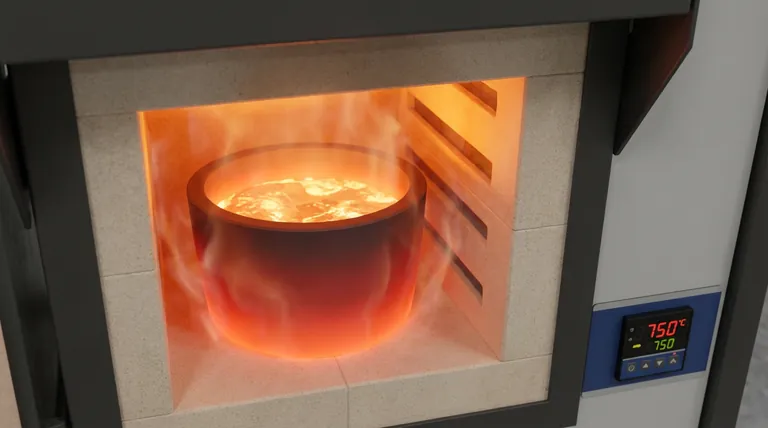
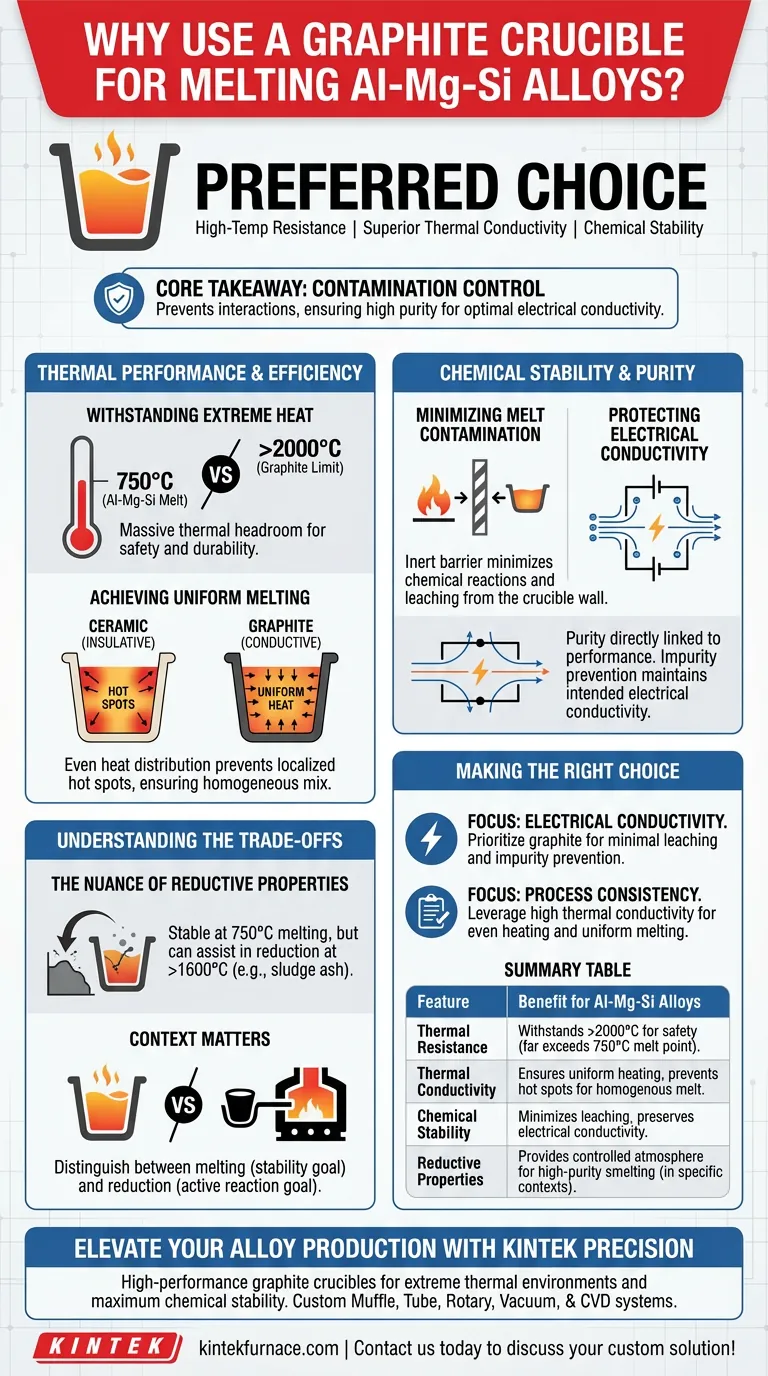
Graphite crucibles are the preferred choice for melting Al-Mg-Si alloys because they offer a unique combination of high-temperature resistance, superior thermal conductivity, and chemical stability. At standard melting temperatures around 750°C, they effectively contain molten aluminum while minimizing chemical reactions, which preserves the alloy's purity and critical electrical properties.
