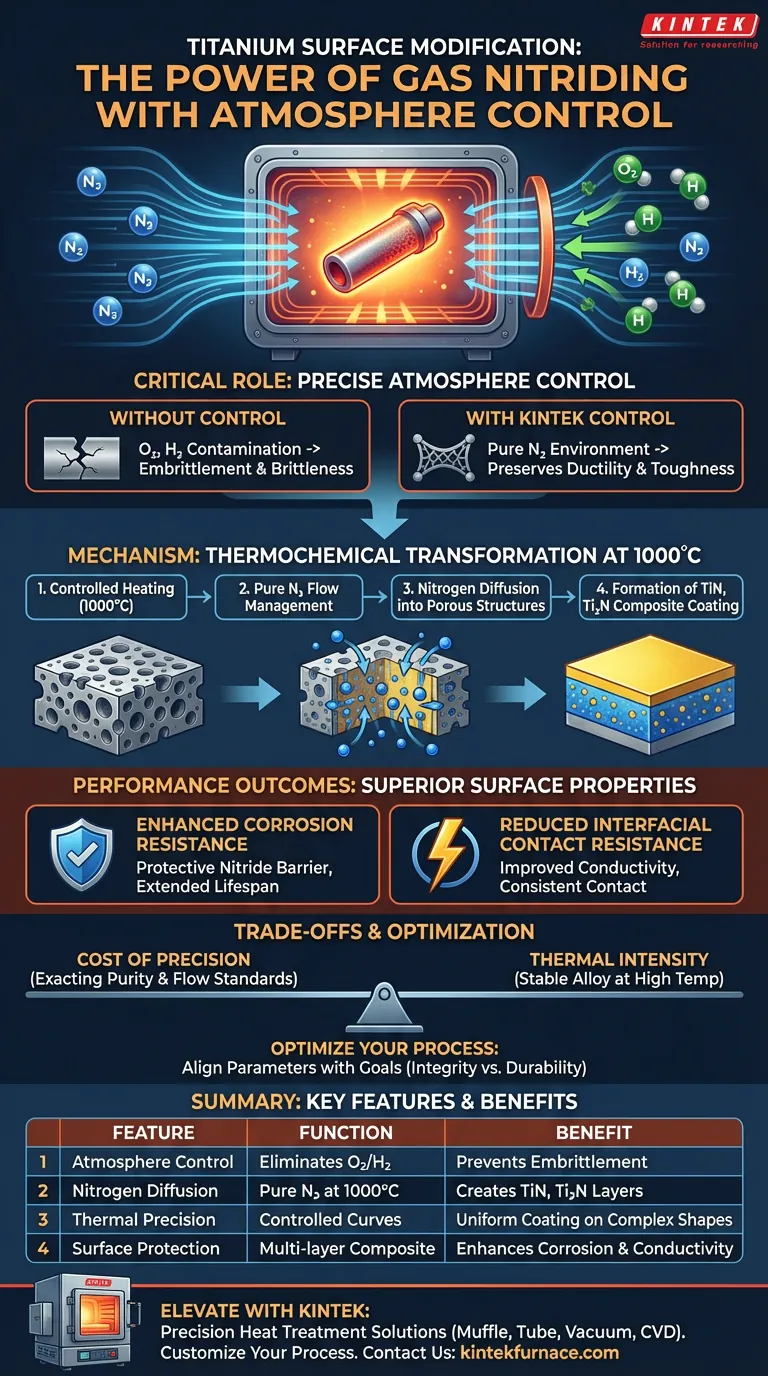
A gas nitriding furnace equipped with an atmosphere control system is critical because it creates the precise thermochemical environment required to modify titanium surfaces without destroying the material's structural integrity. By maintaining a pure nitrogen atmosphere at high temperatures (1000 °C), the system enables nitrogen diffusion into the alloy while rigorously preventing contamination from oxygen or hydrogen. This process creates a robust, multi-layered composite coating that enhances surface performance while preserving the alloy's core mechanical properties.
Core Insight: Titanium is highly reactive at high temperatures; without strict atmosphere control, it absorbs contaminants that cause brittleness. This furnace technology provides the necessary protection to preserve ductility while simultaneously driving the chemical reactions needed to improve corrosion resistance and conductivity.

The Critical Role of Atmosphere Control
Preventing Material Embrittlement
Titanium alloys possess a strong affinity for oxygen and hydrogen when exposed to high temperatures.
If exposed to these elements during heat treatment, the alloy becomes contaminated. This leads to severe embrittlement, compromising the material's structural safety.
An atmosphere-controlled furnace ensures an ultra-clean environment. This preserves the material's original ductility and toughness by preventing unwanted chemical reactions during heating.
