A programmable temperature control box furnace is indispensable for the pre-calcination of Bi-2223 powder because it provides the precise thermal environment needed to decompose residual impurities without damaging the material structure. By strictly managing temperature gradients, it ensures that nitrates and organic components are fully discharged while preventing the premature melting of sensitive, low-melting-point phases.
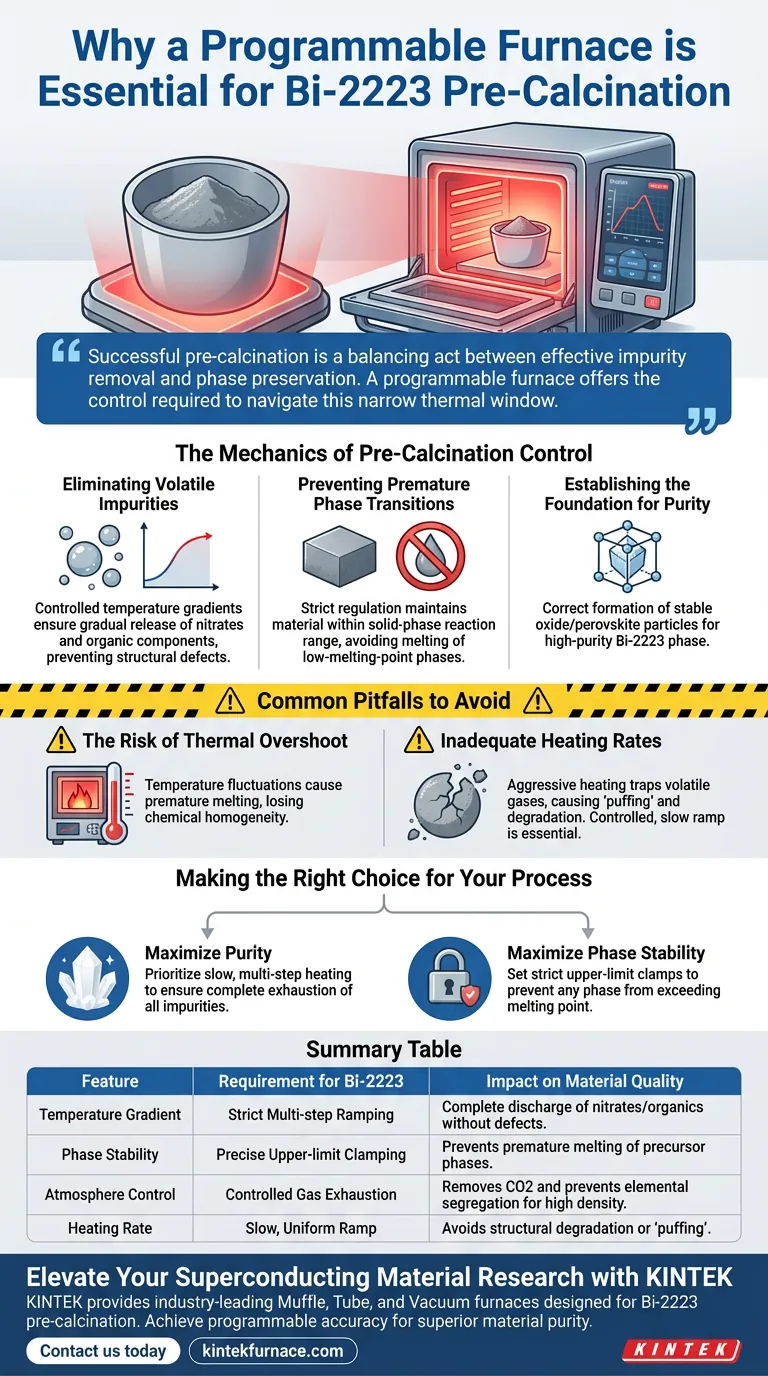
Successful pre-calcination is a balancing act between effective impurity removal and phase preservation. A programmable furnace offers the control required to navigate this narrow thermal window, establishing the necessary purity for high-performance superconductors.

The Mechanics of Pre-Calcination Control
Eliminating Volatile Impurities
The primary objective during pre-calcination is the removal of chemical byproducts. Precursor powders often contain residual nitrates and organic components that must be decomposed and discharged.
A programmable furnace allows for a specific, controlled temperature gradient. This ensures that these volatile components are released gradually rather than explosively, preventing structural defects in the powder.
