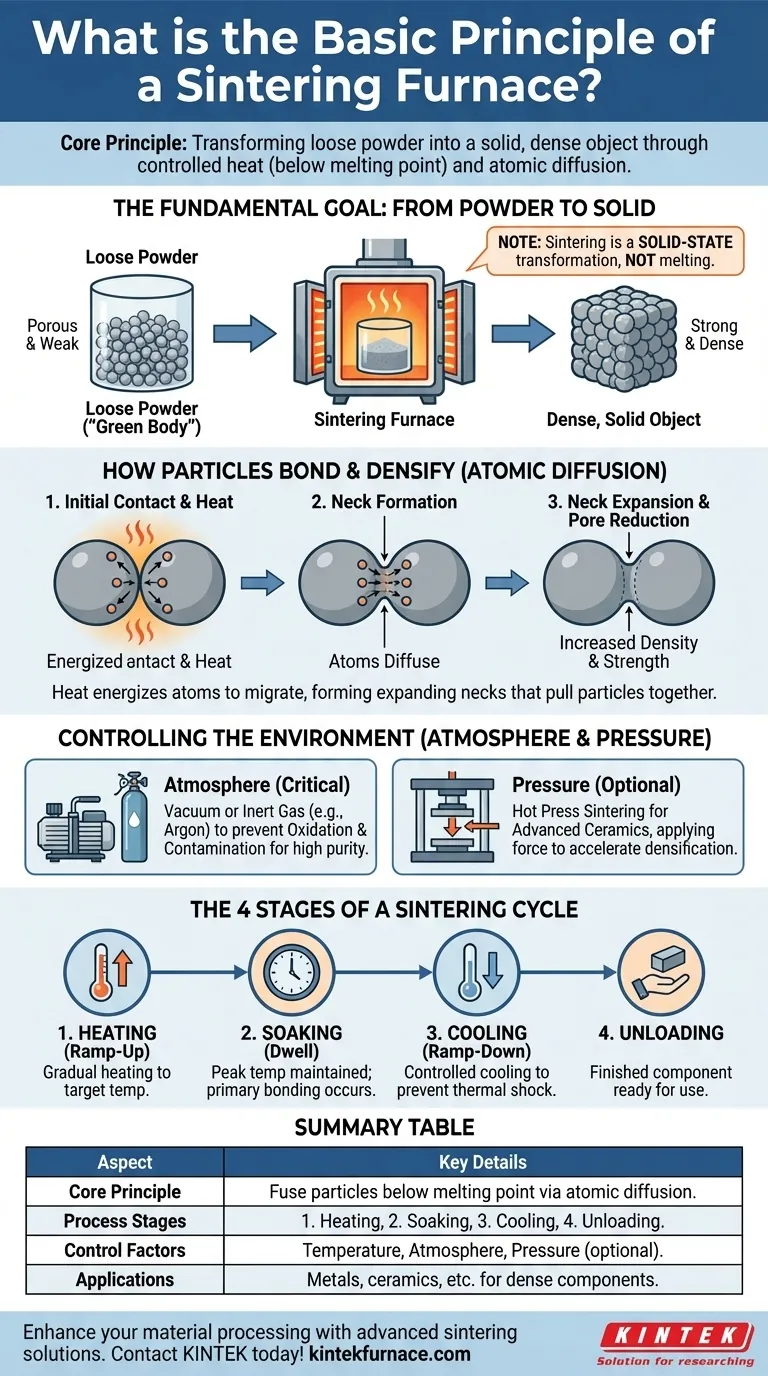
At its core, a sintering furnace is a high-temperature oven that transforms a loose powder or compacted shape into a solid, dense object. It achieves this by heating the material to a temperature just below its melting point, causing the individual particles to fuse together and significantly increase the material's strength and integrity.
Sintering is not a process of melting and re-solidifying. Instead, it is a solid-state transformation where controlled heat, and sometimes pressure and atmosphere, provides the energy for individual particles to bond and reorganize into a stronger, denser structure.

The Fundamental Goal: From Powder to Solid
The primary purpose of a sintering furnace is to take a component made of pressed powder—known as a "green body"—and convert it into a dense, mechanically stable part. This is achieved through atomic diffusion.