Enabling Precise Thermochemical Reactions
The furnace facilitates specific thermochemical reactions by utilizing a pure nitrogen ($N_2$) atmosphere at 1000 °C.
This is not merely about heating; it is about managing the chemical interaction between the gas and the metal.
By controlling nitrogen flow rates and heating curves, the system ensures the reaction proceeds at a controlled pace, resulting in a uniform surface modification.
Mechanism of Surface Modification
Diffusion into Porous Structures
One of the distinct advantages of this technology is its ability to treat complex geometries.
The controlled nitrogen atmosphere allows molecules to diffuse effectively into the internal surfaces of porous structures.
This ensures that even hard-to-reach areas within the titanium component receive the same level of surface treatment as the exterior.
Formation of Composite Coatings
The diffusion process results in the formation of a multi-layered composite coating.
This coating consists of Titanium Nitride (TiN), $Ti_2N$, and nitrogen solid solutions.
These specific chemical compounds are responsible for the drastic changes in surface properties compared to the raw alloy.
Performance Outcomes
Enhanced Corrosion Resistance
The formation of nitride layers acts as a protective barrier.
This atmospheric-protected heat treatment is essential for significantly increasing the material's corrosion resistance, extending the lifespan of the component in harsh environments.
Reduced Interfacial Contact Resistance
Beyond protection, the treatment alters the electrical and physical interaction properties of the surface.
The nitriding process effectively reduces interfacial contact resistance. This is vital for applications where consistent conductivity or low-resistance contact is required.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Cost of Precision
Achieving these results requires exacting standards. The "pure" nitrogen atmosphere and "precise" flow rates mentioned are not optional; slight deviations can result in inconsistent coating or contamination.
Thermal Intensity
The process requires heating to 1000 °C. While necessary for diffusion, this high temperature demands that the specific titanium alloy being treated acts stably at this range without unwanted phase changes that could alter its core mechanical properties.
Optimizing Titanium Surface Treatment
To derive the most value from a gas nitriding furnace, align your process parameters with your specific engineering goals:
- If your primary focus is Structural Integrity: Prioritize the purity of the atmosphere to strictly eliminate oxygen and hydrogen, ensuring the alloy retains its ductility and toughness.
- If your primary focus is Surface Durability: Focus on the precision of the heating curves and nitrogen flow to maximize the formation of the TiN and $Ti_2N$ composite layers for optimal corrosion resistance.
Ultimately, this technology transforms titanium's high reactivity from a liability into an asset, leveraging it to create superior surface properties without compromising the metal's core strength.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Function in Titanium Nitriding | Benefit to Material |
|---|---|---|
| Atmosphere Control | Eliminates oxygen and hydrogen | Prevents embrittlement & preserves ductility |
| Nitrogen Diffusion | Pure N2 delivery at 1000 °C | Creates TiN, Ti2N, and solid solution layers |
| Thermal Precision | Controlled heating curves | Ensures uniform coating on complex/porous shapes |
| Surface Protection | Forms multi-layer composite | Enhances corrosion resistance & conductivity |
Elevate Your Material Performance with KINTEK
Maximize the potential of your titanium alloys with KINTEK’s precision-engineered heat treatment solutions. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, we provide high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to meet the most rigorous atmosphere control standards.
Whether you require uniform surface modification or the prevention of material embrittlement, our systems are fully customizable to your unique research and production needs.
Ready to optimize your thermal processes?
Contact KINTEK today for expert consultation and discover how our advanced furnace technology delivers superior results for your laboratory or industrial facility.
Visual Guide
References
- Juan Villemur, E. Gordo. Fabrication and Coating of Porous Ti6Al4V Structures for Application in PEM Fuel Cell and Electrolyzer Technologies. DOI: 10.3390/ma17246253
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the key considerations when using an atmosphere protection muffle furnace? Ensure Safety and Precision for Your Lab
- What is the primary function of the vacuum atmosphere in diamond tool sintering? Prevent Oxidation & Enhance Bonding
- Why is a rotameter essential for controlling the atmosphere within an oily sludge pyrolysis reactor? Master Gas Flow Control
- How are inert atmosphere furnaces sealed and prepared for operation? Ensure Process Integrity and Prevent Oxidation
- Why is a water-cooling spray system implemented in annealing? Maximize Production Throughput & Material Quality
- How does an inert atmosphere furnace work? Master Controlled Heating for Oxidation-Free Results
- What are the environmental benefits of using furnace atmospheres? Reduce Emissions and Waste with Advanced Control
- What is the function of a controlled atmosphere in Violet Phosphorus research? Achieve High-Purity Material Restoration



















