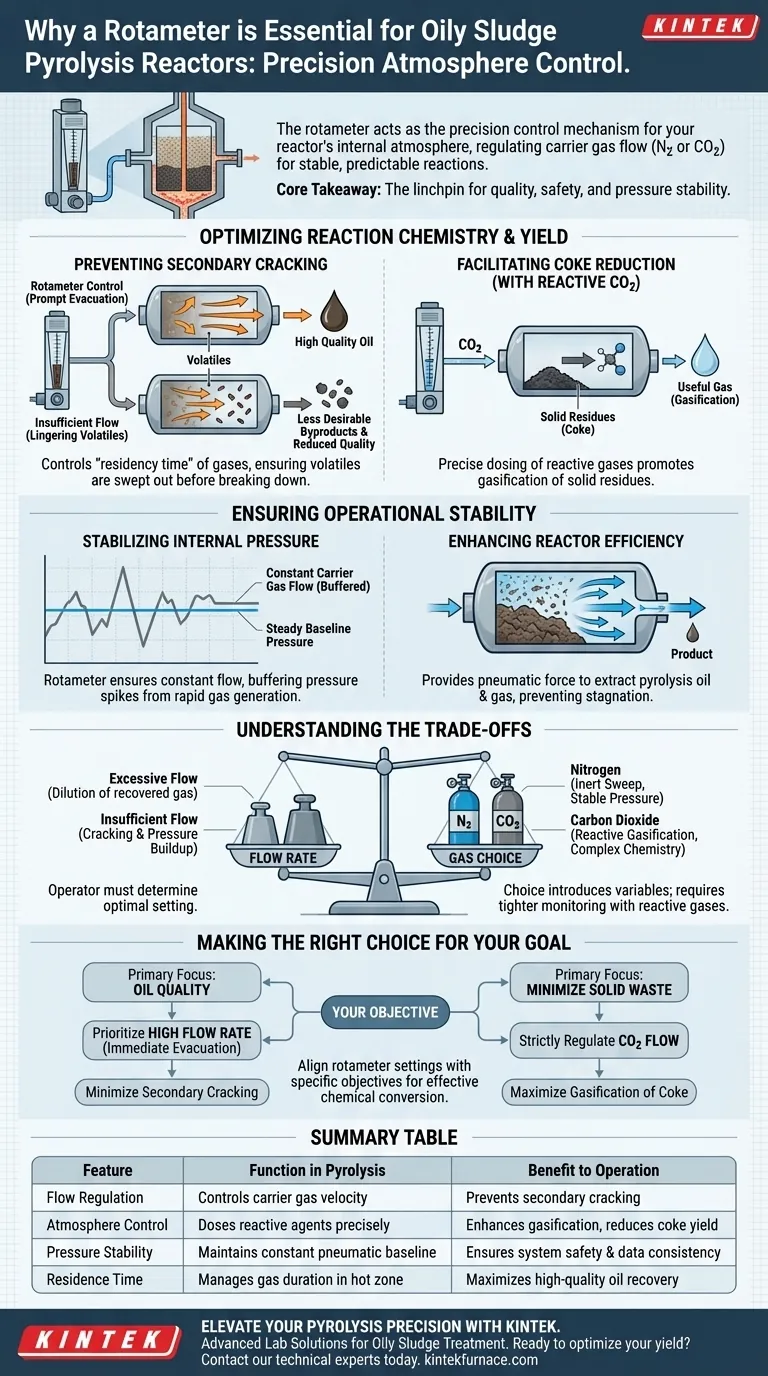
A rotameter acts as the precision control mechanism for your reactor's internal atmosphere. It is strictly employed to accurately regulate the flow rate of carrier gases—whether inert gases like Nitrogen or reactive agents like Carbon Dioxide—entering the oily sludge pyrolysis reactor. By maintaining this precise flow, the device ensures the reaction environment remains stable and predictable.
Core Takeaway The rotameter is the linchpin for preserving product quality and system safety. By ensuring a stable gas flow, it forces the prompt removal of volatiles to prevent unwanted chemical degradation (secondary cracking) while simultaneously stabilizing internal reactor pressure.

Optimizing Reaction Chemistry and Yield
Preventing Secondary Cracking
The primary function of the rotameter is to control the "residency time" of gases within the reactor.
By setting a specific flow rate, you ensure that generated volatiles are promptly swept out of the high-temperature reaction zone.
If these volatiles linger, they undergo secondary cracking, breaking down further into less desirable byproducts and reducing the quality of the recovered oil.