Supplementary data indicates that this control is also vital for discharging carbon dioxide and other gases derived from carbonates. Ensuring these components are fully evacuated is critical for creating a dense, high-quality final product.
Preventing Premature Phase Transitions
Bi-2223 precursors contain phases with relatively low melting points. If the temperature is not strictly regulated, these phases can melt before the desired solid-state reactions occur.
Standard furnaces may suffer from local overheating, which triggers this premature melting. A programmable box furnace mitigates this by maintaining a uniform and stable thermal field.
By keeping the material within the intended solid-phase reaction range, the furnace preserves the stoichiometry required for the superconductor to function correctly.
Establishing the Foundation for Purity
The ultimate goal of pre-calcination is to prepare the material for the formation of the high-purity Bi-2223 phase. The pre-calcination stage creates the material foundation for subsequent processing.
If the initial decomposition is incomplete or if partial melting occurs, the purity of the final superconducting phase is compromised.
High-precision thermal control ensures that stable oxide or perovskite phase particles are formed correctly, paving the way for the complex solid-liquid transformations required in later sintering stages.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
The Risk of Thermal Overshoot
In non-programmable or lower-precision furnaces, temperature fluctuations are common. Even a brief spike in temperature can push the material past the melting point of specific precursor phases.
Once premature melting occurs, the chemical homogeneity of the powder is lost. This often results in irreversible segregation of elements, making it impossible to form the target Bi-2223 phase later.
Inadequate Heating Rates
Heating the material too quickly is as dangerous as overheating it. A programmable furnace allows the user to set specific heating rates.
If the heating rate is too aggressive, volatile gases (nitrates and CO2) may be trapped inside the particles or cause the material to "puff" and degrade. A controlled, slow ramp is essential to allow ample time for diffusion and gas discharge.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
To maximize the quality of your Bi-2223 superconducting powder, align your furnace programming with your specific material constraints.
- If your primary focus is maximizing purity: Prioritize a slow, multi-step heating ramp to ensure the complete exhaustion of nitrates, carbonates, and organics before reaching peak temperature.
- If your primary focus is phase stability: Set strict upper-limit clamps on your temperature profile to ensure no part of the furnace chamber exceeds the melting point of the lowest-melting precursor phase.
Precise thermal management during pre-calcination is not just a procedural step; it is the defining factor that determines the structural integrity and ultimate performance of the superconductor.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Requirement for Bi-2223 | Impact on Material Quality |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Gradient | Strict Multi-step Ramping | Ensures complete discharge of nitrates and organics without defects. |
| Phase Stability | Precise Upper-limit Clamping | Prevents premature melting of low-melting-point precursor phases. |
| Atmosphere Control | Controlled Gas Exhaustion | Removes CO2 and prevents elemental segregation for high density. |
| Heating Rate | Slow, Uniform Ramp | Avoids structural degradation or 'puffing' from trapped volatile gases. |
Elevate Your Superconducting Material Research with KINTEK
Precision is the defining factor in high-performance superconductor synthesis. KINTEK provides industry-leading Muffle, Tube, and Vacuum furnaces specifically designed to meet the rigorous thermal demands of Bi-2223 pre-calcination.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, our systems offer the programmable accuracy needed to eliminate impurities while preserving delicate phase stoichiometry. Whether you require a standard laboratory furnace or a fully customized high-temperature system for unique research needs, our team is ready to support your project.
Ready to achieve superior material purity? Contact us today to find your custom furnace solution.
Visual Guide
References
- Kun Yang, Junwei Liu. Thermal Deformation Behavior and Microstructural Evolution of Multicomponent Mg-Li-Zn-Al-Y Alloys under Hot Compression. DOI: 10.3390/ma17020489
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- How does the furnace wall and roof of a box type resistance furnace transfer heat to the metal? Discover the Key Mechanism for Uniform Heating
- Why is input voltage important for muffle furnaces? Ensure Safety and Peak Performance
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles supported on Bamboo Biochar (Au-NPs/BC)?
- In which industries are muffle furnaces commonly used? Essential for Clean High-Temp Processing
- What factors should be considered when purchasing a box type electric furnace? Ensure Optimal Performance for Your Lab
- Can box type high-temperature resistance furnaces control the atmosphere during heat treatment? Discover the Key Differences
- What role does a Muffle furnace play in chemical reactions? Achieve Precise, Contamination-Free Thermal Processing
- What are the common uses of box type electric furnaces in heat treatment processes? Achieve Precise Material Property Control



















