At its core, an electric arc furnace (EAF) is a high-temperature industrial furnace that melts materials using the intense heat of an electric arc, similar to a controlled bolt of lightning. It achieves extreme temperatures between 1500°C and 3500°C by passing a powerful electric current between conductive electrodes, making it a cornerstone technology for modern metal production, especially steel recycling.
The defining principle of an electric arc furnace is not just about generating immense heat, but how that heat is transferred. The choice between a direct or indirect arc design dictates the furnace's efficiency, its ability to mix materials, and its suitability for a specific industrial process.
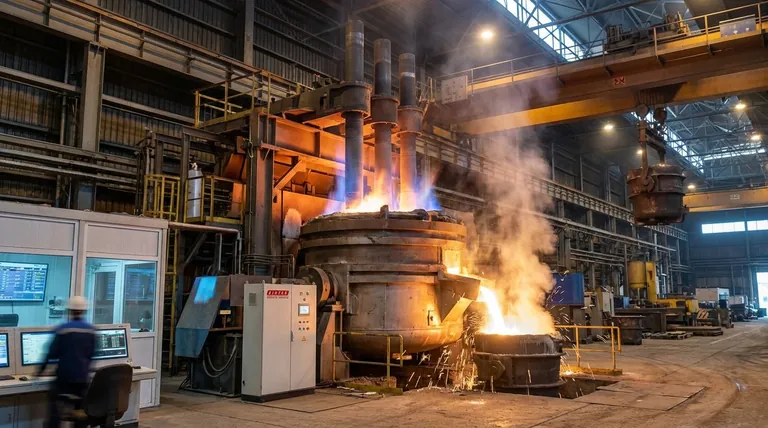

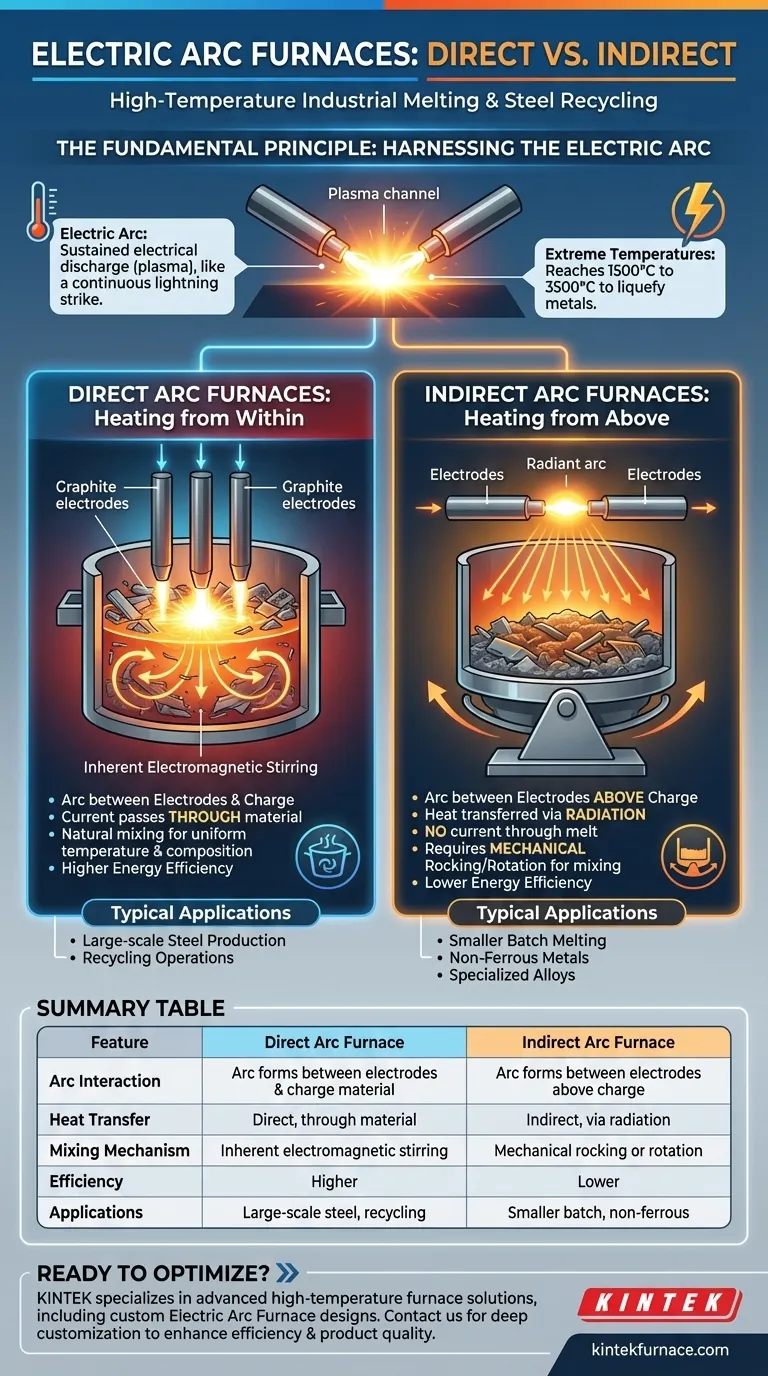
The Fundamental Principle: Harnessing the Electric Arc
An EAF's operation is based on a simple but powerful concept from physics. Understanding this is key to appreciating its function.