Facilitating Coke Reduction
For advanced pyrolysis operations, the atmosphere is an active participant in the chemical reaction, not just a passive carrier.
When using reactive gases like Carbon Dioxide, the rotameter allows for the exact dosing required to promote the gasification of solid residues.
This precise control is vital for investigating and achieving a reduction in coke yield, converting solid waste into useful gas.
Ensuring Operational Stability
Stabilizing Internal Pressure
Pyrolysis involves the rapid generation of new gases, which can create dangerous or disruptive pressure spikes.
A rotameter ensures a constant carrier gas flow, which helps buffer these fluctuations and maintains a steady baseline pressure.
This stability is essential for the safety of the vessel and the consistency of the data collected during operation.
Enhancing Reactor Efficiency
While the reactor body (often rotary) is designed to mix materials and prevent wall sticking, it relies on gas flow to move the product.
The rotameter complements the physical motion of the reactor by providing the pneumatic force necessary to extract pyrolysis oil and gas.
Without this regulated flow, even a well-mixed reactor would suffer from stagnation and thermal inefficiencies.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Balance of Flow Rate
While a rotameter allows for control, the operator must determine the optimal setting; higher flow is not always better.
Excessive flow rates can dilute the concentration of the recovered pyrolysis gas, making downstream processing more difficult.
Conversely, insufficient flow fails to evacuate volatiles quickly enough, leading to the secondary cracking and pressure buildup mentioned earlier.
Reactivity vs. Inertness
The rotameter manages the flow, but the choice of gas introduces its own variables.
Using Nitrogen creates a purely physical sweep, ideal for baseline studies and stabilizing pressure without altering chemistry.
Using Carbon Dioxide introduces chemical complexity (gasification), which can improve coke reduction but requires tighter flow monitoring to prevent runaway reactions or thermal instability.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the effectiveness of your oily sludge pyrolysis reactor, align your rotameter settings with your specific objectives:
- If your primary focus is Oil Quality: Prioritize a flow rate high enough to immediately evacuate volatiles, minimizing the time available for secondary cracking.
- If your primary focus is Minimizing Solid Waste: Use the rotameter to strictly regulate Carbon Dioxide flow to maximize the gasification of coke residues.
Mastering your flow rate transforms your reactor from a simple heating vessel into a precision instrument for chemical conversion.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Function in Pyrolysis | Benefit to Operation |
|---|---|---|
| Flow Regulation | Controls carrier gas (N2/CO2) velocity | Prevents secondary cracking of volatiles |
| Atmosphere Control | Doses reactive agents precisely | Enhances gasification and reduces coke yield |
| Pressure Stability | Maintains constant pneumatic baseline | Ensures system safety and data consistency |
| Residence Time | Manages gas duration in hot zone | Maximizes high-quality oil recovery |
Elevate Your Pyrolysis Precision with KINTEK
Don't let unstable gas flow compromise your oil quality or reactor safety. KINTEK’s advanced lab solutions—including our high-performance Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—are engineered for the rigorous demands of oily sludge treatment. Backed by expert R&D and precision manufacturing, our high-temperature furnaces are fully customizable to meet your unique chemical conversion needs.
Ready to optimize your yield? Contact our technical experts today to find the perfect thermal processing solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- CF KF Flange Vacuum Electrode Feedthrough Lead Sealing Assembly for Vacuum Systems
- 304 316 Stainless Steel High Vacuum Ball Stop Valve for Vacuum Systems
- Stainless Steel Quick Release Vacuum Chain Three Section Clamp
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the structure of a retort furnace? Unlock Precision Heat Treatment with Sealed Chamber Design
- Why is a controlled atmosphere necessary in industrial debinding furnaces? Master the Switch from Nitrogen to Air
- How is a high-temperature atmosphere furnace utilized during the internal oxidation step of Alumina Dispersion Strengthened Copper (ADSC) production? Unlock Superior Material Strength
- Why compare air and nitrogen atmospheres in CZTS post-annealing? Isolate Oxygen's Impact for Higher Efficiency
- How does a high-temperature electric furnace facilitate the sintering process of 3Y-TZP ceramics? Master Densification
- What are the primary uses of retort furnaces in industrial settings? Essential for High-Temperature Material Processing
- How does the inert atmosphere heat treating process work? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Material Quality
- What physical conditions must a high-temp reduction furnace provide for Ni exsolution? Master Your Material Synthesis