The Role of Heat (Below the Melting Point)
The furnace applies intense heat, which energizes the atoms within the material's particles. This energy allows atoms to migrate across the boundaries of adjacent particles.
Crucially, the temperature remains below the material's melting point. This ensures the component holds its shape while its internal structure is fundamentally rearranged.
How Particles Bond and Densify
As atoms diffuse, the contact points between particles begin to grow, forming "necks." These necks expand, pulling the particles closer together.
This process systematically eliminates the empty spaces, or pores, between the particles. The result is a significant increase in the material's overall density and a dramatic improvement in its mechanical properties like strength and hardness.
Controlling the Sintering Environment
The final properties of a sintered part depend heavily on precise control over the furnace's internal environment. Heat is the primary driver, but atmosphere and pressure are equally critical variables.
The Critical Importance of Atmosphere
Many materials will react with oxygen and other atmospheric gases at high temperatures, a process known as oxidation. This can contaminate the material and degrade its final properties.
To prevent this, sintering is often performed in a vacuum or a controlled, inert gas atmosphere. A vacuum furnace removes a vast majority of the air, while an inert gas (like argon) displaces it, creating a non-reactive environment for the sintering to occur.
The Optional Role of Pressure
For certain materials, particularly advanced ceramics, heat alone is not enough to achieve full densification. In these cases, a hot press sintering furnace is used.
This equipment applies high mechanical pressure simultaneously with high heat. The pressure physically forces the particles closer together, accelerating the diffusion and bonding process to achieve maximum density.
The Four Stages of a Sintering Cycle
A typical sintering process in a furnace follows a carefully programmed thermal cycle to ensure a successful outcome and prevent damage to the material.
Stage 1: Heating (Ramp-Up)
The furnace chamber is gradually heated to the target sintering temperature. The rate of this temperature increase is carefully controlled to ensure uniform heating throughout the part.
Stage 2: Soaking (Dwell)
The furnace maintains the peak temperature for a specific period. During this "dwell" or "soaking" stage, the majority of the particle bonding and densification occurs.
Stage 3: Cooling (Ramp-Down)
After the soaking is complete, the part is cooled back to room temperature. This cooling phase is also precisely controlled to prevent thermal shock, which could cause the newly formed part to crack or warp.
Stage 4: Unloading
Once safely cooled, the finished, densified component is removed from the furnace, ready for any subsequent processing or use.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The choice of sintering parameters involves balancing desired outcomes with process complexity and cost.
Temperature vs. Time
Higher sintering temperatures can reduce the required soaking time. However, excessive temperatures risk undesirable grain growth within the material or even accidental melting, which can ruin the part.
Atmosphere vs. Cost
Using a vacuum or inert gas atmosphere produces significantly higher-purity and better-performing parts. However, vacuum furnaces and the cost of inert gas add to the overall operational expense and equipment complexity.
Pressure vs. Complexity
Hot pressing is extremely effective for achieving maximum density in difficult-to-sinter materials. This capability comes at the cost of much more complex and expensive machinery compared to a standard atmosphere or vacuum furnace.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right sintering furnace and process depends entirely on the material you are working with and the properties you need to achieve in the final component.
- If your primary focus is high purity and performance (e.g., refractory metals, advanced ceramics): A vacuum or controlled-atmosphere furnace is essential to prevent oxidation and contamination.
- If your primary focus is maximum density for difficult materials (e.g., specific technical ceramics): A hot press sintering furnace that combines both high heat and high pressure is the most effective solution.
- If your primary focus is general densification of common materials (e.g., some metal powders, zirconia for dental): A furnace focused on precise temperature control through the heating, soaking, and cooling cycles will be sufficient.
By understanding these core principles, you can control the sintering process to engineer your desired material properties with precision.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Details |
|---|---|
| Core Principle | Heating powder below melting point to fuse particles via atomic diffusion, increasing density and strength. |
| Process Stages | 1. Heating (ramp-up), 2. Soaking (dwell), 3. Cooling (ramp-down), 4. Unloading. |
| Control Factors | Temperature, atmosphere (vacuum/inert gas), pressure (optional for densification). |
| Applications | Used for metals, ceramics, and other materials to create dense, stable components. |
Ready to enhance your material processing with advanced sintering solutions? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace systems, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental needs for superior sintering outcomes. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your sintering processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety



















