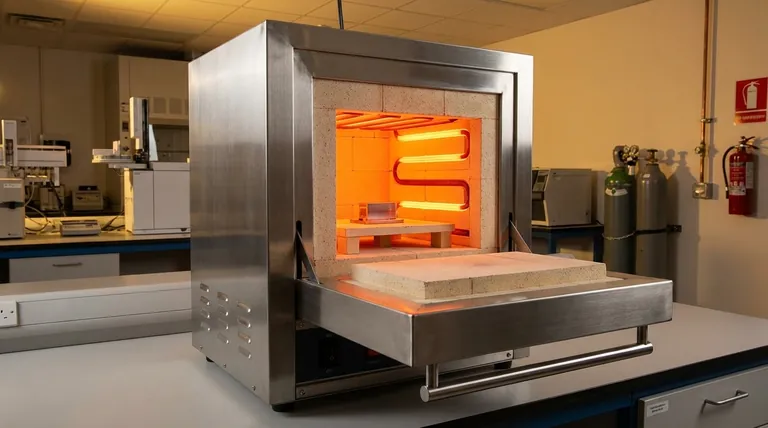
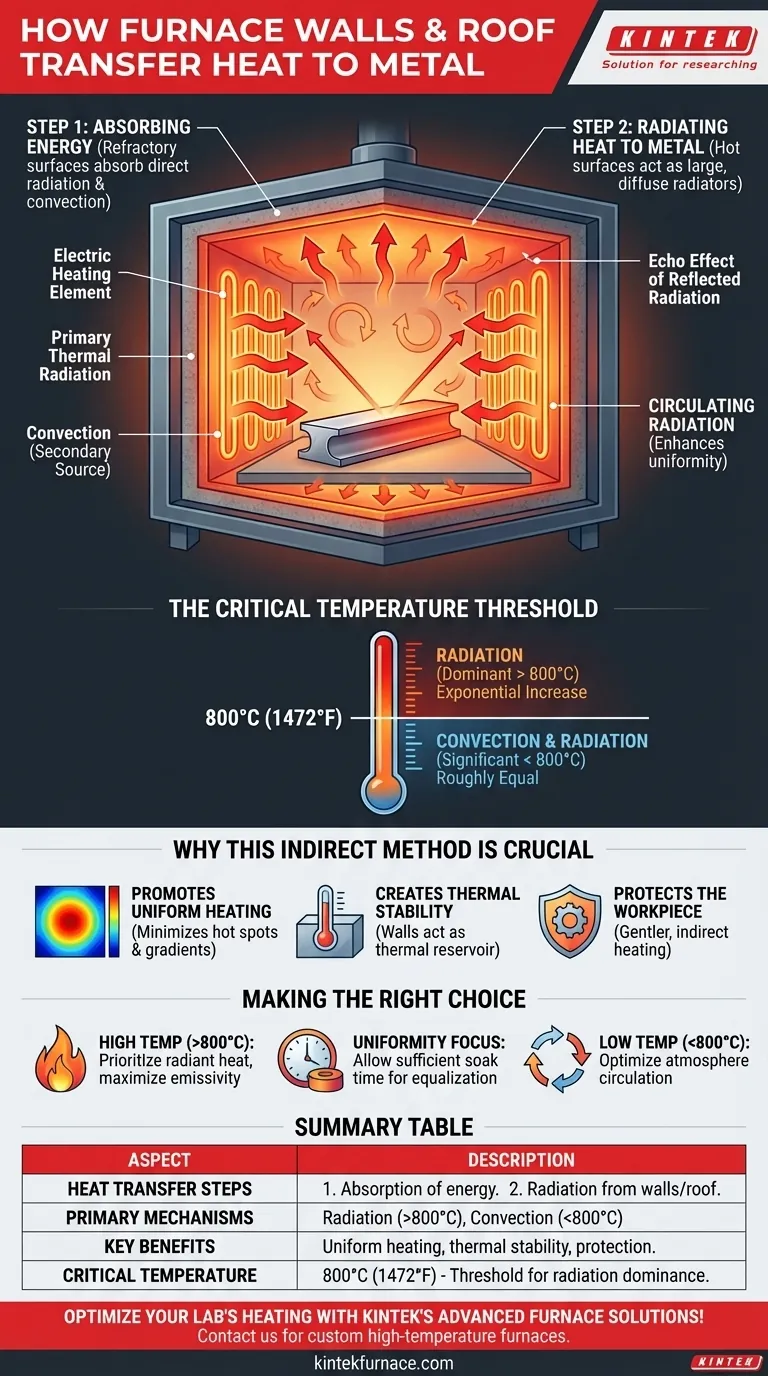
In a box type resistance furnace, the walls and roof transfer heat to the metal workpiece through a two-step process. First, the internal refractory surfaces absorb immense energy from the electric heating elements and the hot furnace atmosphere. Then, these hot surfaces become powerful radiators themselves, blanketing the metal with thermal radiation.
