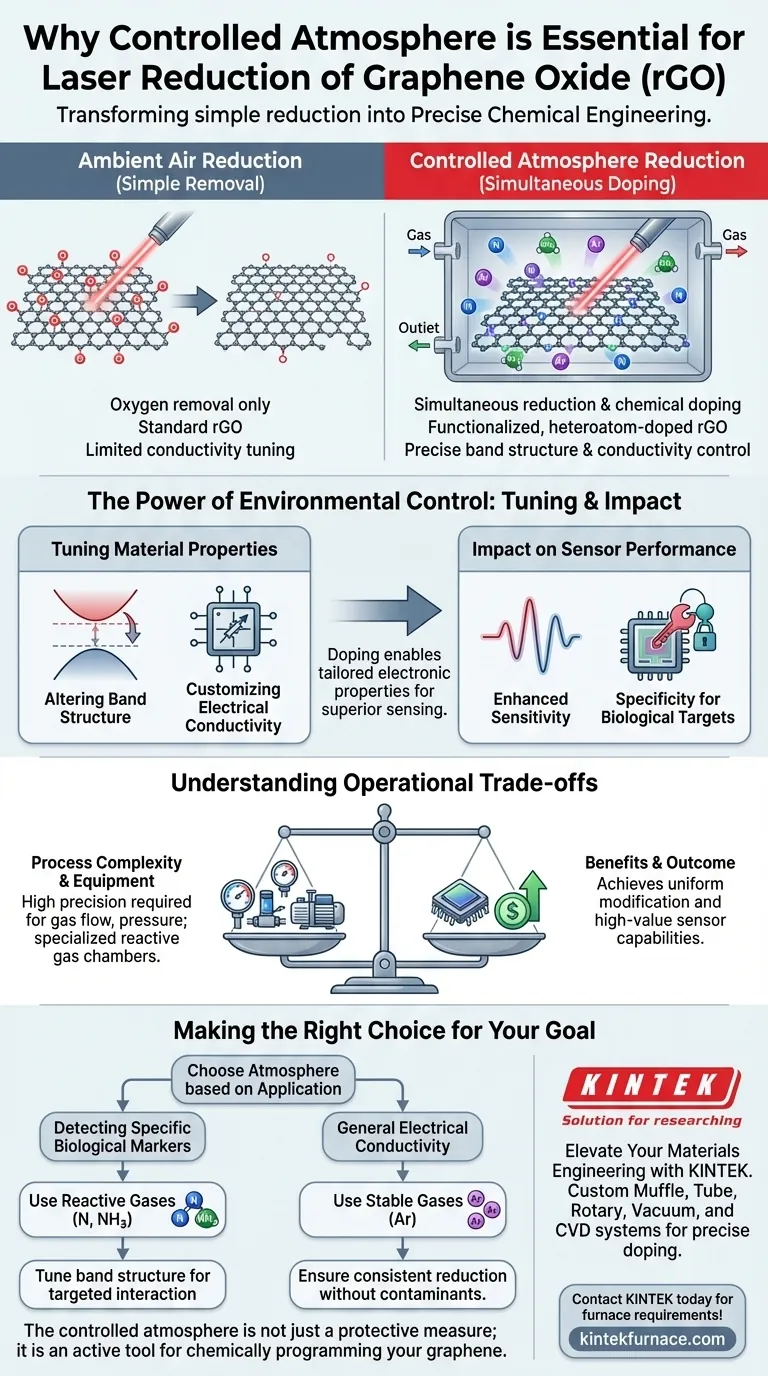
A laboratory chamber with a controlled atmosphere is essential for the laser reduction of graphene oxide (rGO) because it transforms the process from simple reduction into precise chemical engineering. By isolating the environment, you can introduce specific gases to modify the material's atomic structure rather than just removing oxygen functional groups.
Control over the atmospheric environment allows for simultaneous heteroatom doping during laser ablation. This capability is the key to tuning the graphene’s electrical properties and creating sensors with high sensitivity to specific biological targets.

The Power of Environmental Control
Beyond Simple Reduction
In an uncontrolled environment, laser reduction is primarily about removing oxygen. However, a controlled chamber allows you to introduce specific process gases such as nitrogen, argon, or ammonia.
This transforms the laser treatment into a dual-purpose process. It allows you to facilitate chemical reactions that would be impossible in ambient air.
Simultaneous Heteroatom Doping
The presence of these specific gases enables heteroatom doping to occur at the exact moment of laser ablation.