What is an Electric Arc?
An electric arc is a sustained electrical discharge through a gas, creating a plasma. Think of it as a continuous, man-made lightning strike. This arc converts electrical energy into an incredibly concentrated form of thermal energy, or intense heat.
Generating Extreme Temperatures
The plasma channel created by the arc can reach temperatures well over 3,000°C. This is far beyond the melting point of most industrial materials, including iron and steel, allowing the furnace to rapidly liquefy large volumes of solid metal scrap or other raw materials.
The Role of Electrodes
Electrodes, typically made of graphite, are the massive conductors that carry the high-power current into the furnace. By precisely controlling the distance between the electrodes and the material to be melted (the "charge"), a stable and powerful arc is established.
The Two Core Architectures: Direct vs. Indirect
The primary distinction between EAF types lies in how the arc interacts with the material being heated.
Direct Arc Furnaces: Heating from Within
In a direct arc furnace, the electric arc forms between the electrodes and the conductive charge material itself. The current passes directly through the material.
This direct path has a critical secondary benefit: it creates an inherent electromagnetic stirring action within the molten bath. This natural mixing helps ensure the melt achieves a uniform temperature and chemical composition, which is vital for producing high-quality metals like steel.
Indirect Arc Furnaces: Heating from Above
In an indirect arc furnace, the arc is struck between two electrodes positioned above the charge. The material is not part of the electrical circuit.
Heat is transferred to the material primarily through radiation from the arc. Because there is no current passing through the melt, there is no natural stirring. To compensate and prevent hot spots, these furnaces must be mechanically rocked or rotated to mix the material.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The choice between a direct and indirect arc furnace involves critical engineering trade-offs that impact efficiency, complexity, and final product quality.
Efficiency and Heat Transfer
Direct arc furnaces are generally more energy-efficient. Because the heat is generated within the charge itself, less energy is lost to the furnace walls and roof compared to the radiative heating method of an indirect arc furnace.
Process Control and Uniformity
The inherent stirring of a direct arc furnace provides a significant advantage for achieving a homogenous molten product. Indirect arc furnaces depend entirely on external mechanical systems for mixing, which adds a layer of complexity and a potential point of failure.
Scale and Application
Direct arc furnaces are dominant in large-scale operations like steel mills, where their efficiency and mixing capabilities can be fully leveraged. Indirect arc furnaces are typically smaller and better suited for foundry applications, melting non-ferrous metals, or processes where direct interaction with an electric current is undesirable.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The choice between a direct and indirect arc furnace depends entirely on your process requirements for scale, material type, and desired uniformity.
- If your primary focus is large-scale steel production or recycling: A direct arc furnace is the standard due to its superior thermal efficiency and the critical benefit of inherent electromagnetic stirring.
- If your primary focus is smaller batch melting or specialized alloys: An indirect arc furnace provides a simpler setup for melting materials without passing a current through them, provided you can accommodate the need for mechanical mixing.
By understanding precisely how each furnace architecture transfers energy, you can select the technology that best aligns with your industrial objectives.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Direct Arc Furnace | Indirect Arc Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Arc Interaction | Arc forms between electrodes and charge material | Arc forms between electrodes above charge |
| Heat Transfer | Direct, through material | Indirect, via radiation |
| Mixing Mechanism | Inherent electromagnetic stirring | Mechanical rocking or rotation |
| Efficiency | Higher energy efficiency | Lower energy efficiency |
| Typical Applications | Large-scale steel production, recycling | Smaller batch melting, non-ferrous metals |
Ready to optimize your metal melting process? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including custom electric arc furnace designs. With our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems tailored to your unique needs. Contact us today to discuss how our deep customization capabilities can enhance your efficiency and product quality. Get in touch now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- How has vacuum smelting impacted the development of superalloys? Unlock Higher Strength and Purity
- What role does a vacuum induction melting furnace play in Fe-5%Mn-C alloys? Ensure Chemical Integrity and High Purity
- What are the core functions of the High Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace? Optimize DD5 Superalloy Purification
- How does vacuum melting technology contribute to sustainability? Boost Durability and Recycling Efficiency
- Why is a Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace essential? Unlock Purity for Aerospace and Semiconductors



















