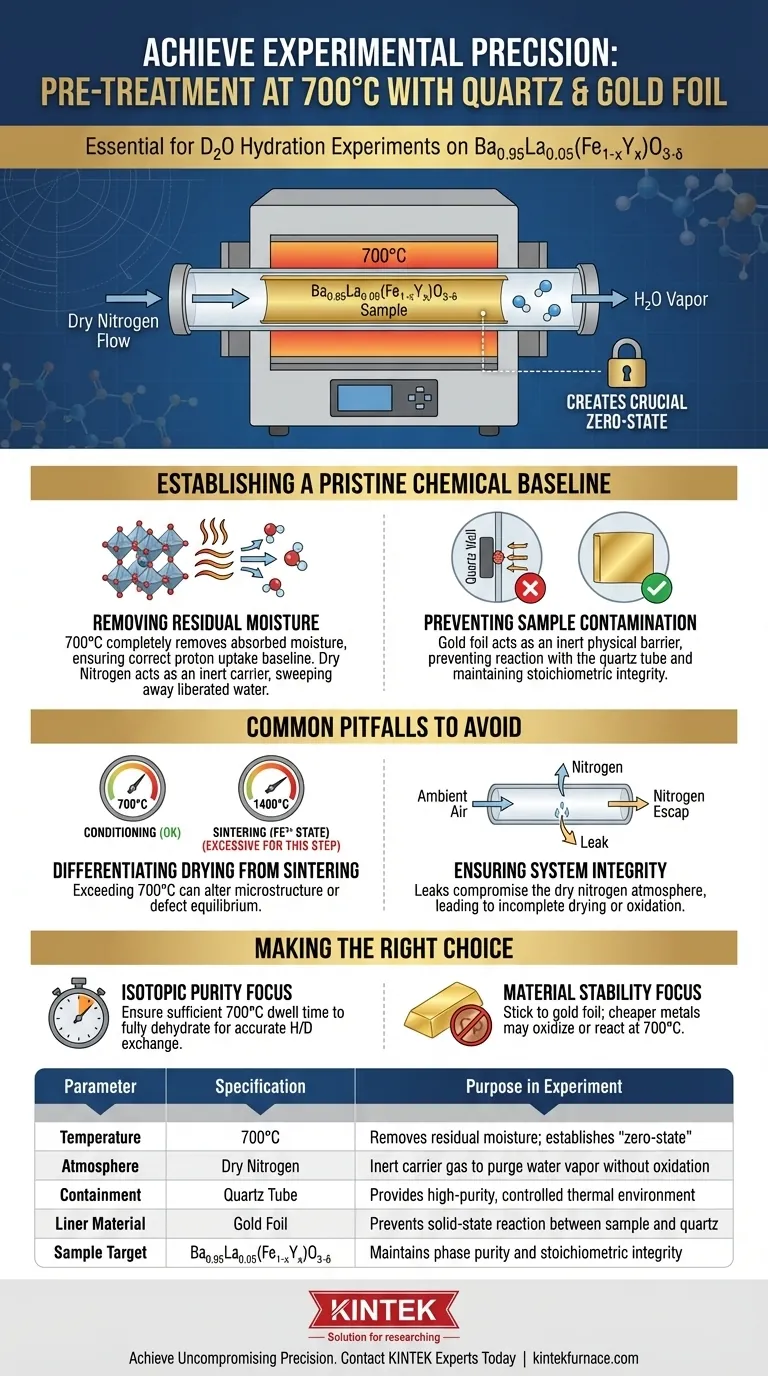
Pre-treatment at 700°C creates a crucial "zero-state" for your material, ensuring that subsequent hydration data is accurate rather than an artifact of pre-existing conditions. By heating the Ba0.95La0.05(Fe1-xYx)O3-δ sample in a dry nitrogen environment, you completely eliminate residual moisture. Simultaneously, the use of gold foil liners within quartz tubes acts as a safeguard against chemical contamination, preventing the sample from reacting with the vessel walls during the heating process.
Core Takeaway Reliable hydration experiments require a sample that is chemically pure and completely dry. This specific pre-treatment protocol isolates variables by purging moisture without altering the material's stoichiometry, ensuring any observed changes are due solely to the introduction of D2O.
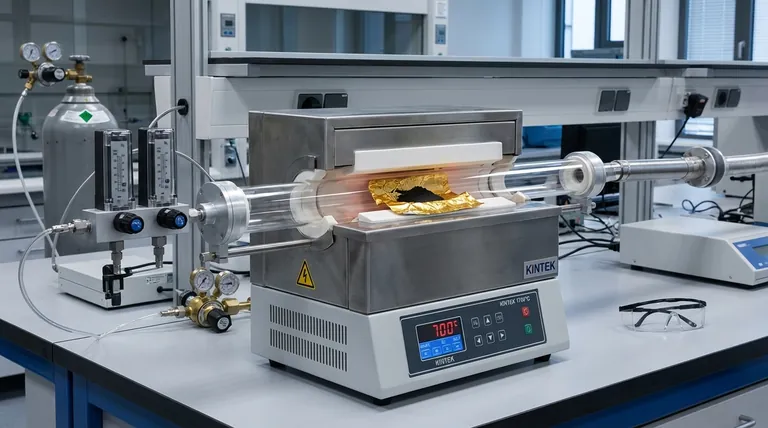

Establishing a Pristine Chemical Baseline
Removing Residual Moisture
The primary objective of the 700°C heat treatment is the complete removal of residual moisture.