As the laser interacts with the graphene oxide, atoms from the surrounding gas (such as nitrogen) are incorporated into the carbon lattice. This integration happens simultaneously with the reduction process, ensuring a uniform modification of the material.
Tuning Material Properties
Altering Band Structure
The introduction of dopants fundamentally changes the electronic properties of the material. By controlling the gas mix, you can directly tune the band structure of the resulting rGO.
This allows you to manipulate the energy gap between the valence and conduction bands, tailoring the material for specific electronic applications.
Customizing Electrical Conductivity
Along with band structure, the electrical conductivity of the rGO is significantly altered by the atmosphere used during reduction.
Doping allows you to enhance or suppress conductivity depending on the requirements of your device. This level of customization is necessary when developing high-performance electronic components.
Impact on Sensor Performance
Enhanced Sensitivity
The ultimate goal of using a controlled chamber is often to improve sensor performance. The structural and electrical changes achieved through doping directly improve the sensitivity of the sensors.
Specificity for Biological Targets
A tuned band structure allows the sensor to interact more effectively with specific targets.
By adjusting the atmosphere to achieve specific doping levels, you can create sensors optimized to detect particular biological molecules or gases, providing distinct advantages over generic rGO sensors.
Understanding the Operational Trade-offs
Process Complexity
While a controlled atmosphere offers precision, it introduces significant complexity to the manufacturing workflow.
You must precisely manage gas flow rates, concentrations, and chamber pressure. Any fluctuation in these variables can lead to inconsistent doping levels across the material.
Equipment Requirements
Implementing this process requires specialized vacuum or gas flow chambers capable of handling potentially reactive gases like ammonia.
This increases the capital cost and maintenance requirements compared to open-air laser reduction setups.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the effectiveness of your laser reduction process, align your atmospheric choice with your end application:
- If your primary focus is detecting specific biological markers: Utilize reactive gases like nitrogen or ammonia to dope the lattice and tune the band structure for targeted molecular interaction.
- If your primary focus is general electrical conductivity: Use the chamber to create a stable environment (potentially with argon) to ensure consistent reduction without introducing unwanted atmospheric contaminants.
The controlled atmosphere is not just a protective measure; it is an active tool for chemically programming your graphene to perform specific sensing tasks.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Ambient Air Reduction | Controlled Atmosphere Reduction |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Oxygen removal only | Simultaneous reduction & chemical doping |
| Material Outcome | Standard rGO | Functionalized, heteroatom-doped rGO |
| Gas Options | Oxygen, Nitrogen (fixed) | Nitrogen, Argon, Ammonia (customizable) |
| Electrical Control | Limited conductivity tuning | Precise band structure & conductivity control |
| Sensor Capability | General-purpose sensing | High sensitivity for specific biological targets |
| Complexity | Low | High (requires pressure/flow management) |
Elevate Your Materials Engineering with KINTEK
Ready to transform your graphene research into high-performance sensor technology? KINTEK provides the precision-engineered laboratory chambers and high-temperature systems required for sophisticated laser reduction processes.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, we offer customizable Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to maintain the exact atmospheric conditions your doping processes demand. Don't settle for inconsistent results—partner with KINTEK to achieve the uniform modification and electrical tuning your unique lab needs require.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your custom furnace requirements!
Visual Guide
References
- Fatemeh Saeedi, Mojtaba Haghgoo. Recent Advances of Graphene‐Based Wearable Sensors: Synthesis, Fabrication, Performance, and Application in Smart Device. DOI: 10.1002/admi.202500093
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-vacuum or atmosphere-protected furnace required for PDC pyrolysis? Engineer Superior Wave Absorption
- What role does an atmosphere furnace play in industrial-scale production? Unlock Precision in High-Temperature Processing
- What heating mechanisms are available for retort furnaces? Choose Electric or Gas for Optimal Performance
- What challenges are associated with inert atmosphere furnaces? Overcome High Costs and Complexity
- How does a laboratory annealing furnace influence glass quality? Master Stress Relief and Precision
- Why is a preheated annealing furnace necessary in glass production? Ensure Structural Integrity & Optical Clarity
- How do atmosphere furnaces achieve energy efficiency? Boost Your Lab's Performance with Advanced Thermal Control
- What are the advantages of a controlled atmosphere furnace over tube furnaces? Superior Process Control for Sensitive Materials



















