At their core, controlled atmosphere furnaces offer superior process control and capacity over most tube furnaces. Their key advantages lie in the ability to maintain a highly stable, uniform atmosphere within a larger sealed chamber, making them ideal for processing large or sensitive materials where preventing oxidation and ensuring precise chemical reactions are critical.
The choice between a controlled atmosphere furnace and a tube furnace is not about which is universally "better," but which is the right tool for your specific goal. Controlled atmosphere furnaces prioritize process integrity and batch size, while tube furnaces prioritize simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and continuous flow.

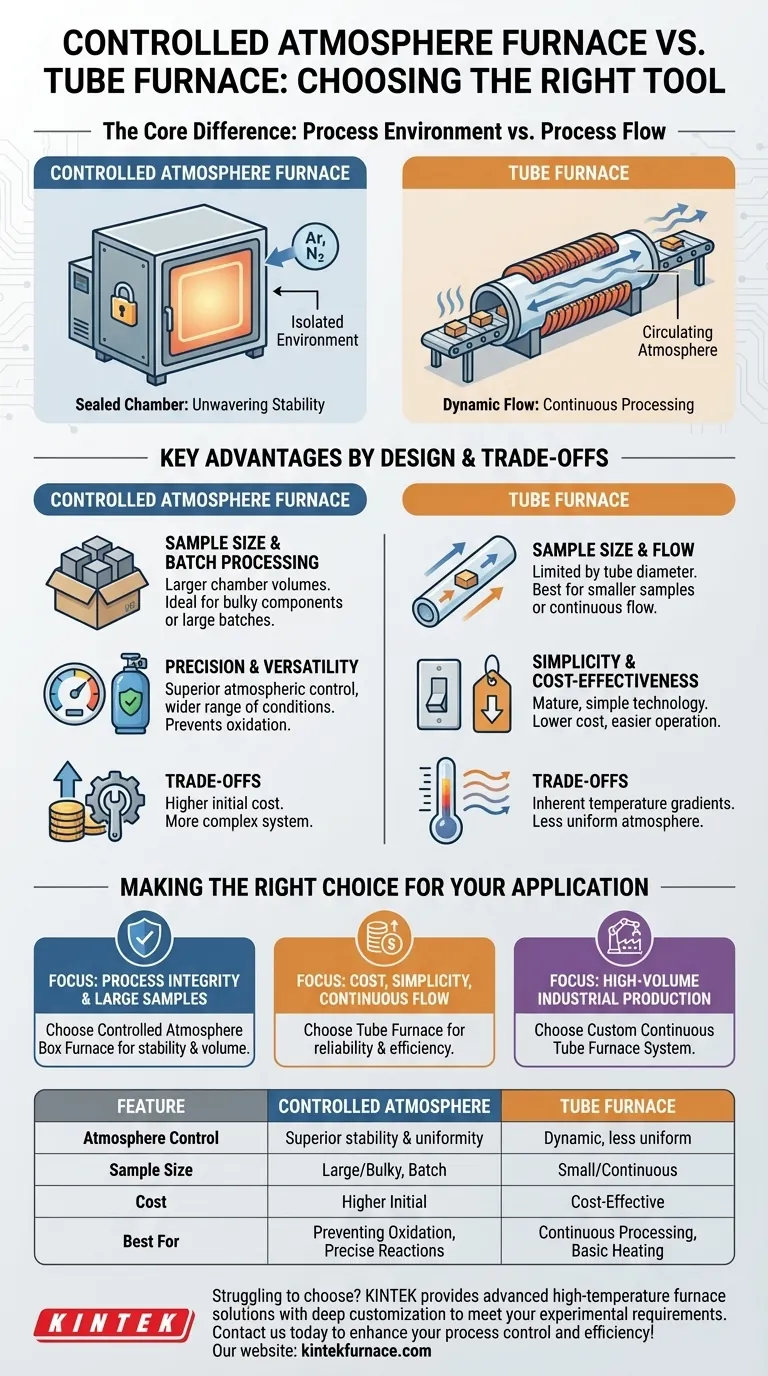
The Core Difference: Process Environment vs. Process Flow
The fundamental advantages of each furnace type stem from their physical design. Understanding this difference is key to making the correct choice.
