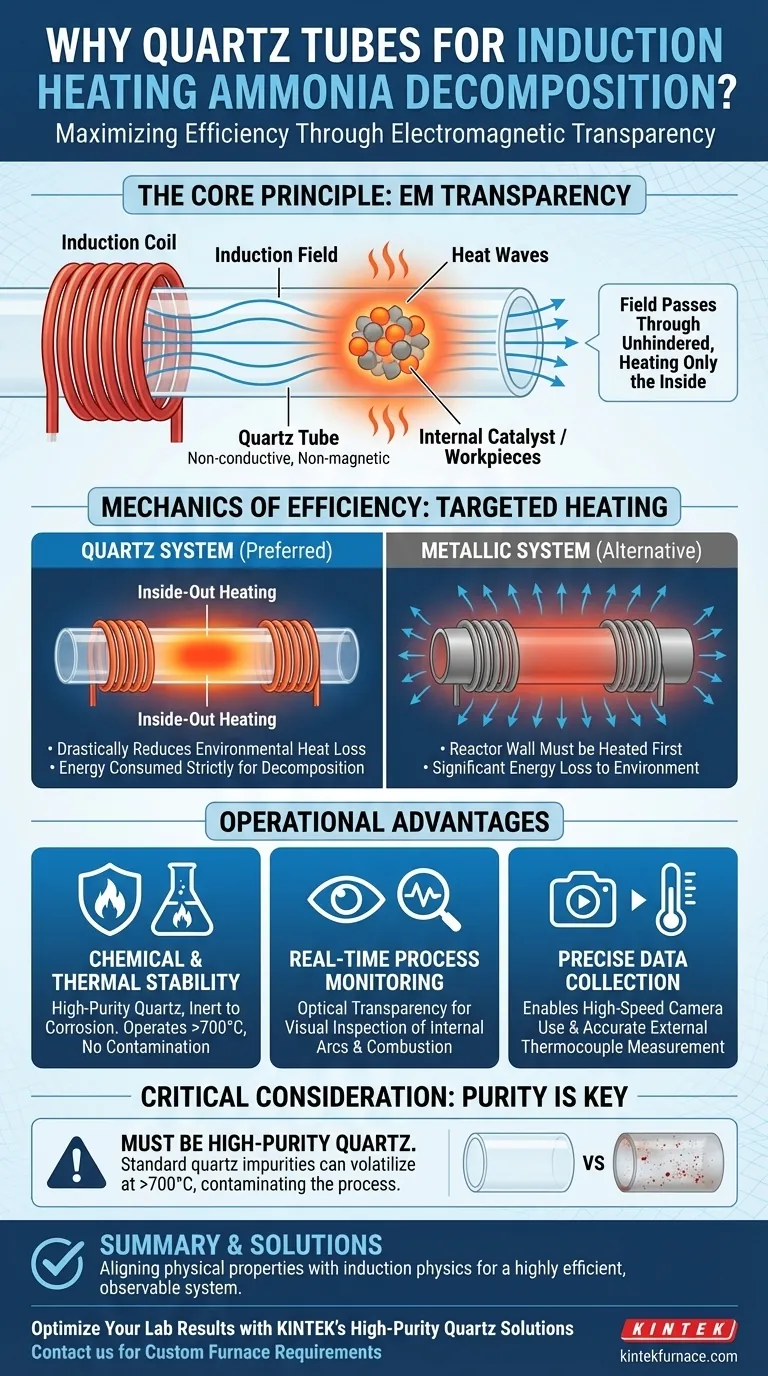
The preferred status of quartz tubes in induction heating ammonia decomposition is driven primarily by their electromagnetic transparency. Because quartz is both non-magnetic and non-conductive, it allows the electromagnetic field from the induction coil to pass directly through the reactor wall without resistance, ensuring that heat is generated only within the internal metal workpieces or catalysts.
By eliminating energy absorption in the reactor walls, quartz maximizes thermal efficiency and ensures the induction field is focused entirely on the decomposition process inside.
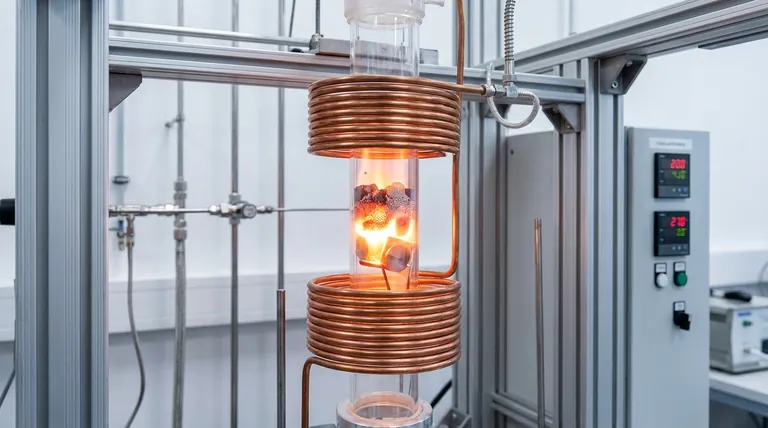

The Mechanics of Efficiency
Electromagnetic Transparency
Unlike metallic reactor tubes, quartz does not interact with the induction field. It effectively acts as an "invisible" window to electromagnetic waves.
