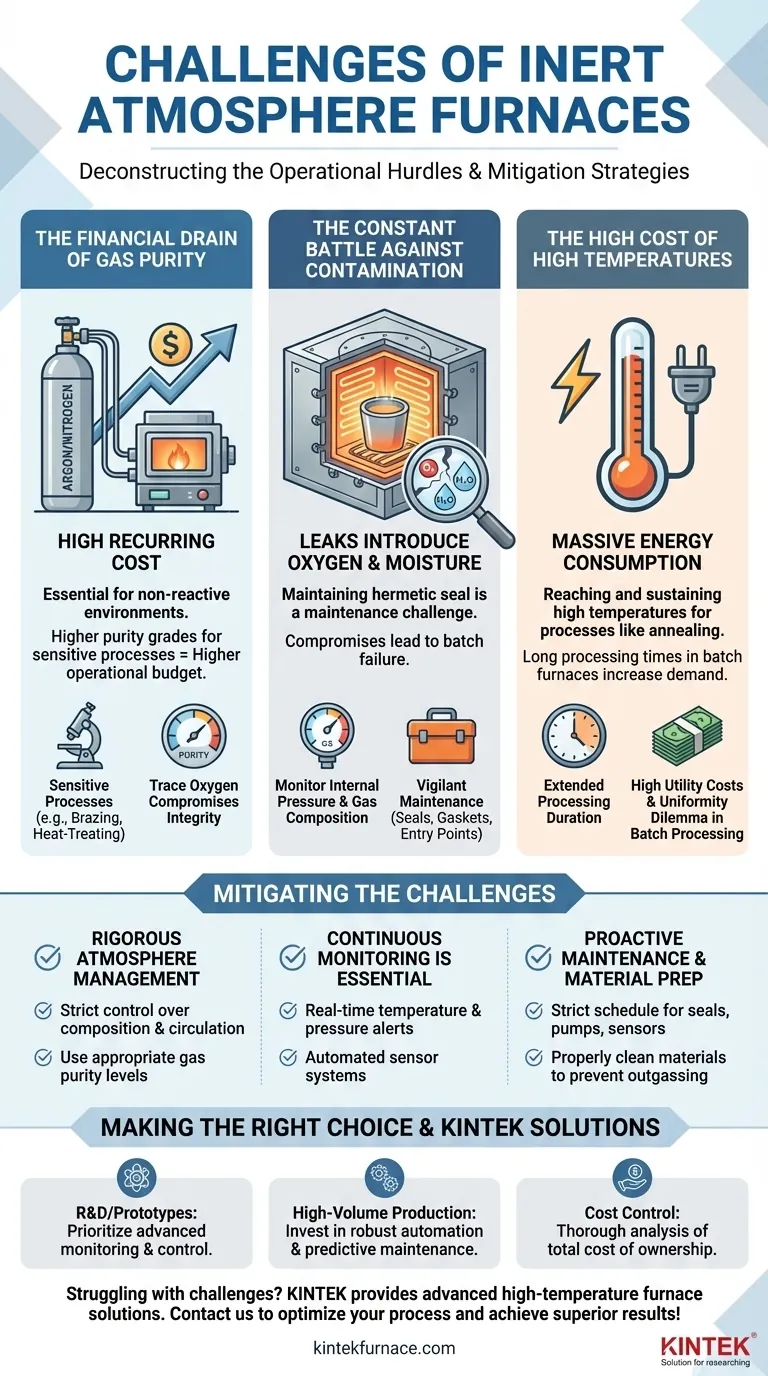
At their core, inert atmosphere furnaces present three significant challenges: the high recurring cost of inert gases, the technical complexity of maintaining a perfectly sealed environment, and the substantial energy consumption required to operate at high temperatures. These factors directly influence both the total cost of ownership and the reliability of the manufacturing process.
The primary challenges of inert atmosphere furnaces are not merely technical inconveniences; they are fundamental operational demands. Successfully managing gas costs, seal integrity, and energy use is the difference between a reliable, high-quality process and a source of costly production failures.

Deconstructing the Operational Hurdles
To effectively use an inert atmosphere furnace, you must understand the nature of its core challenges. These are not one-time problems but continuous operational variables that require constant management.
The Financial Drain of Gas Purity
The most obvious challenge is the direct, recurring cost of high-purity inert gases like argon or nitrogen. These gases are essential for creating the non-reactive environment that prevents oxidation.
For sensitive processes like brazing or heat-treating advanced alloys, even trace amounts of oxygen can compromise material integrity. This necessitates using high-purity, and therefore more expensive, grades of gas, making it a significant line item in your operational budget.