Sealed Chamber for Unwavering Stability
A controlled atmosphere furnace, often a box or muffle design, functions like a sealed vault. The sample is placed inside, the chamber is sealed, and the desired atmosphere (e.g., inert gas like argon or a reactive gas) is introduced and stabilized.
This design creates an isolated environment, cut off from external conditions. This stability is essential for processes that are highly sensitive to oxygen or require precise gas concentrations over a long period.
Dynamic Flow for Continuous Processing
A tube furnace, by its nature, is a flow-through system. Materials are typically placed within a long tube, and the atmosphere is circulated through it.
While this allows for controlled atmosphere work, the environment is more dynamic. This design excels at continuous production, where materials can be fed through the hot zone, but it offers less atmospheric uniformity compared to a sealed chamber.
Key Advantages by Design
Each furnace's design translates directly into distinct operational advantages and ideal use cases.
Sample Size and Batch Processing
Controlled atmosphere box furnaces offer significantly larger chamber volumes. This makes them the clear choice for processing large, bulky components or running large batches of smaller items simultaneously.
Tube furnaces are inherently limited by the diameter of the tube, making them best suited for smaller samples or materials with a consistent, narrow profile.
Precision and Versatility of Atmosphere
Dedicated controlled atmosphere furnaces are built with comprehensive sealing systems and advanced gas management. This allows for a wider range of atmospheric conditions and more precise control over the environment.
This precision directly leads to improved material properties by preventing unwanted oxidation and enabling specific chemical reactions during the heating process. While tube furnaces can be adapted for gas or vacuum, their seals are often less robust, making them less ideal for highly reactive or ultra-pure environments.
Simplicity and Cost-Effectiveness
Tube furnaces represent a mature, simple, and widespread technology. They are often significantly less expensive and easier to operate and maintain for basic heating tasks.
Their simple structure and high availability make them a cost-effective workhorse for many labs and production lines that don't require the stringent atmospheric control or large volume of a specialized box furnace.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither furnace is without its limitations. Being aware of the trade-offs is crucial for a sound investment.
The Cost of Control
The advanced sealing, gas delivery systems, and robust construction of a high-performance controlled atmosphere furnace come at a higher initial cost. They are more complex machines designed for more demanding applications.
The Limitations of Simplicity
While versatile, tube furnaces have inherent temperature gradients, with the ends of the tube being cooler than the center. Achieving a perfectly uniform atmosphere throughout the tube can also be more challenging than in a sealed box.
The Nuance of "Efficiency"
Energy efficiency is context-dependent. A well-insulated, large-batch atmosphere furnace can be more energy-efficient per-part for a large load. Conversely, a continuous-flow tube furnace can be highly efficient for a constant production line, as it doesn't require repeated heat-up and cool-down cycles.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Select your furnace based on your primary process requirement, not on a generic list of advantages.
- If your primary focus is process integrity and preventing oxidation for large or sensitive materials: Choose a controlled atmosphere box furnace for its superior atmospheric stability and volume.
- If your primary focus is cost, simplicity, or continuous processing of smaller samples: A tube furnace is a reliable and cost-effective solution that excels in these areas.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, automated industrial production: A custom-designed continuous tube furnace system is often the industry standard.
Ultimately, the best furnace is the one that directly aligns with your specific material, process requirements, and operational goals.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Controlled Atmosphere Furnace | Tube Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Atmosphere Control | Superior stability and uniformity in sealed chamber | Dynamic flow, less uniform atmosphere |
| Sample Size | Ideal for large or bulky materials and batch processing | Limited to smaller samples or continuous flow |
| Cost | Higher initial cost due to advanced systems | More cost-effective and simpler to operate |
| Best For | Preventing oxidation, precise chemical reactions | Continuous processing, basic heating tasks |
Struggling to choose the right furnace for your lab's unique needs? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet your experimental requirements. Contact us today to enhance your process control and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the significance of nitrogen in atmosphere furnaces? Unlock Enhanced Heat Treatment and Surface Hardening
- How does the inert atmosphere heat treating process work? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Material Quality
- What is the relationship between temperature and the furnace atmosphere in material processing? Master the Critical Heat-Environment Balance
- What are the benefits of inert atmosphere heat treating? Prevent Oxidation and Preserve Material Integrity
- How does nitrogen atmosphere heat treatment improve surface strengthening? Enhance Durability and Performance



















