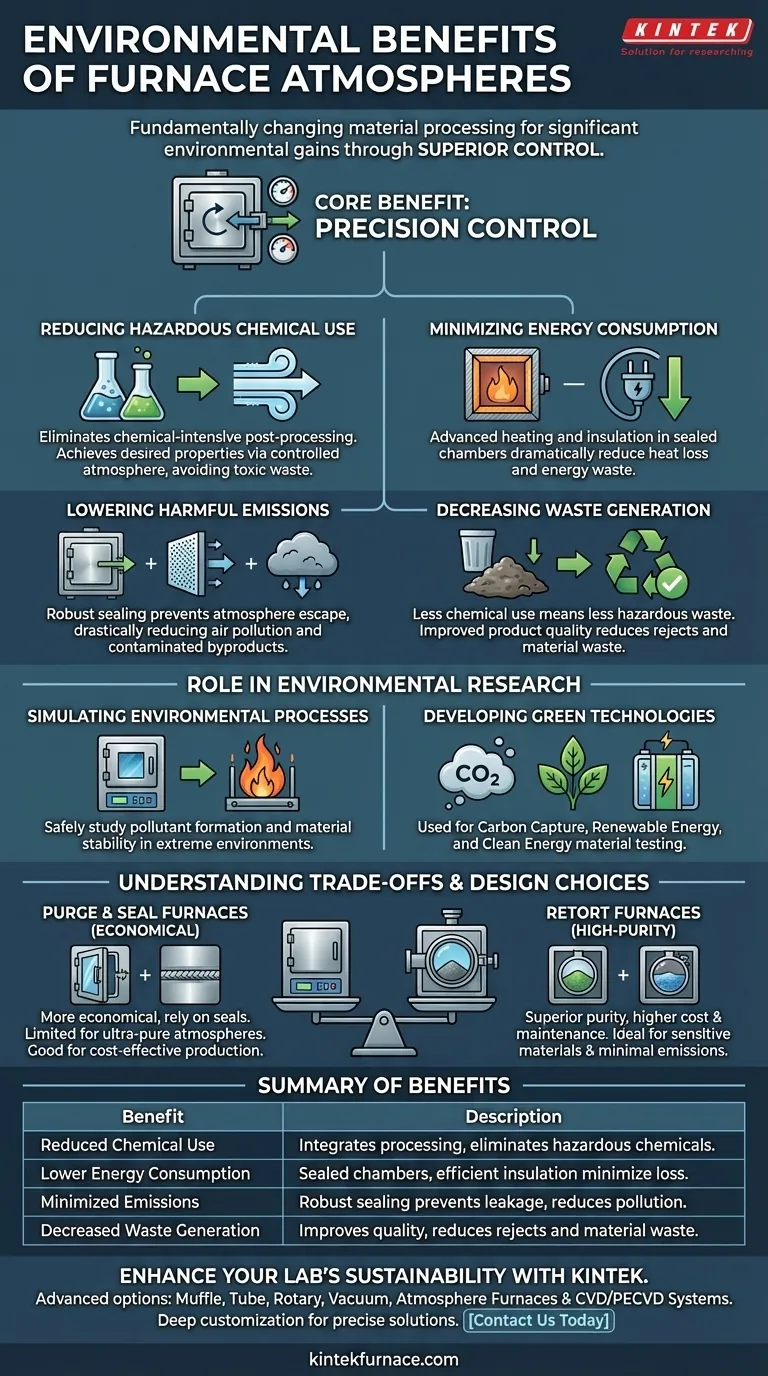
In short, furnace atmospheres provide significant environmental benefits by fundamentally changing how materials are processed. They reduce or eliminate the need for hazardous post-processing chemicals, lower energy consumption through superior efficiency, minimize harmful emissions with sealed designs, and decrease the generation of hazardous waste.
The core environmental benefit of a furnace atmosphere is control. By precisely managing the chemical environment inside the furnace, you can eliminate many of the inefficient, wasteful, and hazardous steps common in traditional open-air or chemical-based material processing.

How Furnace Atmospheres Drive Environmental Gains
The environmental advantages are not just a fortunate side effect; they are intrinsic to the technology's design and purpose. This control manifests in several key areas.
Reducing Hazardous Chemical Use
Traditional manufacturing often requires separate, chemical-intensive steps to clean, prepare, or finish a material after heating.