This property prevents the tube itself from shielding the internal components or generating its own heat via eddy currents.
Targeted Energy Delivery
The induction coil's energy penetrates the quartz wall without loss to heat the internal catalysts or metal workpieces directly.
This "inside-out" heating mechanism drastically reduces environmental heat loss compared to systems where the reactor wall must be heated first.
Thermal Efficiency Gains
Because the reactor body remains cooler than the internal reaction zone, the overall thermal efficiency of the system is significantly increased.
Energy is consumed strictly for the decomposition reaction rather than for maintaining the temperature of the containment vessel.
Operational Advantages Beyond Heating
Chemical and Thermal Stability
Quartz offers exceptional chemical inertness, which prevents electrochemical corrosion even in high-temperature or plasma environments.
High-purity quartz allows the system to operate at temperatures exceeding 700°C without releasing volatile impurities that could contaminate the reaction.
Real-Time Process Monitoring
The optical transparency of quartz provides a distinct advantage for research and process control.
Operators can visually monitor the state of internal arcs or combustion evolution in real-time.
Precise Data Collection
The transparent walls facilitate the use of external high-speed cameras to study flame propagation and fire spread mechanisms.
It also permits the precise measurement of wall temperatures via externally attached thermocouples, ensuring accurate thermal management.
Critical Considerations
The Necessity of Purity
Not all quartz is suitable for these high-stress applications; the system specifically relies on high-purity quartz.
Standard quartz may contain impurities that could volatilize at operating temperatures (>700°C), potentially contaminating the ammonia decomposition process.
Structural Integrity vs. Thermal Load
While quartz has high thermal stability, it is chosen specifically to withstand the unique stresses of electrical arcs and internal plasma.
Engineers must ensure the specific grade of quartz selected matches the thermal shock requirements of the specific induction frequency and temperature ramp rates used.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When designing or selecting materials for your ammonia decomposition reactor, weigh your primary objectives:
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency: Prioritize quartz for its inability to absorb induction energy, ensuring all power is directed to the catalyst.
- If your primary focus is process research: Leverage the optical transparency of quartz to enable high-speed camera recording and direct visual inspection of reaction states.
- If your primary focus is purity and longevity: Ensure the use of high-purity quartz to prevent volatilization and resist electrochemical corrosion in the reaction zone.
By selecting quartz, you align the physical properties of your reactor vessel with the physics of induction heating for a highly efficient, observable system.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Quartz Tube Advantage | Impact on Induction Heating |
|---|---|---|
| EM Property | Electromagnetic Transparency | No shielding; field reaches internal workpieces directly. |
| Conductivity | Non-conductive/Non-magnetic | Prevents eddy currents and energy loss in reactor walls. |
| Visibility | Optical Transparency | Enables real-time monitoring and high-speed camera data. |
| Stability | High Chemical & Thermal Inertness | Resists corrosion and volatilization up to 700°C+. |
| Efficiency | Targeted Energy Delivery | Drastically reduces heat loss to the environment. |
Optimize Your Lab Results with KINTEK's High-Purity Quartz Solutions
Elevate your research and production efficiency with reactor components designed for precision. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK provides high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, along with customizable laboratory high-temperature furnaces. Whether you need electromagnetic transparency for induction heating or high-purity materials to prevent contamination, our engineering team is ready to tailor a solution to your unique needs.
Ready to enhance your thermal efficiency? Contact us today to discuss your custom furnace requirements.
Visual Guide
References
- Débora de Figueiredo Luiz, Jurriaan Boon. Use of a 3D Workpiece to Inductively Heat an Ammonia Cracking Reactor. DOI: 10.3390/suschem6040043
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What role does a non-consumable vacuum arc furnace play in Ti–Cu alloy preparation? Achieving High-Purity Synthesis
- Why is a non-consumable vacuum arc melting furnace used for AlCrTiVNbx alloys? Ensure Purity & Homogeneity
- What are electric arc furnaces and how do they work? Unlock Efficient Metal Melting Solutions
- Why use a vertical induction furnace for magnesium smelting? Achieve Continuous, High-Efficiency Production
- What are the advantages of using PLCs in induction furnaces? Boost Efficiency and Quality with Automation
- What are the primary advantages of using a Vacuum Induction Cold Crucible Furnace (VCCF)? Achieve Extreme Steel Purity
- Why are electromagnetic stirring and repeated melting cycles necessary? Achieving Homogeneity in (AlTiV)100−xCrx Alloys
- What are the key components of an induction-heated vacuum furnace? Uncover the Systems for Pure Melting



