The Constant Battle Against Contamination
An inert atmosphere is only as good as the seal that contains it. Achieving and maintaining a hermetically sealed environment is a significant maintenance challenge.
Leaks can introduce oxygen and moisture, ruining an entire batch of components. You must constantly monitor internal pressure and gas composition to ensure the integrity of the atmosphere, requiring vigilant maintenance of seals, gaskets, and entry points.
The High Cost of High Temperatures
Inert atmosphere furnaces often operate at extremely elevated temperatures for processes like annealing. Reaching and sustaining these temperatures requires a massive amount of electrical energy, leading to high utility costs.
This energy demand is compounded by long processing times, especially in batch furnaces, where the system must be held at temperature for an extended duration to ensure the entire load is processed uniformly.
The Uniformity Dilemma in Batch Processing
Batch furnaces offer flexibility but introduce the challenge of process uniformity. Ensuring every component in a large or complex batch experiences the same temperature and atmospheric conditions is difficult.
Without proper gas circulation and precise temperature control, you risk creating hot or cold spots, leading to inconsistent material properties across the batch and potential part rejection.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Despite these challenges, these furnaces are indispensable for many advanced manufacturing applications. The decision to use one is a trade-off between operational complexity and final product quality.
The Non-Negotiable Need for an Inert Environment
For processes like annealing, brazing, and powder bed fusion additive manufacturing, preventing oxidation is not optional—it is fundamental to the integrity of the final part.
In these cases, the high costs and operational demands are justified because there is no alternative for achieving the required material properties and finish. The furnace's complexity is the price of admission for high-quality results.
The Hidden Costs of Process Failure
The challenges of cost and maintenance must be weighed against the cost of failure. A single compromised batch due to an atmospheric leak can result in thousands of dollars in scrap material, wasted energy, and lost production time.
Therefore, investing in robust monitoring systems, high-quality seals, and rigorous maintenance protocols is a form of insurance against much larger financial losses.
How to Mitigate the Challenges
Success with an inert atmosphere furnace hinges on a disciplined operational approach. The following considerations are critical for ensuring both process quality and operator safety.
Rigorous Atmosphere Management
You must maintain strict control over the atmospheric composition and circulation within the furnace. This includes using the appropriate gas purity levels for your specific material and process.
Continuous Monitoring is Essential
Continuous monitoring of temperature and pressure is non-negotiable. Automated sensor systems can provide real-time alerts to any deviation, allowing operators to intervene before a batch is compromised.
Proactive Maintenance and Material Prep
Implement a strict schedule for regular equipment maintenance, focusing on seals, pumps, and sensors. Additionally, ensure all materials placed in the furnace are properly cleaned to prevent outgassing, which can introduce contaminants into the atmosphere.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your strategy for managing these challenges should align with your specific production objectives.
- If your primary focus is R&D or high-value prototypes: Prioritize a furnace with advanced monitoring and control, as process repeatability and data logging are more critical than throughput.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production: The reliability and operational cost per part are paramount, so invest in robust automation and predictive maintenance to minimize downtime and gas consumption.
- If your primary focus is cost control: Perform a thorough analysis of the total cost of ownership, factoring in energy, gas consumption, and maintenance labor to prevent unexpected expenses from derailing your budget.
Ultimately, mastering the challenges of an inert atmosphere furnace is the key to unlocking the highest levels of material quality and performance.
Summary Table:
| Challenge | Key Issues | Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| High Gas Costs | Recurring expense of argon/nitrogen; purity requirements | Optimize gas usage; use automated monitoring |
| Seal Integrity | Leaks leading to contamination; maintenance demands | Regular checks on seals/gaskets; pressure monitoring |
| Energy Consumption | High electricity use for sustained high temperatures | Improve insulation; efficient heating systems |
| Process Uniformity | Inconsistent conditions in batch furnaces | Enhanced gas circulation; precise temperature control |
Struggling with inert atmosphere furnace challenges? KINTEK can help! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise solutions for your unique experimental needs, reducing costs and improving reliability. Contact us today to optimize your process and achieve superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does an inert atmosphere prevent oxidation? Shield Materials from Oxygen Damage
- What does inert mean in furnace atmospheres? Protect materials from oxidation with inert gases.
- How does the inert atmosphere heat treating process work? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Material Quality
- How does a chemically inert atmosphere function in a furnace? Prevent Oxidation and Ensure Material Purity
- What is nitrogen used for in a furnace? Prevent Oxidation and Control Heat Treatment Quality



