Furnace atmospheres can integrate these steps into the heating process itself. By using a chemically active or inert gas, you can achieve the desired surface properties without resorting to hazardous acids, solvents, or plating solutions that generate toxic waste.
Minimizing Energy Consumption
Modern atmosphere furnaces are engineered for thermal efficiency. They are built with advanced heating elements and superior insulation materials that dramatically reduce heat loss.
By containing the process in a sealed chamber, you only heat the necessary material and atmosphere, avoiding the immense energy waste of heating a larger, open environment.
Lowering Harmful Emissions
Effective sealing is a cornerstone of this technology. Furnaces are often designed with robust door seals and welded casings to prevent the controlled atmosphere from escaping.
This containment is critical for processes like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), which use gaseous reactants. By preventing gas leakage, these furnaces drastically reduce air pollution and avoid the creation of contaminated wastewater or solid waste common in other methods.
Decreasing Waste Generation
The reduction in chemical use directly leads to a decrease in hazardous waste. Fewer chemical baths mean less toxic sludge to treat and dispose of.
Furthermore, the precision of atmosphere control improves product quality and consistency, reducing the number of rejected parts and the associated material and energy waste.
Beyond Manufacturing: The Role in Environmental Research
Atmosphere furnaces are not just a tool for greener manufacturing; they are also essential for developing the next generation of environmental solutions.
Simulating Environmental Processes
In research settings, laboratory furnaces are used to simulate high-temperature industrial processes, like incineration. This allows scientists to safely study pollutant formation and develop methods to mitigate it.
They are also used to test material stability in extreme corrosive or high-temperature environments, helping engineers select materials that will last longer and create less waste over their lifecycle.
Developing Green Technologies
These furnaces are at the heart of critical environmental research. Scientists use them for:
- Carbon Capture: Developing and testing new materials that can absorb CO2.
- Renewable Energy: Optimizing the pyrolysis of biomass to create biofuels.
- Clean Energy: Preparing and testing advanced materials for more efficient fuel cells.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Design Choices
Achieving these environmental benefits involves choosing the right furnace design, which comes with specific trade-offs. The two primary designs illustrate this balance between cost, performance, and environmental purity.
Purge and Seal Furnaces: The Economical Choice
These furnaces rely on door seals and welded case seams to contain the atmosphere. They are more economical to build and operate.
However, their ability to maintain an extremely pure, low-dew-point atmosphere can be limited. This makes them suitable for many applications but less so for the most sensitive materials.
Retort Furnaces: The High-Purity Solution
In this design, the material is placed inside a sealed alloy container (a retort) which is then heated externally. This provides a much cleaner, more tightly controlled atmosphere.
This superior purity comes at a cost. Retort furnaces are more expensive to build, and the retorts themselves require regular maintenance or replacement, adding to operational complexity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your specific objective will determine which approach offers the most practical environmental and operational benefits.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective production with significant environmental improvement: A purge-and-seal furnace is an excellent choice, as it reduces energy, emissions, and chemical use compared to open-air systems.
- If your primary focus is high-purity processing and minimal emissions: A retort furnace provides the ultimate level of atmospheric control, ensuring the cleanest process for sensitive materials, albeit at a higher initial cost.
- If your primary focus is advancing green technology research: A specialized lab furnace is an indispensable tool for developing and testing the materials that will define a more sustainable future.
Ultimately, adopting furnace atmosphere technology is a direct investment in cleaner, more efficient, and more controlled industrial processes.
Summary Table:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Reduced Chemical Use | Integrates processing steps to eliminate hazardous chemicals, lowering toxic waste. |
| Lower Energy Consumption | Sealed chambers and efficient insulation minimize heat loss and energy waste. |
| Minimized Emissions | Robust sealing prevents gas leakage, reducing air pollution and contaminated byproducts. |
| Decreased Waste Generation | Improves product quality and consistency, reducing rejects and material waste. |
Ready to enhance your lab's sustainability with advanced furnace solutions? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace options like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise solutions for your unique experimental needs, helping you reduce environmental impact and boost efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What does inert mean in furnace atmospheres? Protect materials from oxidation with inert gases.
- How does the inert atmosphere heat treating process work? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Material Quality
- What is the use of nitrogen in furnace? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Heat Treatment
- How does an inert atmosphere prevent oxidation? Shield Materials from Oxygen Damage
- What is the main purpose of heat treatment? Transform Metal Properties for Superior Performance



