Core Takeaway The primary value of a graphite crucible in this context is contamination control. By preventing chemical interactions between the vessel and the melt, graphite ensures the final Al-Mg-Si alloy maintains the high purity required for optimal electrical conductivity.

Thermal Performance and Efficiency
Withstanding Extreme Heat
Graphite is engineered to endure thermal environments far exceeding the melting point of aluminum.
While Al-Mg-Si alloys are typically melted at 750°C, graphite crucibles retain their structural integrity at temperatures exceeding 2000°C. This massive thermal headroom ensures safety and durability, preventing structural failure during the melting process.
Achieving Uniform Melting
Consistent heat distribution is critical for alloy quality, and graphite is an excellent conductor of heat.
Unlike insulative ceramics, graphite transfers thermal energy evenly throughout the crucible structure. This prevents localized "hot spots" and facilitates a uniform melting process, ensuring the alloy components mix homogeneously.
Chemical Stability and Purity
Minimizing Melt Contamination
For Al-Mg-Si alloys, maintaining the correct chemical composition is paramount.
Graphite offers high chemical stability, acting as an inert barrier between the heat source and the metal. This minimizes chemical reactions at the interface, preventing material from the crucible wall from leaching into and contaminating the molten aluminum.
Protecting Electrical Conductivity
The physical performance of an alloy is directly tied to its purity.
Impurity contamination during the melting phase can severely degrade the material's final characteristics. By preventing these impurities, graphite crucibles ensure the final solidified material maintains the intended electrical conductivity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Nuance of Reductive Properties
While graphite is chemically stable for Al-Mg-Si melting at 750°C, it is not chemically inert in all scenarios.
Graphite possesses inherent reductive properties, which can be advantageous in specific experiments like processing sludge ash with high iron content. In those contexts, the crucible actively participates in the reaction to help create a reducing atmosphere.
Context Matters
Operators must distinguish between melting and reduction.
When melting Al-Mg-Si, the goal is stability; when smelting other materials at extreme temperatures (above 1600°C), the graphite may react to assist in chemical reduction. Understanding this dual nature is key to selecting the right crucible for the specific chemical process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct crucible material depends heavily on the sensitivity of your final product.
- If your primary focus is Electrical Conductivity: Prioritize graphite to minimize chemical leaching and prevent impurities that impede electron flow.
- If your primary focus is Process Consistency: Leverage graphite's high thermal conductivity to ensure even heat distribution and uniform melting of the alloy.
Ultimately, graphite serves as the foundational tool for transforming raw Al-Mg-Si elements into high-performance alloys without compromising their chemical integrity.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit for Al-Mg-Si Alloys |
|---|---|
| Thermal Resistance | Withstands >2000°C, far exceeding the 750°C melting point for safety. |
| Thermal Conductivity | Ensures uniform heating and prevents hot spots for a homogenous melt. |
| Chemical Stability | Minimizes leaching and contamination to preserve electrical conductivity. |
| Reductive Properties | Provides a controlled atmosphere suitable for high-purity smelting. |
Elevate Your Alloy Production with KINTEK Precision
Don't compromise the electrical conductivity and purity of your Al-Mg-Si alloys. KINTEK provides high-performance graphite crucibles designed to withstand extreme thermal environments while ensuring maximum chemical stability.
Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, along with other lab high-temperature furnaces—all fully customizable to meet your unique metallurgical needs.
Ready to optimize your melting process? Contact us today to discuss your custom solution!
Visual Guide
References
- Phase transformation and property improvement of Al–0.6Mg–0.5Si alloys by addition of rare-earth Y. DOI: 10.1515/secm-2024-0048
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Molybdenum Disilicide MoSi2 Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1200℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the maximum vacuum capacity of the water circulating vacuum pump? Uncover Its Ideal Lab Applications
- Why are fly ash geopolymer specimens subjected to 60 °C drying? Master Accelerated Curing for Maximum Strength
- What is the purpose of a PTFE-lined autoclave in TiO2 synthesis? Unlock Precision Nano-material Growth
- What is the role of a quartz reactor within a vacuum distillation apparatus for metal recovery? Unlocking Efficient High-Purity Extraction
- Why is a laboratory vacuum degasser necessary for biochar? Ensure Accurate BET Structural Characterization
- What is the purpose of applying Boron Nitride (BN) to graphite molds in Mg3Sb2 VHP? Ensure Purity & Easy Demolding
- What is the importance of using external thermometers for lead bath monitoring? Ensure Precision in Chemical Refining
- What is the function of high-purity Alumina (Al2O3) crucibles? Enhance Accuracy in Molten Salt Electrochemical Studies