The furnace walls and roof are not passive insulators; they are active components in the heat transfer system. They act as large, secondary heating surfaces that convert concentrated energy from the elements into diffuse, uniform radiation, which is the primary method of heating the metal at high temperatures.

The Two-Step Heat Transfer Mechanism
To understand how a furnace works, we must see the walls and roof as part of a dynamic system. They don't just contain the heat; they actively redirect and transform it to effectively heat the workpiece.
Step 1: Absorbing Energy
The refractory lining of the furnace walls and roof is designed to withstand extreme temperatures. It absorbs energy from two primary sources.
The main source is direct radiation from the electric resistance heating elements. These elements, glowing at very high temperatures, emit intense thermal radiation that is absorbed by the wall surfaces.
A secondary source is convection from the hot gas or atmosphere inside the furnace. As the air heats up, it circulates and transfers thermal energy to the cooler wall surfaces.
Step 2: Radiating Heat to the Metal
Once the internal surfaces of the walls and roof reach a high temperature, they begin to radiate that energy back into the furnace cavity. This is governed by the principles of black-body radiation.
This secondary radiation travels in all directions, including directly to the surface of the metal workpiece. Because the walls and roof have a very large surface area compared to the heating elements, they provide a more uniform and enveloping source of heat.
The Interplay of Radiation and Convection
While radiation from the furnace structure is a dominant factor, it doesn't work in isolation. It operates in concert with convection, with their relative importance changing dramatically with temperature.
The Critical Temperature Threshold
The relationship between convection and radiation is highly dependent on temperature. This is a core principle of high-temperature furnace operation.
At temperatures around 800°C (1472°F), the heating effects of gas convection and thermal radiation are roughly equal.
Above 800°C, the physics of heat transfer shifts dramatically. Radiant heat transfer increases exponentially with temperature, quickly becoming the overwhelmingly dominant mechanism. Convective heat transfer, meanwhile, becomes far less significant.
The "Echo" Effect of Reflected Radiation
The surfaces inside the furnace—the walls, roof, and the metal workpiece itself—do not absorb 100% of the radiation that strikes them. A portion of this energy is reflected.
This reflected radiation then travels to another surface, where it can be absorbed or reflected again. This process, sometimes called circulating radiation, creates a complex energy exchange that helps ensure heat is distributed into every corner and crevice of the furnace, further enhancing temperature uniformity.
Why This Indirect Method is Crucial
Relying on the furnace walls and roof as a secondary radiator isn't just an accident of design; it is a critical feature that delivers significant process advantages.
Promotes Uniform Heating
Direct radiation from discrete heating elements can create "hot spots" on the workpiece, leading to uneven heating and thermal stress. The large, diffuse radiant surface of the furnace walls provides a much softer, more uniform heat that minimizes temperature gradients across the part.
Creates Thermal Stability
The massive refractory walls act as a thermal reservoir. They store a large amount of thermal energy, which helps to stabilize the furnace's internal temperature. This thermal inertia dampens fluctuations that might occur when a process is started or when the door is briefly opened.
Protects the Workpiece
For some materials, intense, direct radiation from glowing-hot elements can be damaging. The less intense, indirect radiation from the furnace walls provides a gentler heating method, which is essential for processing sensitive components without causing surface damage.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding this heat transfer dynamic is key to controlling your heating process effectively.
- If your primary focus is process efficiency at high temperatures (above 800°C): You must prioritize radiant heat transfer. This means ensuring both the workpiece and refractory surfaces are clean and have high emissivity to maximize energy absorption and emission.
- If your primary focus is uniform heating for complex or sensitive parts: Leverage the role of the furnace walls as secondary radiators by allowing for sufficient soak time, which gives this indirect, uniform heat time to equalize temperatures across the workpiece.
- If your primary focus is heating below 800°C: Recognize that both convection and radiation are significant. In this regime, internal atmosphere circulation patterns can play a much larger role in heating rates and must be considered.
Ultimately, the walls and roof of the furnace are an engineered system designed to deliver uniform, stable, and controllable heat.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Heat Transfer Steps | 1. Absorption of energy from elements and atmosphere. 2. Radiation from walls/roof to metal. |
| Primary Mechanisms | Radiation (dominant above 800°C), Convection (significant below 800°C) |
| Key Benefits | Uniform heating, thermal stability, protection of sensitive materials |
| Critical Temperature | 800°C (1472°F) - threshold where radiation becomes dominant |
Optimize your lab's heating processes with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise solutions for your unique experimental needs, delivering uniform heating, thermal stability, and enhanced efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can elevate your research and production outcomes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety



