Perovskite materials like Ba0.95La0.05(Fe1-xYx)O3-δ can absorb ambient humidity or retain water from previous processing steps.
If this moisture is not purged, your starting baseline for D2O hydration will be incorrect, leading to flawed calculations regarding proton uptake and defect chemistry.
The Function of Dry Nitrogen
This thermal treatment is conducted under a dry nitrogen environment.
Nitrogen serves as an inert carrier gas that sweeps away the liberated water vapor.
This creates a controlled atmosphere that prevents the sample from re-adsorbing moisture or reacting with oxygen in a way that might alter the intended oxidation state of the iron.
Preventing Sample Contamination
The Reactivity of Quartz
While quartz tubes are excellent for maintaining high-purity atmospheres, they are not chemically inert relative to complex oxides at high temperatures.
Direct contact between the Ba0.95La0.05(Fe1-xYx)O3-δ sample and the quartz wall at 700°C poses a risk of solid-state reaction.
This reaction could result in silicon contamination of your sample, altering its phase purity and hydration properties.
Gold Foil as an Inert Liner
To mitigate the risk of reaction, gold foil is used as a physical barrier.
Gold acts as a chemically inert liner that separates the perovskite powder from the silica-based quartz tube.
This ensures that the stoichiometry of your Ba0.95La0.05(Fe1-xYx)O3-δ remains exactly as synthesized, free from foreign elements.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Differentiating Drying from Sintering
It is critical to distinguish this 700°C drying step from higher-temperature processing.
While laboratory tube furnaces are capable of temperatures up to 1400°C for sintering to stabilize the trivalent iron ($Fe^{3+}$) state, the 700°C step is strictly for conditioning.
Exceeding necessary temperatures during this pre-treatment could inadvertently alter the microstructure or defect equilibrium before the hydration experiment begins.
Ensuring System Integrity
The effectiveness of this setup relies entirely on the sealing capabilities of the tube furnace.
Even with gold foil and high temperatures, a leak in the system introducing ambient air would compromise the dry nitrogen atmosphere.
This would render the moisture removal process incomplete and potentially oxidize the sample unpredictably.
Making the Right Choice for Your Experiment
To maximize the accuracy of your D2O hydration results, adhere to the following guidelines:
- If your primary focus is Isotopic Purity: Ensure the 700°C dwell time is sufficient to fully dehydrate the sample, preventing H/D exchange errors later.
- If your primary focus is Material Stability: Do not substitute the gold foil for cheaper metals, as they may oxidize or react with the perovskite at 700°C.
By rigorously controlling the thermal history and contact materials of your sample, you transform a simple heating step into a guarantee of experimental validity.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Specification | Purpose in Experiment |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | 700°C | Removes residual moisture; establishes "zero-state" |
| Atmosphere | Dry Nitrogen | Inert carrier gas to purge water vapor without oxidation |
| Containment | Quartz Tube | Provides high-purity, controlled thermal environment |
| Liner Material | Gold Foil | Prevents solid-state reaction between sample and quartz |
| Sample Target | Ba0.95La0.05(Fe1-xYx)O3-δ | Maintains phase purity and stoichiometric integrity |
Achieve Uncompromising Precision in Your Material Research
Experimental accuracy starts with the right thermal environment. At KINTEK, we understand that even minor contamination or temperature fluctuations can compromise your hydration studies and defect chemistry analysis.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, as well as other lab high-temp furnaces. All our systems are fully customizable to meet your unique research needs, ensuring the integrity of your atmospheres and the stability of your samples.
Ready to elevate your lab's experimental validity?
Visual Guide
References
- Christian Berger, Rotraut Merkle. Ion transport in dry and hydrated Ba<sub>0.95</sub>La<sub>0.05</sub>(Fe<sub>1−<i>x</i></sub>Y<sub><i>x</i></sub>)O<sub>3−<i>δ</i></sub> and implications for oxygen electrode kinetics of protonic ceramic cells. DOI: 10.1039/d5ta03014e
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the process advantages of using an electric melting furnace with an adjustable thermostat? Optimize Copper Scrap Refining
- What is the basic principle of a sintering furnace? Transform Powder into Dense, Strong Components
- What is the necessity of a laboratory vacuum drying oven for photocatalytic powders? Protect Your Material Integrity
- How does magnetron sputtering equipment facilitate BSnO thin films? Precision Control for Semiconductor Bandgap Tuning
- What hardware characteristics are required for a reactor system to support a three-step redox process in chemical looping?
- How do industrial cameras and CNN improve surface defect detection? Revolutionize QC with 95%+ Accuracy
- Why is a stainless steel high-pressure autoclave essential for starch hydrogenation? Unlock Peak Reaction Efficiency
- What is the significance of high-temperature furnace processing for biomass EMI shielding? Optimize Carbon Conductivity



















